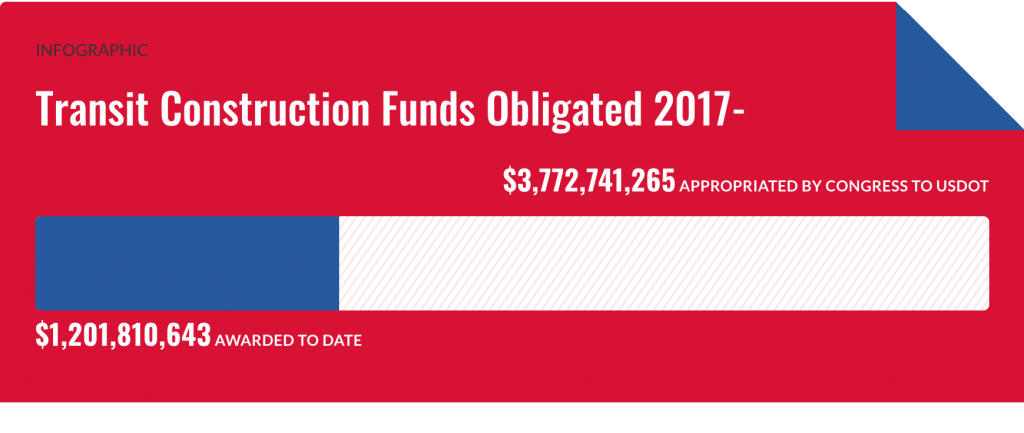
A deceptive announcement by USDOT two weeks ago resulted in mistaken headlines across the country giving credit to USDOT and the Federal Transit Administration (FTA) for “awarding” funding to a number of transit projects. A closer read reveals that USDOT didn’t actually distribute or award a single dime to advance new transit projects.
In a self-congratulatory press release on April 9, USDOT Secretary Elaine Chao touted the agency’s efforts to “strengthen our country’s transit infrastructure and improve mobility” and “announced a total of $1.36 billion in federal funding allocations to 16 new and existing transit projects.” [italics ours]
In reality, no dollars for new transit projects were awarded or obligated. No new grant agreements were signed to allow projects to proceed. No new shovel-ready transit projects got a check in the mail from FTA. Why is that? Because FTA is just announcing “funding allocations.”
A “funding allocation” is just fancy language for an internal plan to award money…eventually
Here’s a way to understand “funding allocations.” Let’s say you’re planning to buy a new roof for your house. To prepare, you “allocate” some money to yourself by moving it from your savings account into your checking account so that when the time comes, you can cut a roofer a check. But you still haven’t actually hired a roofer, written them a check, and you certainly haven’t started replacing your roof yet. Should the roofer you haven’t yet hired be celebrating?
In other words, USDOT put out a press release that’s mostly about them moving some numbers around on a spreadsheet and posting it on their website. Congrats? It’s an extraordinary display of verbal gymnastics by USDOT to make it appear that they’re doing much more to fund transit than they actually are—notably released just the day before Secretary Chao testified before the House Appropriations Committee about USDOT’s budget.
And they are succeeding at misleading the public— look no further than the resulting media coverage thus far.

Want to know what’s actually happening with federal transit funding? See Stuck in the Station >>
But this press release has—perhaps inadvertently—also helped illuminate some troubling developments from an agency that has become much less transparent under the Trump administration. Here are five things we found:
1) USDOT wildly overstates how much money they’ve spent
The press release says, “with this announcement, FTA has advanced funding for 22 new [transit Capital Investment Grant] projects throughout the nation under this administration since January 20, 2017, totaling approximately $5.06 billion in funding commitments.”
In fact, FTA has only actually spent a fraction of that $5.06 billion, and if you define advancing funding as actually awarding (i.e., spending) it, FTA has only advanced 10 new projects with money from 2017 or later, far short of the 22 as they claim.
They take credit for providing more than $3.3 billion to 13 ongoing projects (including the canceled Wave streetcar in Ft. Lauderdale, more on that later), three of which are multi-year projects. Though FTA is legally required to continue funding such multi-year projects under binding “full funding grant agreements,” those transit projects have not yet received the full amount. And FTA is also counting more than $1.7 billion in funding for nine projects that they have not actually signed agreements to fund or advance.
2) USDOT is claiming progress by allocating more FY 2018 funding to two projects that already received 2018 funding
At first glance this sounds like good news: Two large-scale projects with grant agreements that were signed during the Obama administration will get an extra dose of money to perhaps speed them along. The Peninsula Corridor Electrification Project in San Carlos, CA and the Red and Purple Modernization Project in Chicago, IL are scheduled to receive an extra $100 million dollars each on top of the $100 million FTA had previously allocated to each project this year. That’s $200 million each for the 2018 fiscal year.
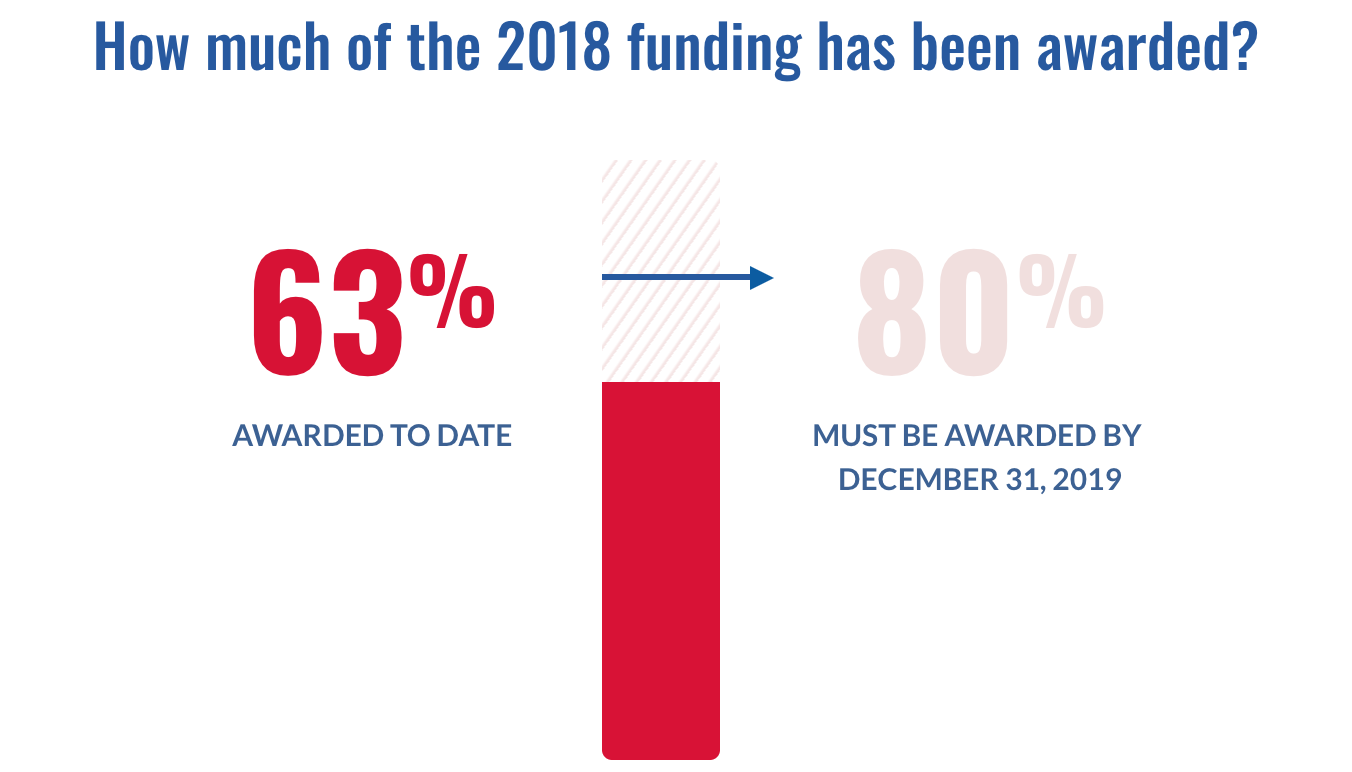
This is highly unusual, and it could also be a way for USDOT to do an end-around of requirements from Congress. FTA usually allocates no more than $100 million to a single project in a given year. The fact that FTA is doubling up on 2018 dollars is most interesting in light of new requirements that Congress imposed requiring USDOT to spend at least 80 percent of their FY 2018 funding by the end of this calendar year. Stuck in the Station now tracks USDOT progress towards that benchmark.
Double dipping in 2018 funds to expedite funding for existing projects allows USDOT to come closer to meeting Congress’ requirements without actually funding any new transit projects.
3) No new projects are being funded
The major development at first glance is that FTA is “allocating” money to five new transit projects. But none of these projects were actually approved or awarded money, even though local media fell for FTA’s misdirection. These five projects will join four other projects that FTA announced “allocations” for months ago. None of these nine “allocated” projects have a funding agreement in place yet, nor are we aware of FTA notifying Congress of their intent to sign any grant agreements (which is legally required).
4) USDOT wants credit for allocating money to a canceled project
The Wave streetcar in Fort Lauderdale is an unfortunate story. It was set to receive $60.66 million from USDOT in October of 2017 but local politics intervened at the last second and torpedoed the project. The streetcar was canceled and no federal money was spent. But FTA still claims credit for allocating that $60.66 million to the now defunct project and counts The Wave as one of the 13 projects they’ve advanced.
5) Minneapolis is left in limbo, and Los Angeles is still awaiting a final guarantee of funding
Late last year, FTA made news by sending what’s known as a letter of no prejudice to both Los Angeles and Minneapolis for their Purple Line and Green Line extensions, respectively. Such letters don’t guarantee future funding but they are generally seen as an implicit approval giving localities permission to begin work on a project with their own money.
Los Angeles’ Purple Line extension is included in the list of nine future projects that FTA anticipates funding (but still hasn’t yet). But Minneapolis’ Green Line extension is notably absent from this list, even though they have the same letter as LA. This could just be an egregious error on the part of the agency, but it’s more likely that FTA has no intention of signing a grant agreement with Minneapolis this year.
Delay, mislead, misdirect
FTA chose its words very carefully in this press release. They never say that they’re “funding” or “approving” new projects. They use the words “allocation” and “advancing” repeatedly. While all of this makes it sound like they’re spending lots of money and advancing lots of projects, that’s simply not true. Stuck in the Station tracks how much funding has been actually obligated to new transit projects, which projects are currently eligible and waiting for funding, and how close USDOT is to meeting congressional requirements for its 2018 funding.
USDOT is still working diligently to hinder predictable and stable federal funding for transit. We’ll keep holding them accountable. When USDOT finally moves beyond creating new spreadsheets and does advance new projects, we’ll be the first to commend them for it. But for now, it appears that USDOT is more interested in looking like it’s doing its job than actually doing its job.
View Stuck in the Station









 President Trump’s just-released 2020 budget would cut federal transit capital grants by $1 billion. Although this is a slight improvement from the administration’s past efforts to eliminate all funding for new transit projects, it comes after a backlash against USDOT—stoked by Transportation for America’s
President Trump’s just-released 2020 budget would cut federal transit capital grants by $1 billion. Although this is a slight improvement from the administration’s past efforts to eliminate all funding for new transit projects, it comes after a backlash against USDOT—stoked by Transportation for America’s 
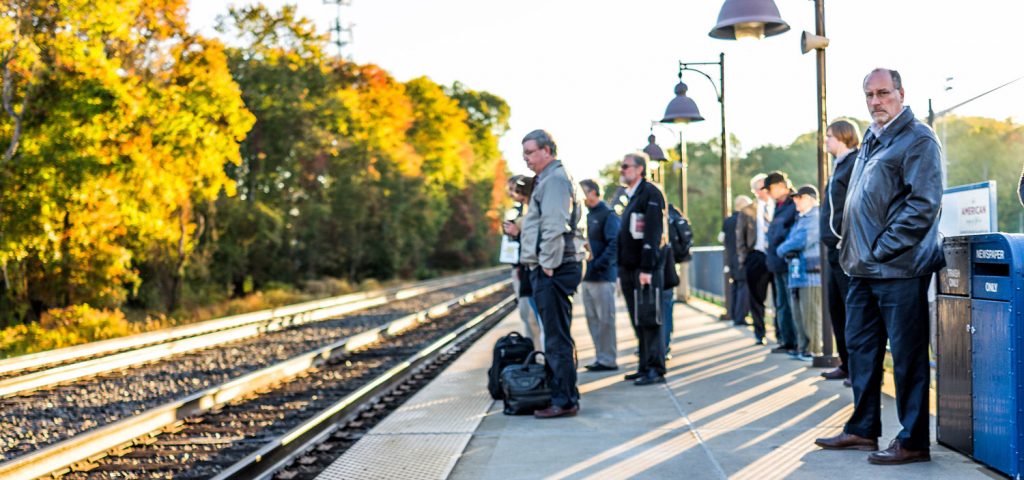
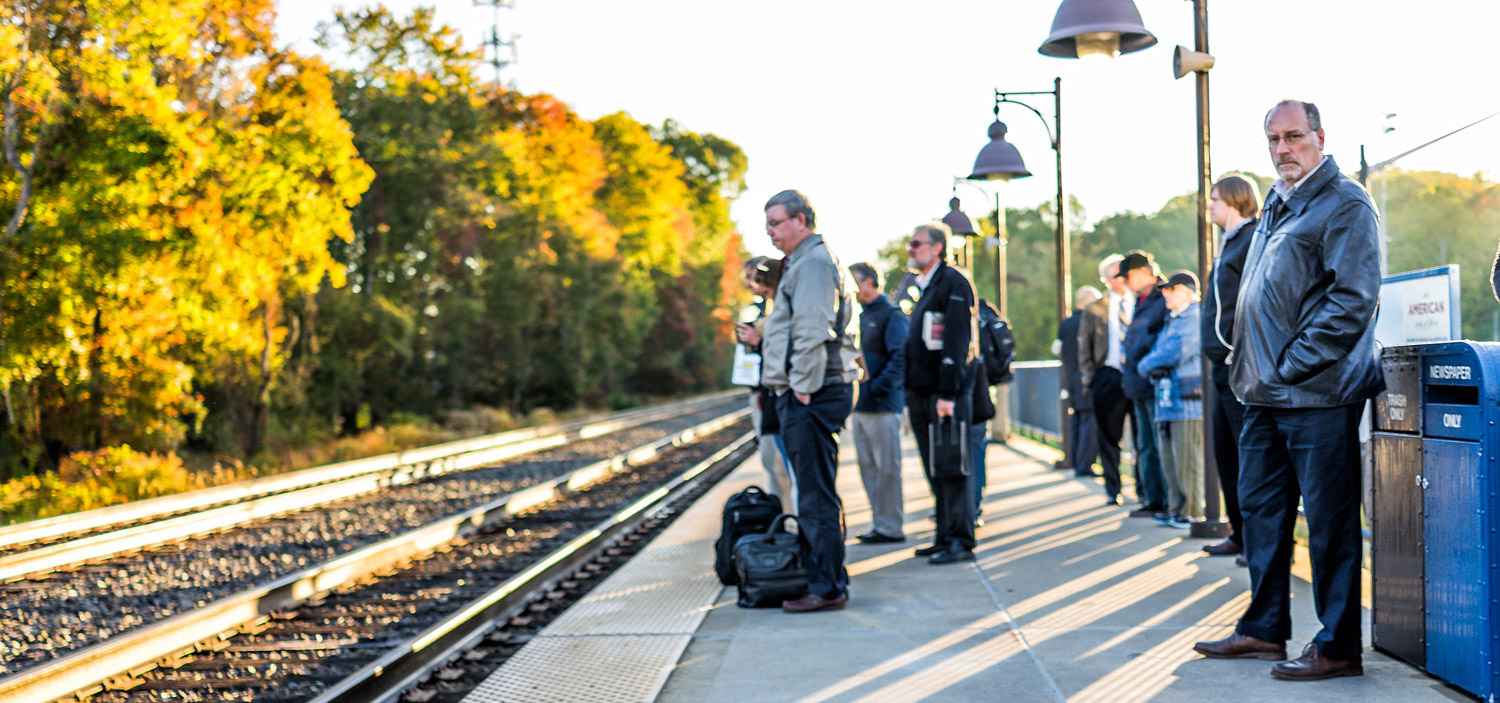




 With federal employees at the Federal Transit Administration furloughed during the recent record-length shutdown, transit funding wasn’t being distributed and grant/loan programs ground to a halt. New projects were further delayed and transit providers were faced with hard choices about service cuts, showing the vital importance of federal funding for transit.
With federal employees at the Federal Transit Administration furloughed during the recent record-length shutdown, transit funding wasn’t being distributed and grant/loan programs ground to a halt. New projects were further delayed and transit providers were faced with hard choices about service cuts, showing the vital importance of federal funding for transit.