A new report from TransitCenter finds that 2.8 million transit riders are considered “essential workers” during the COVID-19 emergency, underscoring just how essential it is to keep transit running. Under normal circumstances, they account for more than a third of total transit commuters in the country.
Transit is part of the public health response to COVID-19. Transit agencies across the country transport millions of essential personnel—including hospital staff, grocery store workers, and pharmacists—to and from jobs everyday. It’s essential to keep transit running frequently and reliably to get these workers where they need to go as millions of others are forced to forgo their usual transit trips to abide by “shelter in place” mandates.
The latest report from TransitCenter finds that nationwide over 600,000 transit commuters work at hospitals, in doctor’s offices, or as home health providers; 165,000 people take transit to jobs in grocery stores or pharmacies; and 150,000 workers in social services commute on transit. On a normal day before this crisis, essential workers accounted for 38 percent of transit commuters in New York City, 33 percent in Seattle, and 36 percent in Miami.
Now that transit agencies across the country have started to reduce service frequency and cut routes due to financial shortfalls and lost fare revenue, many of these essential workers can’t easily get to work. With less frequent service, buses and subways are more likely to be crowded and therefore unsafe due to the inability to adequately keep a safe distance from others.
If service stays frequent, TransitCenter writes, “at stops, stations, and on vehicles, commuters will have space to distance themselves from each other, protecting themselves and others from potential virus spread.” Maintaining frequent transit service will help these workers stay safe and healthy.
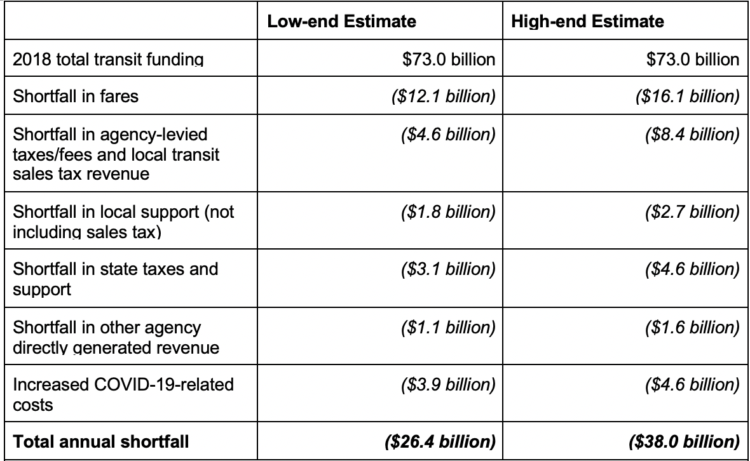
According to a previous report put out earlier this week, transit agencies could see an annual shortfall of $26-$38 billion. It’s welcome news that Congress has struck a deal to provide $25 billion in emergency aid for transit, but we’ll need sustained help from Congress to keep service running during this pandemic and keep millions of essential workers working. And we’ll need transit to be able to return to full strength in the aftermath of this crisis and help fuel our recovery by carrying millions of people back to work.
Lessons from the last Recession
What would it look like if transit service is unable to survive through the pandemic and bounce back with reliable service to help fuel our economic recovery? We don’t have to guess—we can look back at what happened during the Great Recession a decade ago. Because of declining sales tax revenues, agencies were being forced to cut service, raise fares, and lay off employees—even as transit ridership was actually on the upswing back then. At T4America, we chronicled the impact on riders, and gathered hundreds of stories from real people who were affected:
I work closing shift at a restaurant in downtown Sacramento and take the bus to and from work five days a week. I get off work at 10:40 and the last bus is at 10:50 so I have to run to make it. Sometimes I need to stay late to finish closing the restaurant after a busy night and don’t get a bus. The taxi fare is $40 to get home. Now the bus schedule might change with reduced hours. I don’t want to get a car because it is expensive, dangerous, and I don’t have a license to drive. Driving without a license will be my only option with the new hours. Pablo – Sacramento, CA
I live in North San Diego county and because of transit routes being canceled I have been unable to take better paying jobs and it has cut down on recreational activities. It takes longer to go to the grocery store, I have to walk farther after I get off the bus and times have been changed so I end up missing appointments. Leah – Encinitas, CA
The cuts in the bus service occurred a few years ago. The one that has been difficult to adjust to, is [the route] by the hospital where I have doctor’s appointments. The service was cut from one hour to every half-hour. If I don’t want to wait too long, I can walk a few blocks to another stop, but it is a more difficult walk for me as I am blind, and the crossing of one of the streets is somewhat more dangerous. I prefer to take the bus instead of using the ADA paratransit service when I can. Janet – Hartford, CT
That’s just a small slice of what we heard 10 years ago when transit agencies were struggling in the face of a recession. Transit service is vital today and Congress’ plan to provide transit agencies with $25 billion in emergency assistance will provide a lifeline—for now. But we don’t know how long this crisis will continue. And we’ll never be able to get our economy back on its feet without robust transit service in cities large and small that collectively move millions of people.