Posts Tagged "PRIIA"
Statement in response to introduction of the Railroad Reform, Enhancement and Efficiency Act

Senators Roger Wicker (R-MS) and Cory Booker (D-NJ) today introduced a multi-year bill to authorize funding to Amtrak and support passenger rail, dubbed the Railroad Reform, Enhancement and Efficiency Act. It would be the successor to the existing rail authorization, the Passenger Rail Investment and Improvement Act. In response, T4America Chairman John Robert Smith, a former chair of the Amtrak board, released this statement:
15 issues to watch in ’15, Part I: Capitol Hill developments

Already, 2015 feels like it could be a big year for transportation, at the federal, state and local levels alike. As the year began, we thought it would be fun to identify 15 people, places and trends that seemed to be worth keeping an eye on the next 12 months. In some years, 15 would be a stretch, but this year we had a tough time whittling the list to match the number of the year.
T4America statement in response to passenger rail reauthorization bill

The House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee today released a long-awaited update to the Passenger Rail Investment and Improvement Act, the law that funds passenger rail. James Corless, director of Transportation for America, issued this statement in response:
T4 brings mayors to Washington to tell Secretary Foxx about the importance of passenger rail
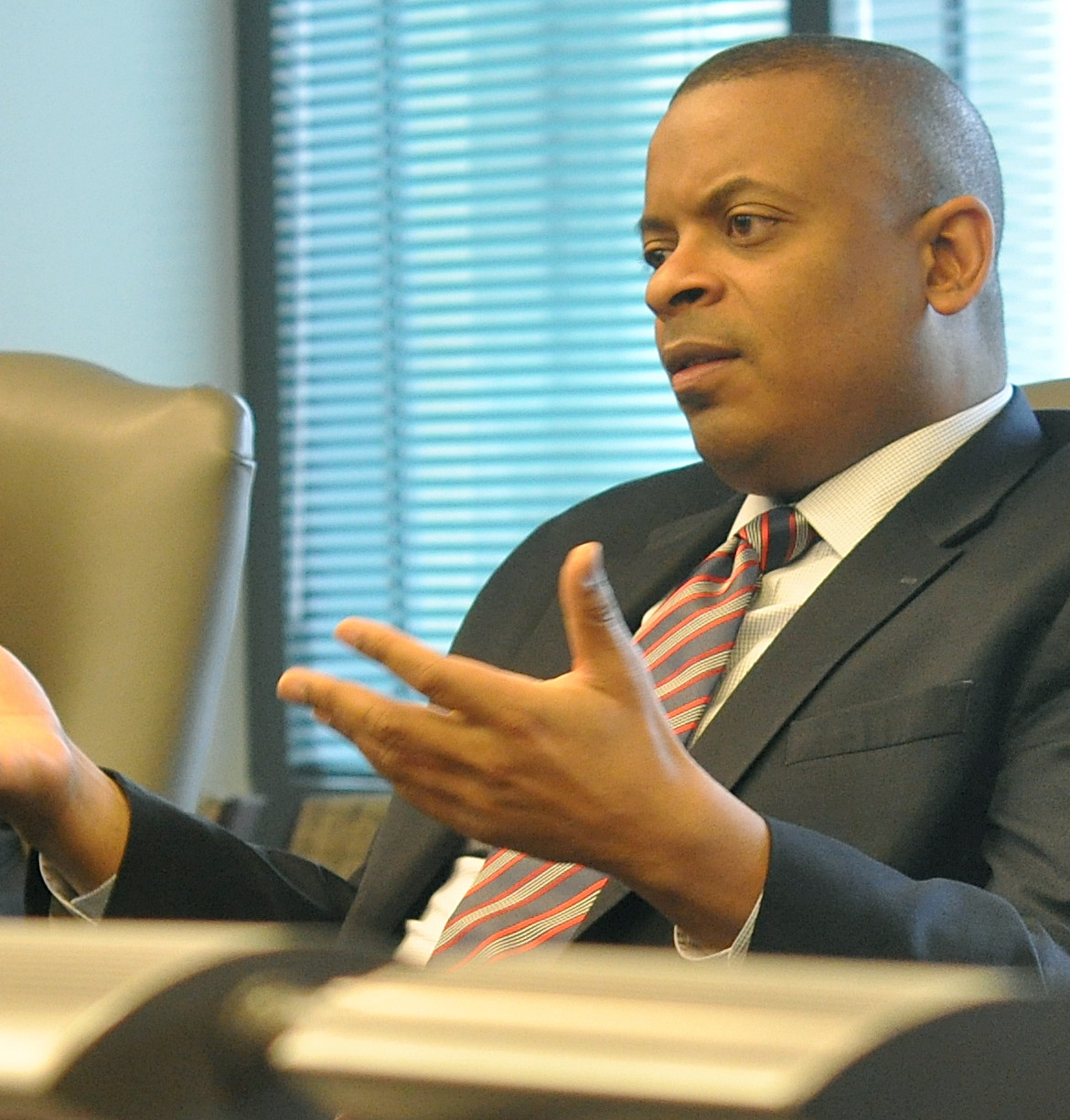

T4America brought together a group of mayors to visit with U.S. Secretary of Transportation Anthony Foxx — a former mayor himself — and deliver a message about the importance of passenger rail to the economies of those communities they represent.