The Senate’s first transportation reauthorization bill gets an F
EDIT, March 2021: If you represent an organization or are an elected official, please sign our letter urging the Senate to pass a long-term law completely unlike this one—a bill that orients the program transportation program around what counts: getting to where you need to go.
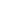
Authorizing federal spending on surface transportation is complicated, with different Congressional committees writing separate portions of the bill. That’s why we’ll score every reauthorization bill by how well it achieves our three simple principles for transportation investment. The America’s Transportation Infrastructure Act fails on all counts.
With the current authorization for federal transportation spending—the FAST Act—set to expire in 2020, it’s time for Congress to set transportation policy for the next five to six years. Once passed, this legislation will set federal funding levels for transportation for another five to six years.
We’re tired of the same old transportation bills that pump money into building highways at the expense of our crumbling roads and bridges, people’s access to essential jobs and services, and human life. That’s why we’ll score every reauthorization bill on how well they achieve our three simple principles.
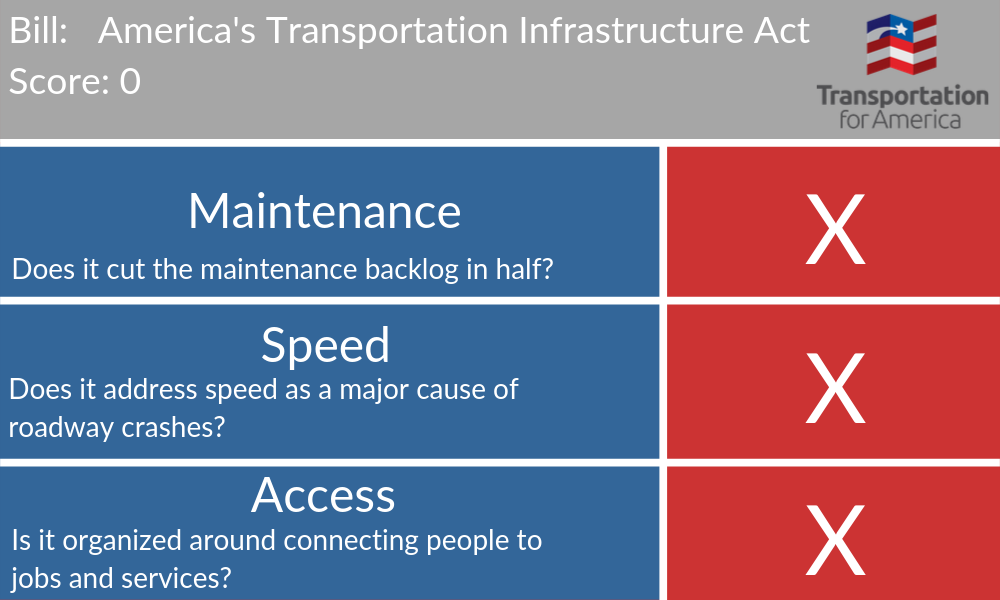
By our scorecard, the first reauthorization bill—America’s Transportation Infrastructure Act, which the Senate’s Environment and Public Works Committee approved in July—gets a big fat F. Here’s why.
Maintenance
This bill fails to take steps toward cutting our country’s maintenance backlog in half because it contains zero new, binding requirements to ensure that states use federal funds to actually bring their roads and bridges into good condition. The bill provides an additional $32 billion annually—on top of the $40 billion they already receive— for existing road building policy. History has shown that without any requirement to invest in maintenance, many states simply won’t. While the inclusion of a new bridge maintenance program is a welcome step, it’s a relative pittance at just 2 percent of overall funding.
Speed
We are in the midst of a massive safety crisis for people walking, with an alarming 35 percent increase in people struck and killed by drivers while walking from 2008-2017. And nearly 40,000 people die each year in traffic crashes.
This bill includes significant new formula and discretionary safety programs and language encouraging states and planning organizations to adopt complete streets designs and plans. However, we’re concerned that these programs will be undercut by substantial funding increases for high speed roadways in the base formulas without any additional constraints to improve safety. Complete streets designs shouldn’t be optional, as this bill considers them. History has shown us that “optional” will result in many states failing to take action to save lives.
Access
We were happy to see that the bill included a pilot program based on the COMMUTE Act to help a select group of states and metros measure whether or not their investments are connecting people to jobs and services. But a pilot program isn’t enough. Access to jobs and services has to be the core of any transportation authorization. We need to reward the boldness of this pilot proposal by measuring whether all $358 billion in this bill is connecting people to jobs and services.
Multiple states, including Virginia and Hawaii, have already started prioritizing their spending on projects that improve access. It’s possible—and necessary—to prioritize federal spending this way. We can’t afford another five or six years of wasted investment from using vehicle speed as our outdated measure of success.