Safety over speed week: The U.S. builds death traps, not streets
We took a look at one busy road outside of Orlando where a dozen people have been struck and killed by drivers in recent years. The mix of high-speed traffic with people walking, biking, and taking transit is a dangerous combination; in the event of a crash, people die. The Complete Streets Act of 2019 would go a long way to give local government more resources to redesign these dangerous streets so everyone can travel along them safely.
South Orange Blossom Trail isn’t a pleasant path through an orange grove, as the name would suggest, but rather a busy street in the Orange State that runs south from downtown Orlando. South Orange Blossom Trail is like many similar ‘arterial’ roads across the country: grocery stores, places of worship, clothiers, gas stations & auto repair shops, apartments & homes, restaurants, and a multitude of other businesses have sprouted along the route. And like so many similar streets surrounded by development in cities and towns of all sizes, it’s also a death trap for people on foot.
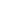
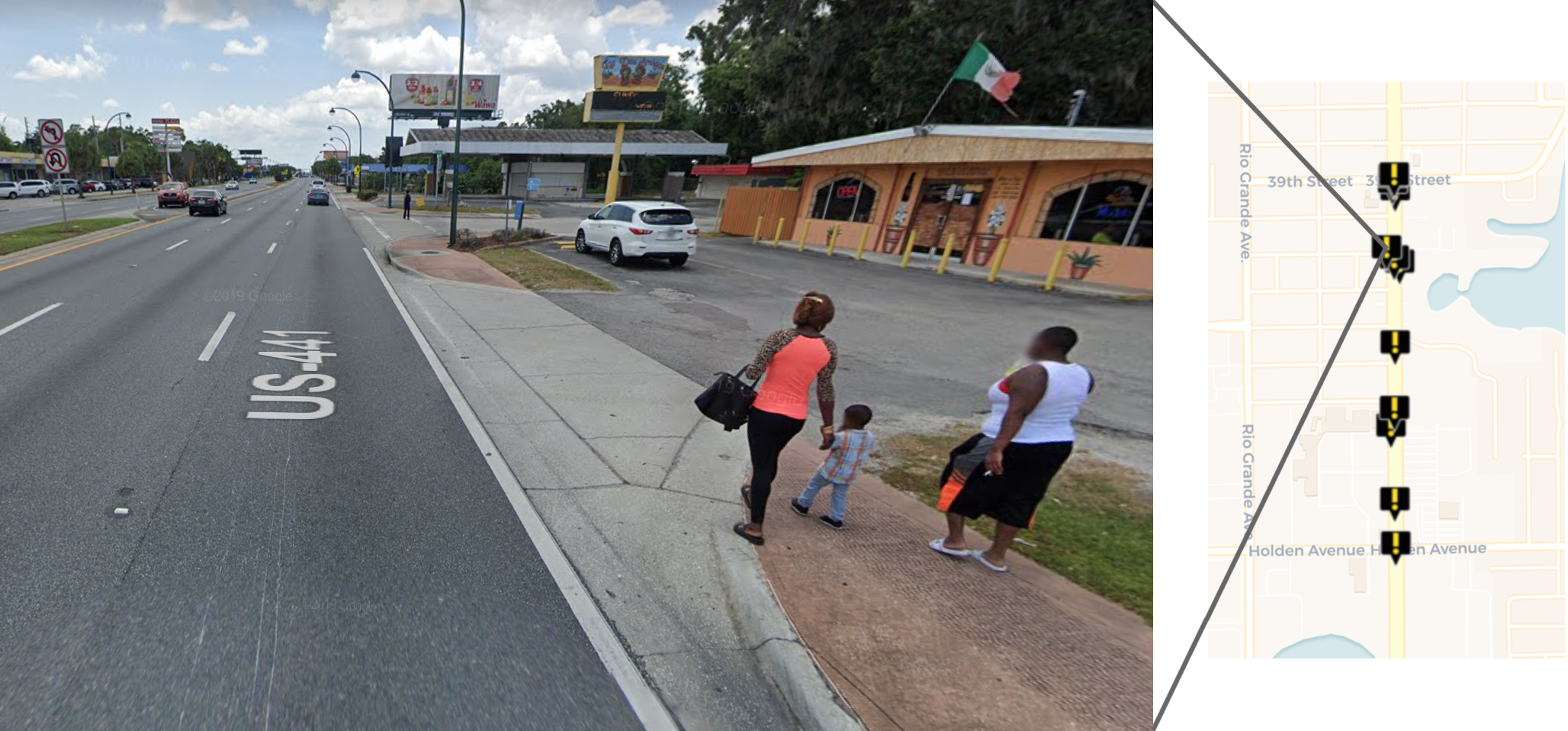 A street view of South Orange Blossom Trail and the location of this image relative to the 12 pedestrian deaths along this stretch of road from 2008 to 2017.
A street view of South Orange Blossom Trail and the location of this image relative to the 12 pedestrian deaths along this stretch of road from 2008 to 2017.
Between 2008 and 2017, 12 people walking were struck and killed by drivers along a 3,400 foot stretch of South Orange Blossom Trail. This six-lane thoroughfare (three lanes in each direction) is a gauntlet for people walking, and with the multitude of shops and homes in the area and bus stops regularly dropping people off on the side of the road, people walking are everywhere.

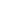
The nearest crosswalk isn’t even visible from this bus stop outside an apartment building.
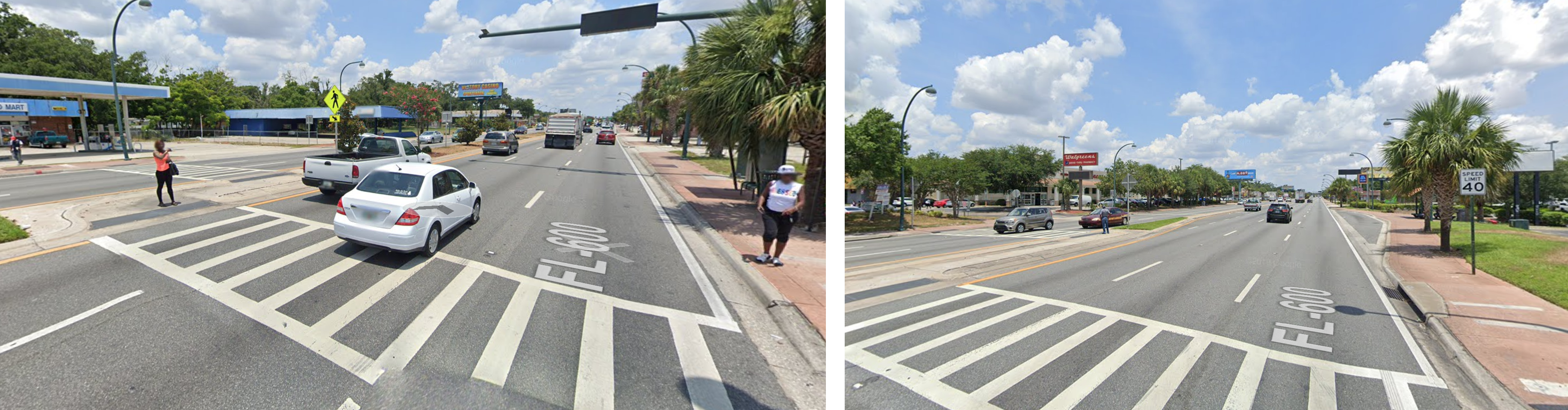
This particular segment has a posted speed limit of 40 mph, but there is absolutely nothing about the design of this road that would encourage drivers to observe that limit. The wide, straight lanes and open skies communicate to drivers that this is a highway and you should thus be driving at high speeds. There are even signs that tell you which intersection you’re coming up on (because you’re certainly driving too fast to see it, as in the picture above). The only two signalized crosswalks along this stretch for pedestrians are at either end, 3,400 feet apart or about a 15 minute walk. While there are some unsignalized mid-block crosswalks, you have to be brave, stupid, or have no other choice to try crossing three lanes at a time hoping drivers going 50+ mph will stop for you. This street was built for speed not safety. It’s no wonder that a dozen people have been killed while walking along it in recent years.
South Orange Blossom Trail is the quintessential example of how U.S. street design standards and a focus on speed above all else have created such dangerous roads and why we have an epidemic of pedestrian deaths in this country. It’s a street designed for speed and to avoid vehicle delay. People walking, biking or taking transit are merely afterthoughts, just guests on this road designed for cars. Simply ask the people waiting to cross in the middle of these six lanes if it feels like this street was designed with someone walking in mind.

It’s also the quintessential example of a street that the Complete Streets Act of 2019 in Congress is designed to fix. The Complete Streets Act would designate a small slice of federal highway funding to create Complete Streets that are safe for people walking, biking, taking transit, or driving. Any community with a Complete Streets policy—be it a county, city, town, or tribal government—would be able to apply for this funding directly to retrofit dangerous streets with safer designs.
Under the Complete Streets Act, counties could adopt a Complete Streets policy (if one isn’t already on the books) and then apply for dedicated funding to retrofit roads like South Orange Blossom Trail in unincorporated areas. Depending on the context, a safer street could include narrower lanes, protected bike lanes, signals at mid-block crosswalks, street trees, and other design interventions that can help slow cars and make space for different uses. On locally-owned roads, cities and towns could use the same pot of federal funding to implement similar improvements on dangerous roads.
For too long, prioritizing cars going fast above all else has been the top consideration in the design of our streets. It’s how we ended up with dangerous streets that look more or less exactly like South Orange Blossom Trail in all 50 states (even in Alaska, just add mountains along the skyline). According to current U.S. street design standards, this road and its ilk are designed exactly as they should be; that’s the problem.
We have to start putting safety over speed. Safety—literally keeping people alive—is more important than shaving a few seconds off a driver’s commute. And prioritizing safety is fundamentally incompatible with high speeds on these kinds of streets. The Complete Streets Act of 2019 would be a major step in the right direction, if Congress can pass it.
Send a message to your representatives urging them to support the Complete Street Act.


















Pingback: Transportation For America – Destination access week: How bad metrics lead to even worse decisions