With a range of notable ballot measures for transportation considered by voters Tuesday, how did the issue fare at the ballot box? Did the recent trends for transportation-related measures continue?
Compared with two years ago when there were a number of major, big-ticket ballot measures to raise billions in new local revenue for transit on the ballot, there were relatively few local ballot measures raising new money for ambitious bus or rail transit projects in 2018. We’ll get into what actually happened at the local level, but this year, one of the more interesting trends emerged at the state level.
[member_content]
T4America members: We’ve produced a more detailed post-election analysis for you. You can download that short document here. Reach out to us if you have any questions.
[/member_content]
Statewide
The biggest question on the ballot was Proposition 6 in California, which would have undone the state’s 2017 legislation that increased fuel taxes to raise more than $50 billion to prioritize repair and pledge billions toward transit, safe streets for walking and biking, and an overall multimodal approach to solving the state’s transportation challenges. The legislation also gave money directly to California localities to spend on their greatest needs, allowing for a strong measure of local control.
Proposition 6 was defeated—preserving 2017’s tax increase—with just 45 percent in favor. Of all the states that have raised new transportation revenues since 2012, California was one of the few that raised new money that could be used on a diverse range of needs. Voters just signaled their approval for this approach a year later.
By contrast, statewide proposals to raise new revenues for transportation—almost all for only roads—failed in Missouri and Colorado, as well as a non-binding advisory measure in Utah that went down by a wide margin. While a portion of Colorado’s gas tax dollars (those directed to localities) can be used on any transportation purpose, both Missouri and Utah have constitutional prohibitions on 100% of their gas tax dollars, preventing them from being spent on any other transportation needs.
What’s the trend to extrapolate from these four measures? The latter three measures were essentially status quo referenda on whether or not voters want to put more money into the existing state system for transportation. The taxpayers resoundingly answered “no.” In Missouri’s case, this was their second run at raising state fuel taxes for only roads, and like in 2014, voters in the state’s metro areas widely rejected the measure, viewing the taxes as regressive and a way to funnel money out of their metro area to pay for needs elsewhere in the state. All three contrast with California’s new system to devote new taxes toward a range of multimodal projects that was reaffirmed by voters.
This will be the most pressing question of 2019 as Congress ramps up to work on reauthorization. Do the American taxpayers believe that the federal transportation system works for them? Will they be supportive of federal legislators raising their taxes or creating new revenues to put into the same old system?
Local
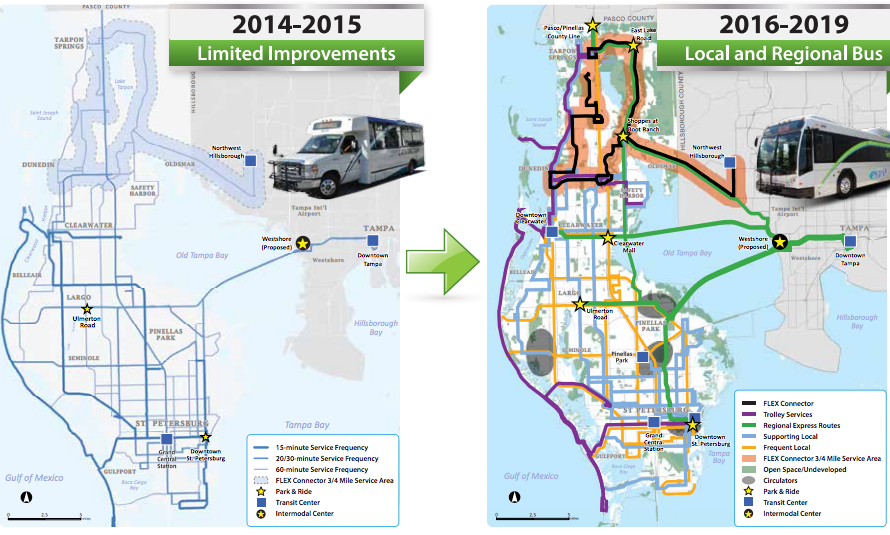
At the local level, there were notable measures approved in Broward County (north of Miami) and Hillsborough County (Tampa). Broward’s penny sales tax increase would raise $15.6 billion over 30 years, largely for transit with about $9 billion earmarked for new light rail lines. In Tampa’s case, after a few failed attempts, they finally passed a measure with money for transit that raises the sales tax by a penny to raise about $275 million annually for transportation. (Revenues are split 45/55 between transit and roads/other projects.)
Federal
Many want to know how the changeover in House leadership will impact transportation, and particularly transit funding. It’s worth noting, however, that it’s been a bipartisan effort in Congress to press on USDOT to keep these transit projects moving. It was a Republican House and Senate that approved an unprecedented provision to the 2018 appropriations bill requiring USDOT to obligate all of their 2018 transit capital grants before the end of 2019. And it was a Republican move in the Senate to require Trump’s USDOT to use President Obama’s TIGER grant qualifications for the last round of TIGER grants.
Will much else change with the House’s leadership transition? The top Democrat on the House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee—the committee charged with writing policy for the 2020 reauthorization—went on the record today saying that federal transportation policy is just fine as it is. All we need is more money.
No notable reforms for 2020 fed reauthorization in wake of House flip? “We don’t need much more policy changes. We have pretty good policy in the FAST Act. It’s just inadequate funding,” @RepPeterDeFazio told Bloomberg.
— Transport. 4 America (@T4America) November 7, 2018
We’ll have more on the federal angle in the coming days. View our tracker for 2018 state and local ballot measures for transportation here.