The US Department of Transportation’s Smart Cities Challenge was just the latest event to expose the growing interest for cities using technological solutions to solve pressing transportation problems like reducing transportation costs while also making it easier to get around, making housing more affordable and ensuring that low-income residents benefit from our increasingly prosperous cities.

Flickr photo by Paul Krueger. https://www.flickr.com/photos/pwkrueger/9220398978/
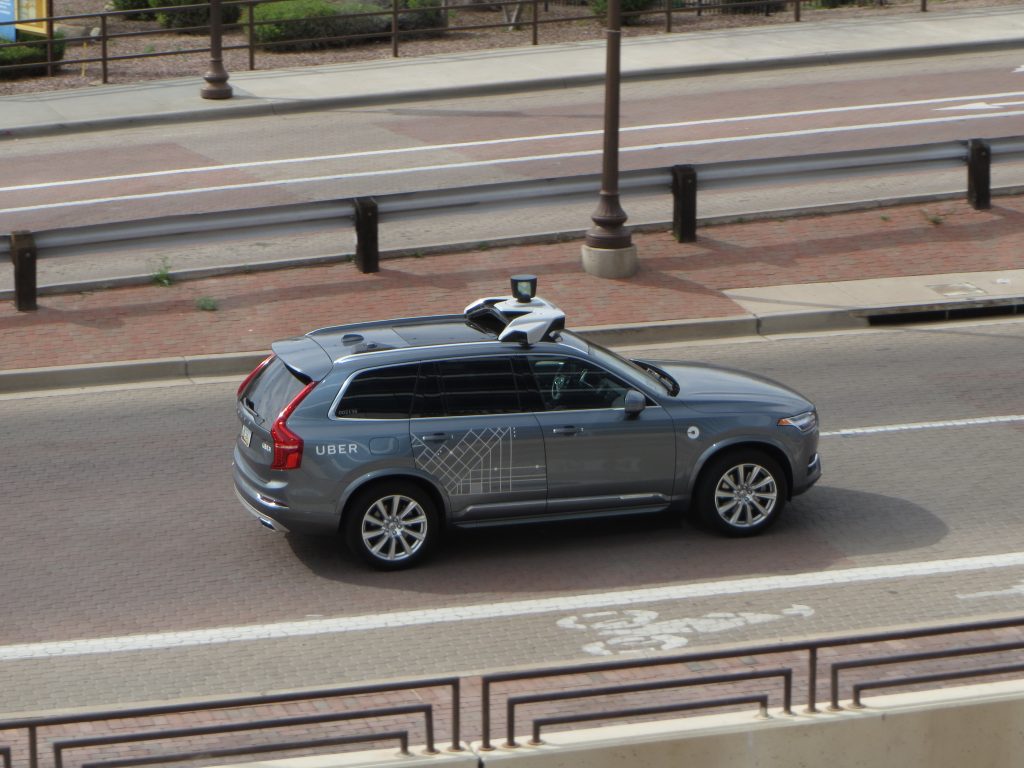
While the verdict is out on just how the trends we outline below will affect our cities, one thing is certain: we’re in the midst of the most significant shift in urban transportation in decades. To wit, just a few weeks ago, Uber’s self-driving pilot kicked off in Pittsburgh.
The creation of the interstate system to connect cities (and also speed commuters through them to new outlying suburbs) was the last truly epochal shift in urban mobility. We’re on the cusp of the next one right now. So why does this appear to be “the moment” for the interest in being a smart city?
Cities are bursting at the seams with new residents
Since 2008, for the first time in human history, more than 50 percent of the global population lives in cities. Experts estimate cities will house 70 percent of the global population by 2050. In the United States alone, urban areas account for 85 percent of the total population and nearly one in three Americans lives in the ten largest metro regions.
This surge has created new opportunities for thriving urban areas, but it also brings new challenges and exacerbates existing ones.
Cities of any size thrive on their ability to efficiently move people, goods and ideas from point to point, yet many cities still struggle to provide the basic infrastructure to do so, whether a comprehensive transit system to move large numbers people in limited space, well-maintained roads and streets for automobiles, buses or bikes, or safe sidewalks — because almost everyone begins or ends their trip with a walk. And it’s an ongoing struggle to keep it all running smoothly. Washington D.C.’s Metro is currently undergoing a such an extensive repair project that whole sections of the system are shut down for weeks at a time, while New York is preparing to close one of its most popular subway lines for 18 months.
The demand for urban living is at an all-time high, but that opportunity comes with a greater challenge of moving even more people safely, affordably and efficiently.
High-speed internet access is ubiquitous and consumer demand is growing
Since 2000, whether at home, at work or on mobile devices, high-speed internet access has become ubiquitous in cities, driven both by innovation and consumer demand. High-speed internet availability hovers near 100 percent in urban areas in the U.S. and Wi-Fi coverage is also available for free or low cost in most buildings, stores, and coffee shops. Contrary to conventional wisdom, the cost of broadband has actually dropped by a factor of nearly 40 times over the past 10 years.
Beginning largely with the release of Apple’s iPhone in 2007, smartphones have saturated the market. 68 percent of Americans owned a smartphone last year, nearly double the number of just five years ago.

Unfortunately, far too many lower-income residents still lack affordable access to broadband or a connection to the useful tools driving this movement. Though this movement presents cities with additional challenges of equity and access to solve, the fact that the majority of urban residents now have an internet-connected supercomputer in their pocket all day long has fed a growing demand for more data and real-time information about the cities we inhabit. Which leads us to…
Data sensors and processing power have become more affordable and accessible
While the demand for having more information at our fingertips is also driving an expectation that everything should be online and connected, two other factors are making this possible.
First, over the last decade prices for sensors — that can monitor everything from when your laundry is done to air quality to location — have dropped by roughly 50 percent over the last decade. Second, during that same time period, the low-cost and availability of virtually limitless computing power through cloud computing has given the power of aggregation, analytics and visualization to anyone with a desktop computer or smartphone. The result of all of this is that startups, entrepreneurs and “makers” are testing the addition of sensors in every conceivable context.
There are hundreds of civic applications for these sensors — such as measuring air quality in low-income neighborhoods to water pipe leakage to knowing precisely where a bus or train is located to predict its arrival — that cities can take advantage of to give them a better idea of what’s happening in their communities.
Huge private sector investments in new business models & disrupting old ones
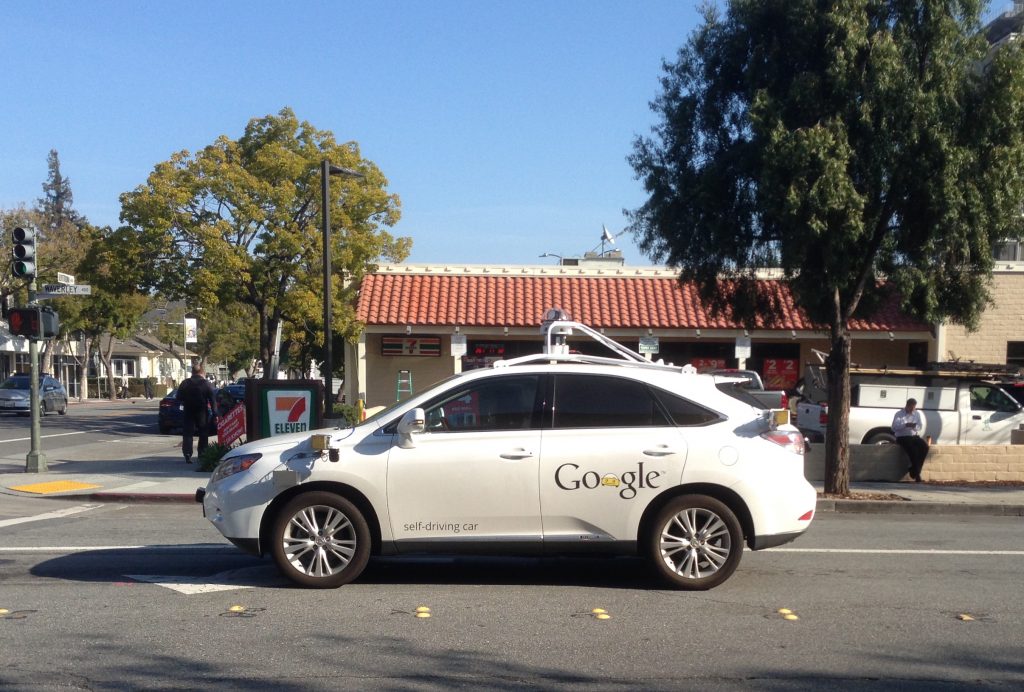
Enabled by all this data and processing power, the penetration of smartphones and the desire for improved urban mobility, the last five years have been marked by private sector efforts to “disrupt” traditional transportation markets. Scores of private companies, whether old guard car companies like Daimler (through Car2go) or new providers like Lyft or Uber, have been investing money and resources to provide new options for getting around. Google is a primary investor in Uber, while also developing its own self-driving car.
Uber, Lyft and other ride-hailing companies are also still on shaky ground when it comes to their business models and are ultimately seeking automated solutions (i.e., self-driving cars) to bypass their biggest cost: labor. Uber has lost over $4 billion since it was founded with $1.2 billion in the first half of 2016 alone. And, while some of that is certainly caused by developing automated vehicles and their expansion troubles in China, much of it comes from incentivizing drivers to maintain their market share in the U.S.a

With the decline in auto ownership led by millennials, even some old guard auto manufacturers are attempting to rebrand themselves as mobility companies, investing in or acquiring dozens of startups and testing out new product lines unthinkable for them just five years ago. Just a few weeks ago, Ford not only purchased shuttle service Chariot, but also launched a partnership with Motivate to expand bike-sharing operations in San Francisco.
It’s a perfect storm right now, and the “smart” cities will be the proactive ones
We’ve reached a tipping point where the ubiquity of technology has coincided with a growing need for our cities to become or remain prosperous, equitable, enjoyable places to live. While connected and automated vehicle technology certainly has the potential to dramatically improve pedestrian and driver safety, decrease traffic congestion, and improve freight and shipping technology, there are real consequences to be mindful of.
We’re clearly at a crossroads as we tip over into this monumental shift in urban transportation. But as we mentioned in our last blog post, smart cities are those that thoughtfully take advantage of the new technological tools at their disposal to accomplish what’s most important to them.
The smartest cities will take advantage of this moment in time and this transformation to become more prosperous, efficient, affordable and equitable.
What will happen to the cities that innovate without including everyone?
This post was written by our smart cities team of Russ Brooks, Rob Benner and Steve Davis






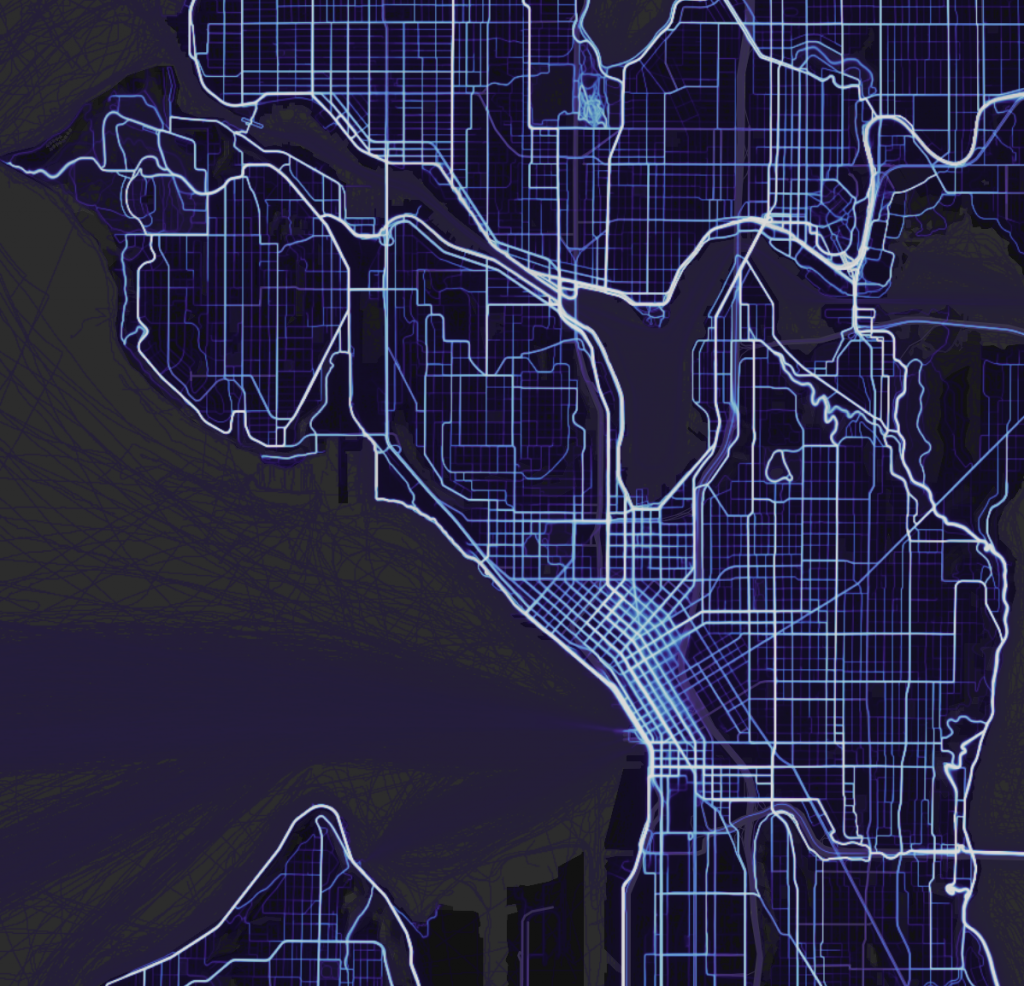











 Much of that conversation centered on how cities can drive the discussion and lead at the state level on those policies that will have the largest impact on our cities. Keynote speaker Seleta Reynolds, the head of the LA Department of Transportation, reminded the participants that, no matter what policy levers are controlled by the state, cities still have an enormous amount of leverage — if they’re willing to work together and think outside of the box.
Much of that conversation centered on how cities can drive the discussion and lead at the state level on those policies that will have the largest impact on our cities. Keynote speaker Seleta Reynolds, the head of the LA Department of Transportation, reminded the participants that, no matter what policy levers are controlled by the state, cities still have an enormous amount of leverage — if they’re willing to work together and think outside of the box.
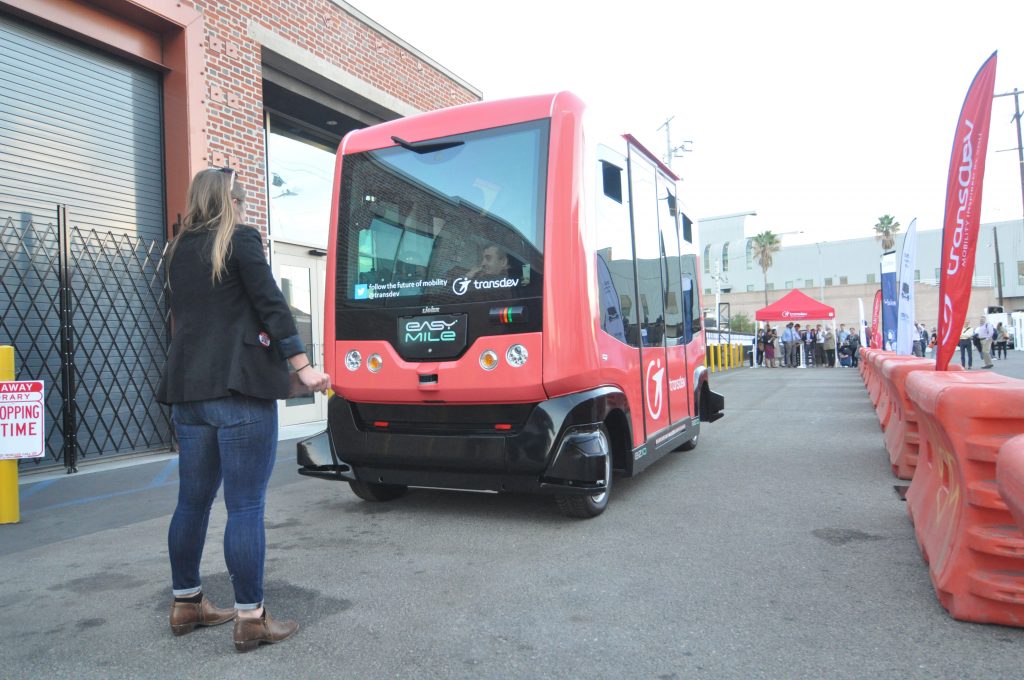




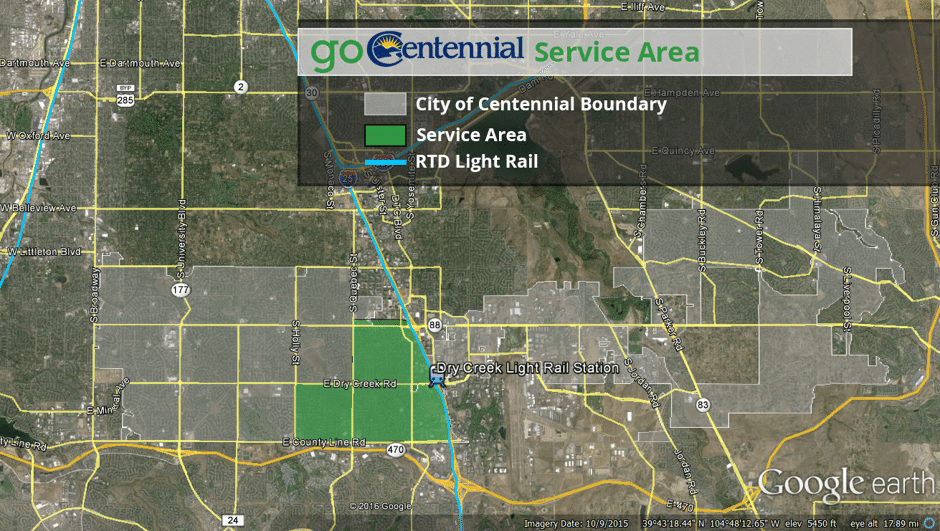
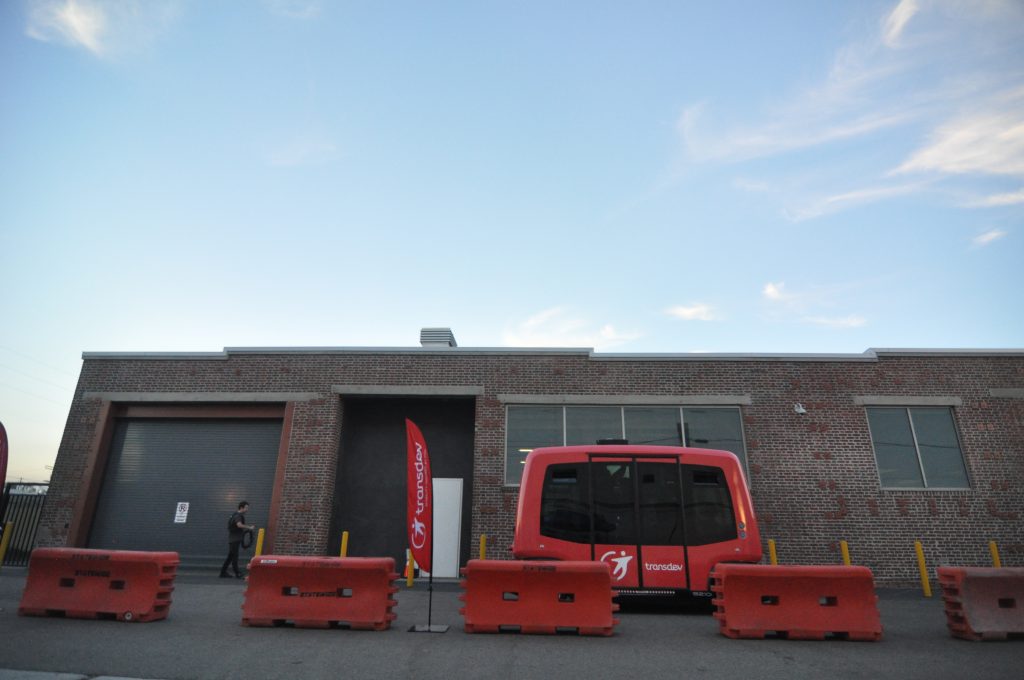
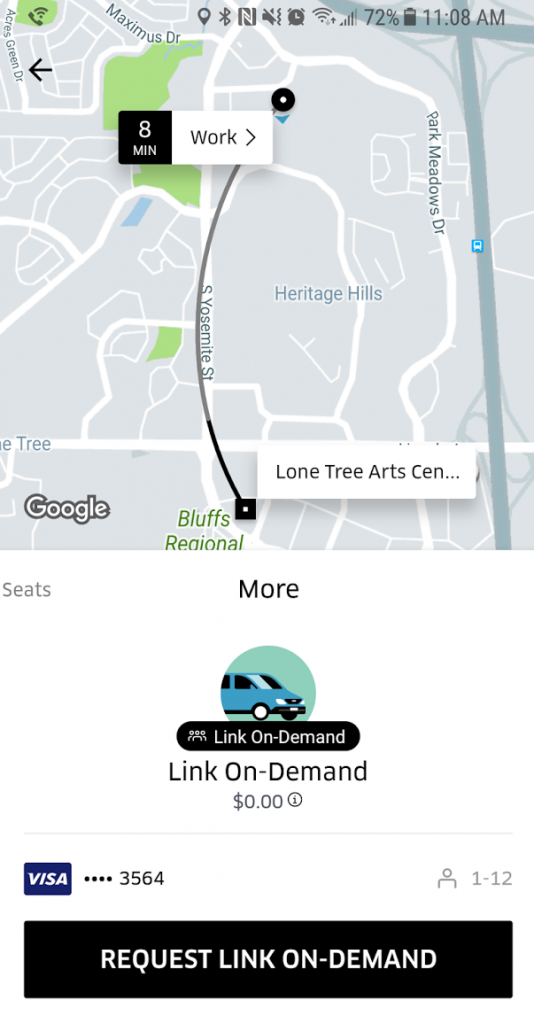 For the pilot, Holwell said that they removed one of the four buses from the fixed route and reassigned it to the on-demand service, allowing the city to better calibrate their service with the need. And the returns have been positive thus far.
For the pilot, Holwell said that they removed one of the four buses from the fixed route and reassigned it to the on-demand service, allowing the city to better calibrate their service with the need. And the returns have been positive thus far.