Three strategies for smart electrification

When it comes to the climate crisis, we at T4A have historically been focused on the land use and transportation options that can reduce driving to cut emissions. However, transportation electrification is also essential to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Here are three key strategies for doing it right.
T4America got involved in the Coalition Helping America Rebuild and Go Electric (CHARGE), an effort we are co-leading with the Clean Vehicles Coalition, to help bring a smart growth perspective to electrification. CHARGE is made up of transportation, industry, environmental, labor, health, equity, and civic organizations that support smart policy to electrify America’s transportation system. If your organization is interested in joining up with CHARGE, let us know!
T4America’s long-standing position has been that transportation electrification is essential but insufficient to meeting our GHG reduction goals. Our signature report Driving Down Emissions lays out the strategies we need to implement in order to reduce emissions through provision of more transportation and housing options, which not only results in fewer emissions but economic, environmental and equity benefits as well.
We can’t expect electrification to solve our climate woes. However, the way we electrify will impact our ability to implement smart growth strategies, and it will influence job creation, equity and environmental impacts beyond the climate. That’s why we’ve decided to start weighing in on the electric vehicle transition.
There are three key strategies for electrifying America’s transportation system in a way that supports smart growth and transportation options and ensures we get the most out of taxpayer investments.
1. Put public transit operations first
We know that one of the best ways to reduce emissions is to move more trips from driving to public transit. Improving public transit to attract more riders to this affordable option better serves lower income families and BIPOC communities, supports healthier walkable development, and requires less road space.
Electrifying public transit also has great benefits including cleaner air in our cities and the potential to reduce transit operating costs. But we need to make sure that the higher upfront cost of electric buses in no way hampers our efforts to improve public transit service. An electric bus can only significantly reduce emissions if people choose to ride it.
By engaging with our electrification advocate allies, we’ve been able to establish public transit service as the first priority in fighting GHG emission from transportation, immediately followed by electrification.
2. Integrate electric options and EV charging into communities

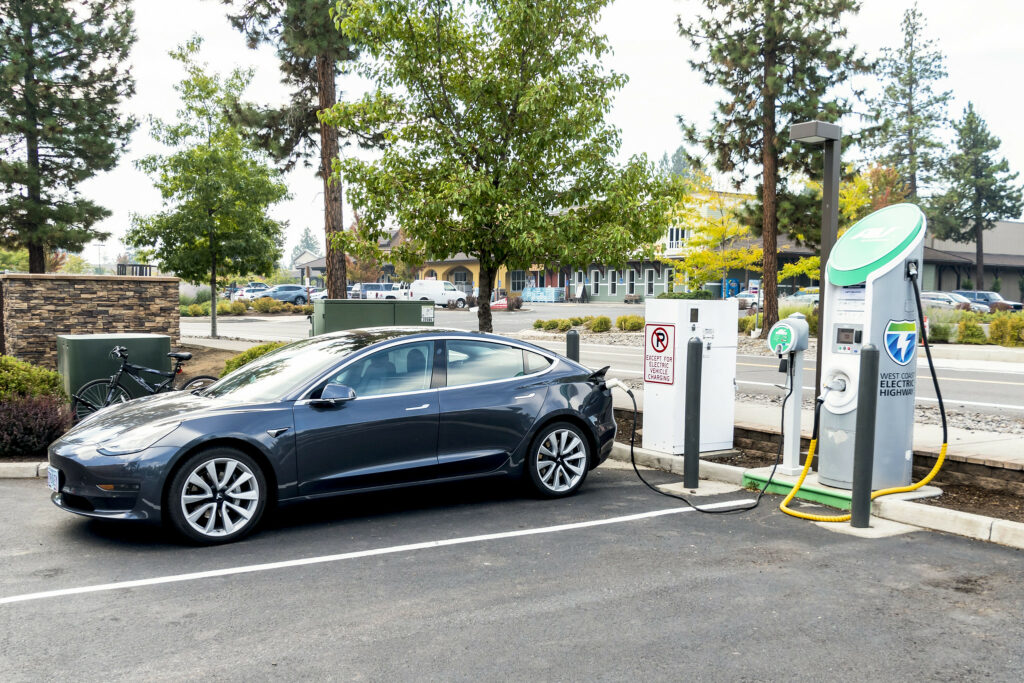
People deserve access to convenient modes of transportation outside of car travel, but the reality is a lot of folks will continue to rely on cars thanks to the current design of our cities. To reduce emissions, we need to electrify our vehicles and figure out where people will charge them. For people who own their own home with a dedicated parking spot, it’s relatively easy to just charge overnight in your driveway or garage. But for many folks in apartments, there may be no dedicated parking, or no charging available in the parking provided. EV users also need charging options when they take a road trip beyond the range of their vehicle.
The infrastructure law is working to address this with lots of investment in public charging. We can create a charging network that supports smart growth, economic development, and even transportation options other than driving. How?
The first thing to consider is the age-old smart growth strategy of co-location, in other words, putting things near each other. Charging an EV takes longer than gassing up an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle–anywhere from 20 minutes to a couple hours depending on the type of charger and the charge needed. The car occupants are going to want something to do, and the community where the charger is, be it urban or rural, has the opportunity to serve customers if they can walk to local businesses. The administration should invest in chargers in disadvantaged communities where they can support economic development.
We also need to think about how our communities are shaped by the shift to EVs and what kind of transportation options people have in denser urban areas where dedicated parking (and the easy charging that goes along with it) is less common. These are the kinds of neighborhoods where walking, biking and public transit are more viable, so we want to support and encourage them. We need to make sure public charging is available for apartment dwelling car-owners. Better yet, we can get more bang-for-the-buck supporting fleet vehicles–e.g. carshare vehicles, municipal fleets, and corporate fleets that see more use and, in the case of carshare, provide a mobility option for more people while supporting a low-car lifestyle.
We also can’t forget electric bikes, a clean, healthy and affordable mobility option that has been rapidly gaining traction in many communities nationally and worldwide. We can support continued growth in electric bikes with better bike infrastructure, secure bike parking, charging opportunities, and purchase incentives. We also need to make sure that car chargers aren’t located at the curb in such a way that precludes future bike lanes or bus lanes.
3. Clean up the trucks and fleets
As the government supports the shift to electric vehicles, we need to make sure that we get the most for our tax dollars. Trucks are a large source of emissions, and an area where more support is needed to make the transition to electric (and in some cases hydrogen) vehicles. We can bolster the economy and create good-paying jobs by focusing this support on domestic manufacturing of electric trucks and conversions in places where improved air quality can benefit frontline communities such as adjacent to heavily-polluted ports. As mentioned above, investing in fleets and carshare before personal cars will support more emissions reductions, and be more in line with a parallel smart growth strategy.
It’s true that transportation electrification can’t be the sole answer to our climate crisis. But it’s clear that EVs are part of the answer, and the way we electrify matters. By taking into account these three strategies, decision makers can make electrification a valuable part of our climate solution.
Rules for the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program are currently open to public comment. This program can help shape our nation’s approach to electrification. Learn more about the program and how to submit comments here.


















2 Comments