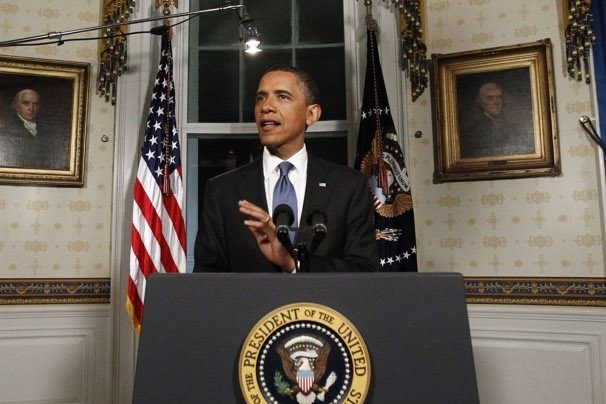
The theme of President Obama’s State of the Union address last night was winning the future, and investing in America’s infrastructure was an integral part of it.
The theme of President Obama’s State of the Union address last night was winning the future, and investing in America’s infrastructure was an integral part of it.
“The third step in winning the future is rebuilding America,” the President said, after discussing his vision for innovation and education. Other nations have outpaced our investment in roads and railways, and our own engineers have graded our infrastructure a “D,” he noted.
President Obama rightly emphasized the need for a 21st century transportation system on top of fixing what we built in the 20th. He also pointed out that we create more jobs and greater opportunity when we embrace an array of transportation options. The transcontinental railroad, rural electrification and the Interstate Highway System did not just put Americans to work in construction, he said. Jobs also came from “businesses that opened near a town’s new train station or the new off-ramp.”
“We were thrilled to hear the President come right out and say that investment in transportation and other infrastructure is central to rebuilding and growing our economy,” said Transportation for America Director James Corless. “An upfront investment in the most needed, clean transportation projects is a great opportunity to create near-term jobs and lay the groundwork for the future economy.”
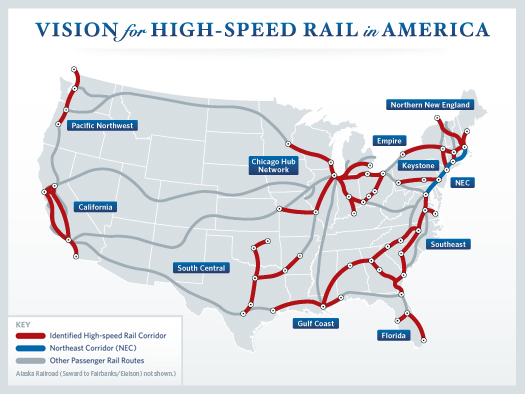
The President also reiterated his strong support for high-speed rail, with the goal of giving 80 percent of Americans access to the system within 25 years. “This could allow you to go places in half the time it takes to travel by car,” he said.
“For some trips, it will be faster than flying –- without the pat-down,” he added, to laughter.
Although he did not identify the program by name, President Obama endorsed the principles behind an infrastructure bank, saying we ought to “pick projects based (on) what’s best for the economy, not politicians.” And he vowed to harness private capital to help pay for new projects, a goal shared by House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee Chairman John Mica, a Florida Republican.
A number of groups, including business and labor, hailed the President’s focus on investing in the future. U.S. Chamber of Commerce President Tom Donohue echoed Obama’s call for “a world class infrastructure” and called for “common ground to ensure America’s greatness into the 21st century.” ALF-CIO’s Richard Trumka said, “We strongly support the President’s vision on infrastructure to create good jobs and succeed in a global economy, and working people are ready to work with him and hold him to his promises.”
AASHTO, the trade group representing state departments of transportation, was “encouraged that President Obama supports investing in America’s transportation infrastructure – recognizing the role it plays in creating jobs, growing the national economy and balancing the federal deficit,” according to Executive Director John Horsley, who added that he looks forward to working with the Administration and Congress on a reauthorization bill.
The Equity Caucus at Transportation for America said that “smarter transportation investments can unleash the under-realized economic power of communities across America.”
T4 America echoes these sentiments, and we are especially pleased with the President’s dual commitment to job creation today and economic prosperity tomorrow.
“The President’s vision for infrastructure is not just about near-term construction jobs,” Corless said. “It is, as he said, about growing new businesses, livable neighborhoods and dynamic regions that can attract a young and mobile workforce and compete internationally.
“It’s about jobs associated with new transportation technologies and manufacturing modern transit vehicles, everything from real time information systems to make our highways and transit corridors smarter, to the new rail cars being built today by United Streetcar in Oregon that can breathe new life into our cities and suburbs,” he added.
You can read T4 America’s entire statement here. You can learn more about the Equity Caucus at Transportation for America and read their entire statement here.
Photo: AP