Report comes as Oregon’s legislature considers new transportation funding in part to address precisely these types of ongoing repair and maintenance needs
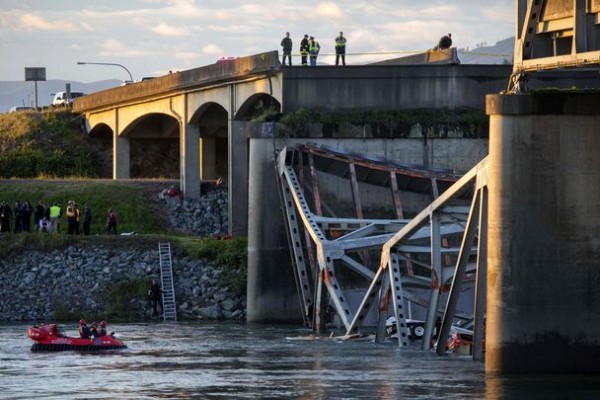
OREGON – A new Transportation for America report analyzes the condition of Oregon’s bridges and finds that 439 are structurally deficient — requiring urgent repair, rehabilitation or replacement. These 439 bridges represent 5.5 percent of all Oregon bridges.
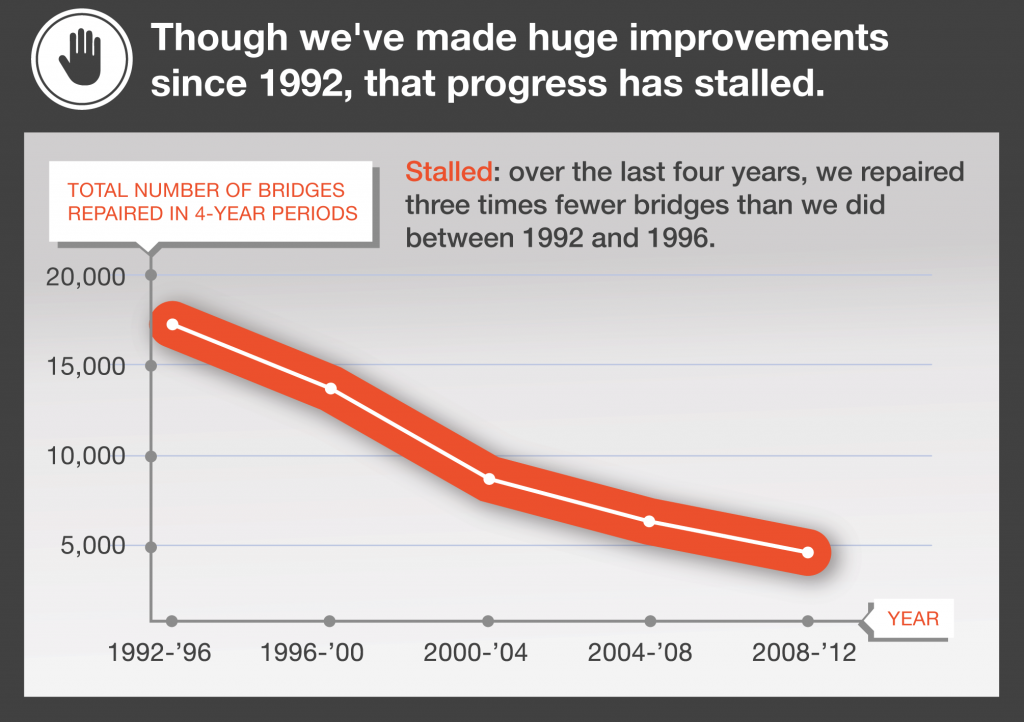
These bridges are located in areas urban and rural and serve as critical links in moving people to work and goods to market each day. In 2014, Oregon drivers took 1,000 trips per minute over these deficient bridges. Compared to other states, Oregon has done a better job keeping their bridges repaired, but 439 structurally deficient bridges is still far too many, and without continuing to prioritize and fund their repair, progress could slow or even reverse course.
Most bridges are designed with a 50-year lifespan, but these structurally deficient bridges are an average of 55 years old, 14 years older than the average age of all Oregon bridges. One in twelve bridges were built before 1948, which means that 680 bridges have been carrying traffic since before the Korean War and the creation of Medicare.
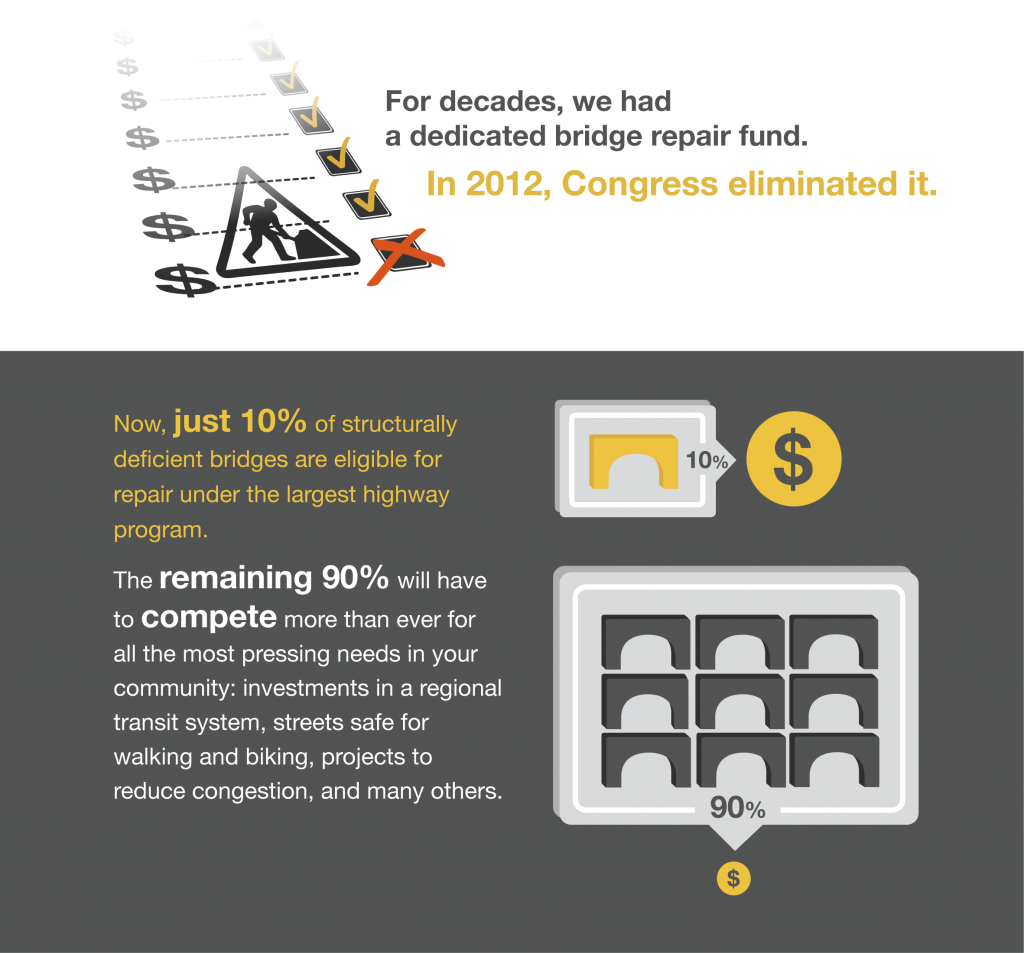
“Federal and state transportation funding simply hasn’t kept up due to declining gas tax revenues, inflation and improved vehicle fuel efficiency,” said T4America director James Corless. “With action by the legislature, Oregon could join a growing list of states — 20 and counting — that have raised their own transportation revenues since 2012. While increasing state funding is a good step, Congress needs to reward those efforts by fulfilling the historic federal role as a trusted partner in transportation investment and passing a long-term transportation bill with stable, increased funding. Doing so would allow the State of Oregon and local officials to better address these sorts of ongoing maintenance needs.”
Oregon’s 2003 OTIA bond package prioritized the repair of the state’s busiest structurally deficient bridges, but now the bill is coming due for those bonds and is eating into yearly transportation budgets. Without new funding — and in light of Congress’ inability to pass a long-term transportation funding bill to support states like Oregon — the state will face more competition for fewer financial resources to address the state’s transportation needs.
“Even though the state of repair of our bridges is in relatively good shape in Washington County, we will see declines if we don’t increase revenue to address our backlog of maintenance needs,” said Andrew Singelakis, Washington County’s Director of Land Use and Transportation.
4,032 of the state’s 8,052 bridges are locally-maintained, and 7.2 percent of those locally-maintained bridges are structurally deficient — significantly higher than the state’s average rate of 5.5 percent for all bridges. And a staggering 66.5 percent (292 total) of Oregon’s 439 deficient bridges are maintained by local entities.
Though Oregon does direct a portion of state gas tax revenues to local governments — 30 percent to counties and 20 percent to cities — that money is flexible and with a range of pressing local needs, these local jurisdictions have to make difficult decisions with those funds, and they’re already feeling the squeeze.
“The average value of Wasco County’s yearly agricultural production is over $80 million dollars,” said Arthur Smith, Wasco County Public Works Director. “Most of the cherries, wheat and other products grown here are hauled on county roads, so any closures or load limits placed on county bridges can have a very significant impact. We laid-off 30 percent of our workforce in 2007 because of loss of forest receipts, and are now, more than ever, totally dependent on state and federal funding to fix our bridges. It’s vital that those structures remain in good shape.”
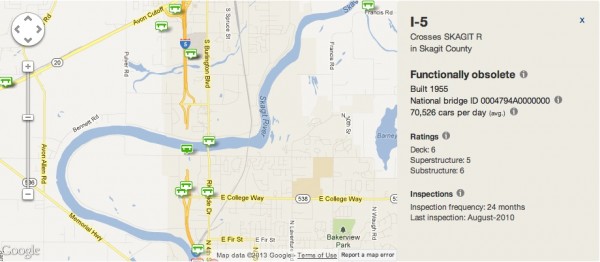
This report can be found online at https://t4america.org/maps-tools/bridges. That site includes an interactive map that allows one to map all bridges within a ten-mile radius of any U.S. address and see their condition and other vital statistics.
Contact:
Oregon: Chris Rall, 971-230-4745
NW Field Organizer
chris.rall@t4america.org
DC: Steve Davis, 202-971-3902
Deputy Communications Director steve.davis@t4america.org