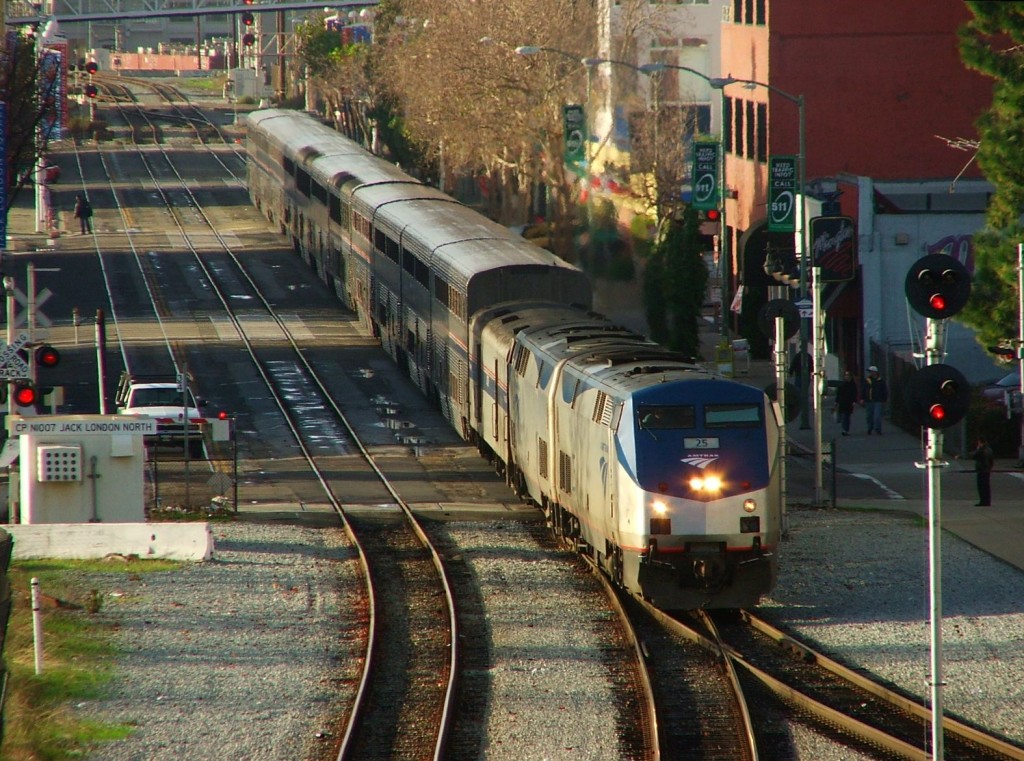
Our country’s burgeoning passenger rail renaissance has not gone unnoticed in the deep South, and at least one coalition of southern leaders are working hard to grow and expand service in three states in the deep South. This week I had the privilege of traveling on the rails through the northeast with the Southern Rail Commission on a trip to inspire and see firsthand how other regions and cities have invested in passenger rail and used it as an economic catalyst for their communities.
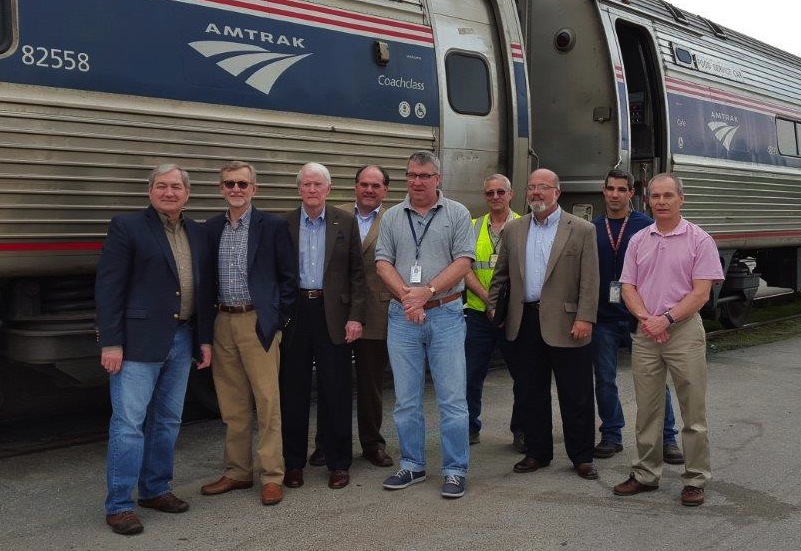

John Spain, left, John Robert Smith, Dick Hall, Knox Ross, Joe McHugh, an Amtrak employee, Greg White, a second Amtrak employee and Bill Hollister pose outside an Amtrak train during the trip. John Spain, Knox Ross and Greg White are members of the Southern Rail Commission’s executive committee, Dick Hall is the Mississippi Central District Transportation Commissioner, and Joe McHugh and Bill Hollister are with Amtrak.
Transportation for America is proud to partner with the Southern Rail Commission on their work to help restore and expand passenger rail service through the states of Alabama, Mississippi and Louisiana. SRC’s mission is to promote “the safe, reliable and efficient movement of people and goods to enhance economic development along rail corridors; provide transportation choices; and facilitate emergency evacuation routes.”

T4America chair and former Mayor of Meridian, MS, John Robert Smith
While expanded service in the booming northeast corridor or between other major coastal cities gets frequent publicity, many Southern states have moved past merely fighting to preserve what limited passenger rail service they have, to aggressively seeking opportunities to grow and expand service. Leaders in these states are seeking to connect more people to the tourism markets, health care systems and educational centers that drive their regional economies, and they see passenger rail as a critical option for doing so.
And the South wants to do it right the first time. They eagerly want to learn from the successes of other regions that have created, implemented, marketed and managed passenger rail that is responsive and right-sized for the populations they serve.
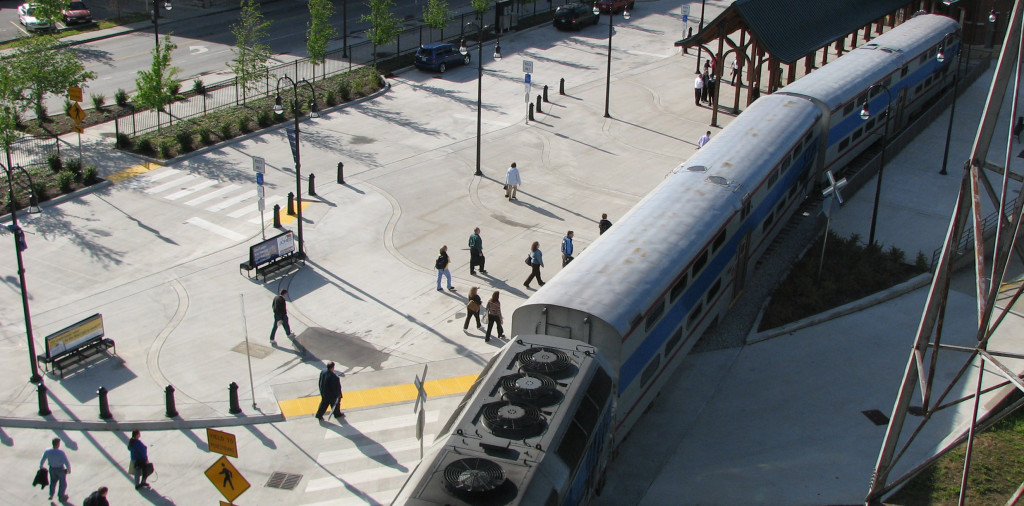
To that end, I led a delegation of the Southern Rail Commission (SRC) and Mississippi Central District Transportation Commissioner Dick Hall to experience and learn from two services in the Northeast. Although they’re structured differently, both lines we rode are highly successful and located far beyond the Mason-Dixon Line: the Downeaster and the Vermonter. The Downeaster runs from Boston through Portland and onto Brunswick, ME and the Vermonter runs from St. Albans, VT to New York City through Massachusetts and Connecticut.
Getting inspired along the route
Traveling north from Boston’s South Station, our departure point, the Downeaster carried us through urban centers and college towns, all with an inviting face turned toward the track. It was clear that each city and town recognized that the asset traveling through their backyards is an important part of who they were and who they aspired to be.
The similarities between these northeastern towns and our own southern hometowns were striking.
The train station in Durham, which sits in the middle of the campus of the University of New Hampshire, got me thinking: what would such a station placement mean to Tuscaloosa and the University of Alabama or Baton Rouge and Louisiana State University? Imagine getting on the train in Atlanta on a fall Friday with hundreds of other alumni to head to your old college town for a weekend of college football.
In Saco, ME, the warehouses and abandoned garment mills we saw transformed and reborn as upscale apartments and condominiums could be replicated in Hattiesburg or Meridian, Mississippi. Old Orange Beach, ME, was alive with beach and carnival goers on Memorial Day evening and the train filled with families from Boston and Montreal headed to join the fun. Don’t all of our southern cities have festivals and events worthy of sharing with our neighbors? And equally important, wouldn’t we all want to see our neighbors leaving their tax dollars in our cash registers?
Learning how to run a successful passenger rail service
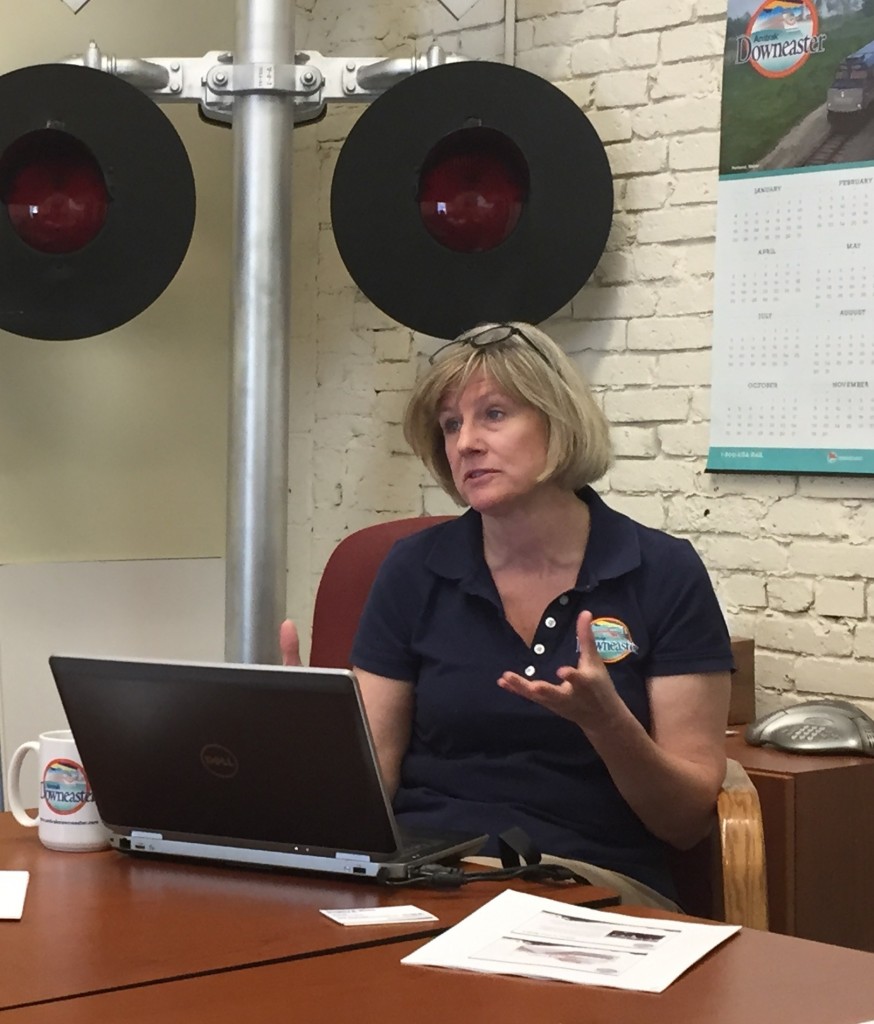

Patricia Quinn
Time spent with Patricia Quinn, executive director of the Northern New England Passenger Rail Authority (NNEPRA), while in Portland, was invaluable for SRC as they seek management models for expanded passenger rail service in the South. The strong state-supported Downeaster line managed by Patricia and her small but efficient staff demonstrates the value that attention to detail, on-time performance and a quality ride has for their customers — and potential new customers.
Wayne Davis, chairman of Train Riders Northeast and a NNEPRA board member, gave the tour of Freeport, ME beginning at their well-located Downeaster stop that welcomes visitors directly into the extensive retail shopping Freeport is noted for — anchored by the L.L. Bean main corporate store. Retail activity was brisk and many beautiful historic structures were enjoying new life as retail, restaurant and office space; all within an easy walk of the Downeaster rail connection.
Transit-oriented development, indeed!
Traveling through the White Mountains and Crawford’s Notch brought us to Montpelier, VT, and our meeting with Chris Cole, Deputy Secretary of Transportation, and his staff. The Vermonter and Ethan Allen lines are also state-supported routes, but unlike the Downeaster, they are operated not by an authority but by the Vermont Agency of Transportation (VTrans).
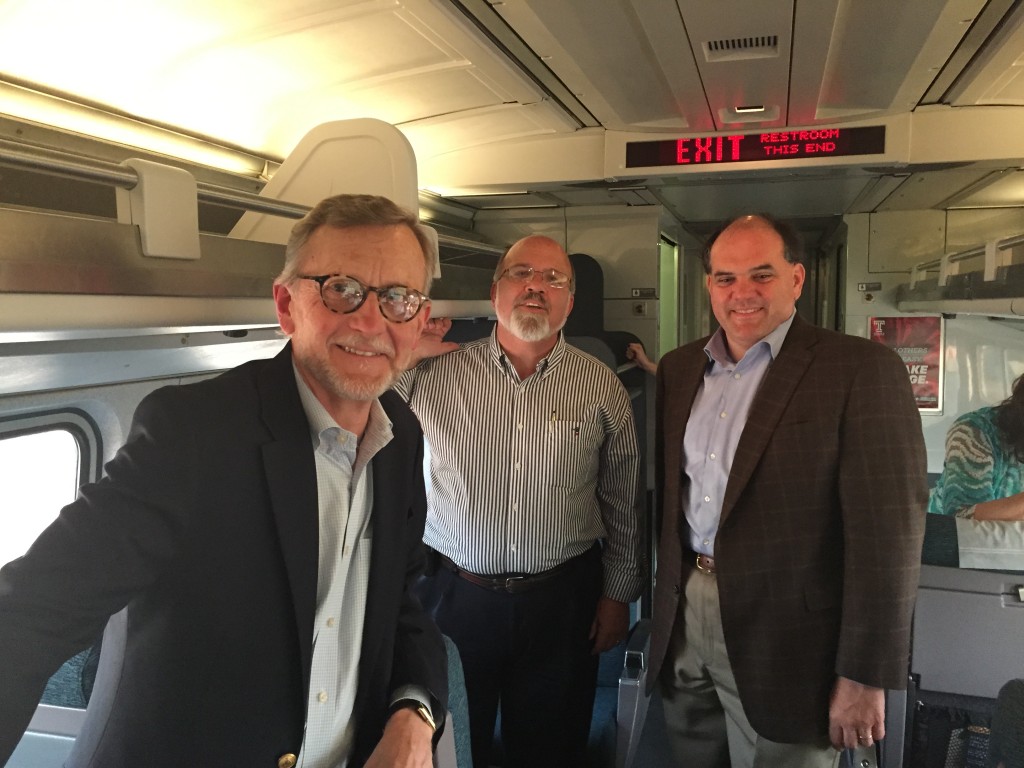

Deputy Secretary Cole explained their need for a dedicated Amtrak liaison staffer within VTrans — similar to the position that Maine and the Downeaster has — whose only mission is to manage their passenger rail contacts and focus on the on-time performance, maintenance and rider experience; a position that will be filled in the future.
Vermont has felt the positive economic impact of investing at the state level in both freight and passenger rail, buying closing shortline railroads, re-laying tracks and actively marketing the passenger rail service to its people. An especially smooth ride on the Vermonter back to New York City proved the value of VTrans’ investment.
Chris Parker, executive director of the Vermont Rail Action Network, riding with us as far as Brattleboro, Vermont, shared with us successful examples of advocacy built on partnerships and timely information shared with constituents. These goals are already a focus of the SRC and were validated by the visit with Chris, and lessons for improvement were also provided.
A special thank you to both Joe McHugh and Bill Hollister with Amtrak for coordinating and facilitating the trip to make this sharing of ideas, best practices and lessons learned, possible.
While the gracious hospitality we received rivaled that we’re accustomed to receiving in the South, it was the Yankee efficiency and ingenuity we witnessed that most impressed. Like all good southerners, SRC has the hospitality down, but taking a solid dose of that Yankee efficiency and ingenuity back home would serve the SRC well.
We’re excited to help our friends at SRC use these lessons learned to build something that will help their regions prosper. As they say at SRC: “Ya’ll Aboard.”