
For the first time in a decade, Congress is on the cusp of passing a five-year transportation authorization bill that will carry us into the next decade. Though we await final floor votes and the President’s signature, it will almost certainly be approved in a matter of days. So how does the bill stack up against the pressing needs of our country? Here’s the good, the bad, and the ugly of the FAST Act.
While the final bill has changed only slightly from the separate versions passed by the House and the Senate since July, we’re going to take a slightly different tack than our usual “ten things you need to know,” and break this bill up into the good, the bad, and the ugly.
T4America members can find a link to our full detailed memo with funding tables below,
[member_content]
Read and download the full members-only summary of the five-year FAST Act.
Note: This and all other bill summaries also live under the “legislative content” tab within the members-only portal.[/member_content]
The good
Preserves stable funding for transportation over five years
While this bill falls far short of meeting any financial sustainability test, it is nonetheless remarkable that Congress is about to pass a five-year bill with no cuts to overall funding levels — including funding for public transportation, which was targeted for outright removal by the House in 2012. The FAST Act provides a slight plus-up in funding over MAP-21 levels (estimated at about $10 billion over the life of the bill) by authorizing $230 billion for highways, $60 billion for public transportation, $10 billion for passenger rail and $5 billion for highway safety programs. While this bill will put a five-year hold on devolutionists calling for ending the federal program outright and dumping all the responsibility on cash-strapped states and metro areas, this “fully funded” bill comes at a steep cost in general fund revenues (that could be used elsewhere, remember) and a number of significant, innovative and locally-driven proposals that were left on the cutting room floor — which we’ll cover further down.
More support for smart transit-oriented development projects
Due in part to the hard work of T4America, Smart Growth America and LOCUS over the last year, transit-oriented development projects will be eligible for the low-interest TIFIA and RRIF federal financing programs. The small pilot program of TOD planning grants was also preserved; grants that help communities make the best use of land around transit lines and stops, efficiently locate jobs and affordable housing near new transit stations, and boost ridership.
Authorization for passenger rail is in the surface authorization for the first time
While the bill does far too little for truly making our system multimodal and making greater investments in more transportation options, it takes a positive step by bringing passenger rail into the larger surface transportation authorization for the first time ever. (This was typically passed as a standalone bill and Congress usually had little impetus for quick action.) Passenger rail will still have to go through the general appropriation process each year (getting started now for FY16, if you’ve been following along) to get their funding, but this positions it well for the long-term hope: including and funding passenger rail with guaranteed funds from a multimodal, 21st century transportation trust fund in the years ahead.
A (slight) increase in funding for metropolitan regions
Though the final product was far short of what we had been pushing for, local governments will receive slightly more money to invest in their priority projects, with an increase in what’s known as suballocated funds by 1 percent per year of the bill, up to 55 percent in 2020. Unfortunately, this bill does nothing to give smaller communities under 200,000 in population any more control over how these funds are spent in their areas — the state will retain authority and can continue to choose to ignore local needs. Overall, funding directed to local communities is an improvement over MAP-21, but the funding and especially the control over those dollars still falls far short of what we need. (More on this below.)
Locals have greater access to low-cost federal loans
To apply for a TIFIA loan today, the total project cost has to be over $50 million, which makes it difficult or impossible for the projects in places that aren’t our biggest metro areas to receive funds. Our colleagues at LOCUS worked with other partners to get the threshold successfully lowered to $10 million, which opens the door to a wider range of project types in communities of all sizes, including complete streets, urban street retrofits, trails and other low-cost projects that are often the highest priority for local communities.
Safer streets for all users
Working alongside our colleagues at the National Complete Streets Coalition, we were successful in winning the requirement that state DOTs and metropolitan planning organizations (MPOs) consider all users of the roadways when designing and building projects. Further, we were able to include a provision in the bill that allows local governments to use the street design manuals of their preference (like the NACTO guide) and preempt their state DOT’s design manual for locally constructed projects. Far too often, local governments are working hard to develop complete, safe streets, but are stymied by their state DOT’s desire to maintain fast speeds and wide lanes at the expense of other people who need to use the street and would benefit from narrower lanes, safe bike lanes or wider sidewalks.
The bad
Very little for innovation
In a world where demographic and technological change is upending the transportation industry, the FAST Act does alarmingly little to advance innovation. Despite a few glimmers of hope such as a new $60 million advanced technology deployment fund, the remainder of the bill is remarkably silent on how and where technological innovation can help improve mobility and accessibility. Even smaller changes to make car-sharing eligible for federal funds failed to get included in the bill, and Congress has even made it tougher for states to advance innovative tolling ideas as means of both managing traffic and raising new revenue.
No new performance measures
MAP-21 took a cautious first step into developing a system of measuring the performance of our transportation investments, but this bill generally refuses to continue that progress. Specifically, Congress missed an opportunity to include a new measure that would improve accessibility and measure how investments affect residents’ access to jobs and opportunity. A new national goal and performance measure was included in the House version by Reps. Waters and Carson (supported by many of their colleagues) that would require USDOT to develop a new performance measure on accessibility for urban disadvantaged populations. The conference stripped this provision.
No increase in accountability or transparency
The House and Senate shot down any and all provisions to improve accountability and transparency for the current way by which public agencies select projects, a process that the public feels is murky, mysterious, and overly political. At a time when Congress needs to take steps to restore taxpayer confidence in the system, we’ve preserved a system that wastes billions annually and fails to improve the experience of the traveling public or improve accessibility and quality of life for all Americans.
Funding for biking and walking preserved, but capped over the life of the bill
While the small but popular Transportation Alternatives Program that helps states and local communities build safe routes for biking or walking wasn’t eliminated, it’s one of the few programs where funding doesn’t grow with the overall increases in bill — it’s capped at $850 million. A new provision was included that will allow large metro areas to “flex” away half of this program to any other project they choose, so some decision-makers at the metro level will be allowed to ignore the demand for (and economic potential of) safer streets and other community-driven mobility projects.
The ugly
A one-size-fits-all freight program
Freight moves across the country on every mode of travel imaginable and our freight issues are inherently multimodal, but Congress didn’t see it that way when they earmarked 90 percent of the funds in a new freight program for highway projects. This new combination of a formula and separate discretionary grant program is the first time Congress has funded a freight program in the transportation bill, but unfortunately other options like ports, railroads, intelligent transportation systems, or better demand management are only eligible for a small share of the freight dollars. The bill creates a discretionary grant program with $800 million this year, rising to $1 billion in 2020, and creates a new formula program with $1.15 billion in the first year rising to $1.5 billion in 2020.
The bill requires states and metro areas to analyze their freight movement and come up with a multimodal plan to improve things (good!) but then only gives them funding to build highway solutions (bad!). This is a backdoor way to provide more unaccountable funding to states for highway projects that may have been on the drawing boards for decades, and does little to promote cost-effective solutions to freight mobility. One additional issue is that this new formula program relies on current highway formulas unrelated to freight movement and completely ignores freight tonnage or value that would ensure we get the biggest bang for the buck from these investments.
Local communities are left out and behind
Despite our best efforts and those of a handful of champions in both the House and the Senate, this bill does not provide significantly more transportation funding or control over that funding to local communities of all sizes. (It does increase suballocated funds by 5 percent over the life of the bill as noted in “the good” above.) It does nothing for smaller metro areas under 200,000 in population, leaving decisions about which projects to build in the hands of the state DOT, which often ignores local wishes and spends locally-earmarked funds on the projects of the state’s choosing. By failing to bring more dollars, control and accountability closer to the local level, the bill fails to restore the trust of the American people in how our transportation decisions are being made.
An astonishing cut to TIFIA loans
Just three years after MAP-21 increased the TIFIA loan program up to $1 billion, the FAST Act slashes it down to $275 million, leaving a far smaller pot for local communities to compete for. Despite some good reforms made to the program overall and at a time when Congress is eager to stimulate more investment with local or private dollars, it’s hard to fathom why the champions of TIFIA in MAP-21 sat by while this financing program was cut by 70 percent.
Using tomorrow’s funding to pay for yesterday’s policies
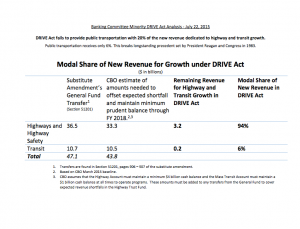
Rather than raise transportation user fees (or even talk about it) to fill the ever growing chasm between spending and gas tax receipts, Congress scrounged up $70 billion in non-transportation related general funds to pay for this bill. Somewhere between a third and a quarter of this bill’s cost will be covered by all taxpayers, which means places with more taxpayers and more revenue will be paying more. There won’t be a single project with its cost covered by its users over the life of this bill, and every state will be getting back far more money than they contribute in fuel taxes. This is a bad precedent and will make the hole all the harder to dig out of in 2021 when it comes time to reauthorize this program.
Wrapping it all up — the big picture
While states and metropolitan areas will appreciate the certainty of a five-year bill that guarantees funding for their planning and investments, almost a third of the bill’s cost will be paid up front by general tax revenue — not transportation user fees — offset by accounting maneuvers and budget gimmicks. We will all be paying the tab for Congress’ refusal to have an adult discussion about revenue, whether you buy a lot of gas or none at all.
With almost $75 billion in general taxpayer dollars transferred into the highway trust fund to keep it solvent over the last seven years, and more than $75 billion now pledged over the next five years, the notion of a true trust fund for transportation, funded by users of the system, is dead. Only a handful of elected leaders were willing to even broach the topic of raising or indexing the gas tax to cover the cost of their desired spending levels. The majority of our elected representatives, along with most of the traditional transportation industry, were all too willing to pass a bill at almost any cost.
As far as the bill’s policy goes, it uses tomorrow’s dollars to pay for yesterday’s ideas and represents a missed opportunity to do something much better. On the whole, Congress looked at our system for investing in transportation and said, “the approach we’ve been using for the last decade or so seems to be working. Let’s double down on that.”
Do you and your community’s leaders agree? Do you feel like the current system is working for you and your town or city? The answer to that question will tell you how you should feel about this piece of legislation.






 Most transportation spending comes from the trust fund and the levels are already set (for the most part) by the current authorization — like the long-term transportation bill currently being debated. But important discretionary programs that aren’t “authorized” receive their funding each year from House and Senate appropriators.
Most transportation spending comes from the trust fund and the levels are already set (for the most part) by the current authorization — like the long-term transportation bill currently being debated. But important discretionary programs that aren’t “authorized” receive their funding each year from House and Senate appropriators.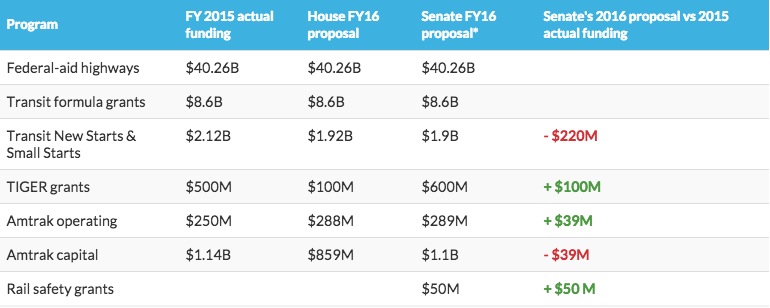











 Since 2009, the federal TIGER program has made projects like Normal’s downtown transportation hub and civic centerpiece a reality,
Since 2009, the federal TIGER program has made projects like Normal’s downtown transportation hub and civic centerpiece a reality,