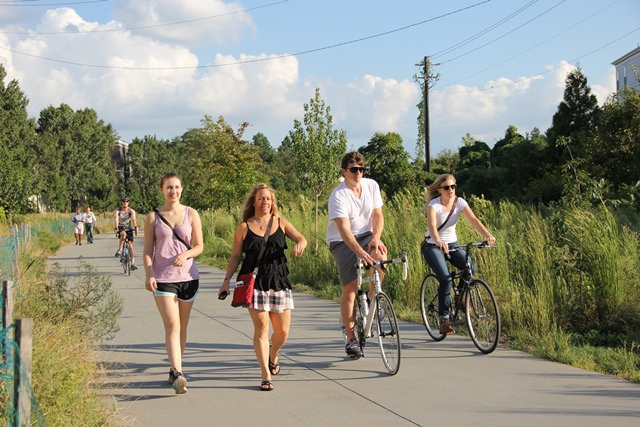
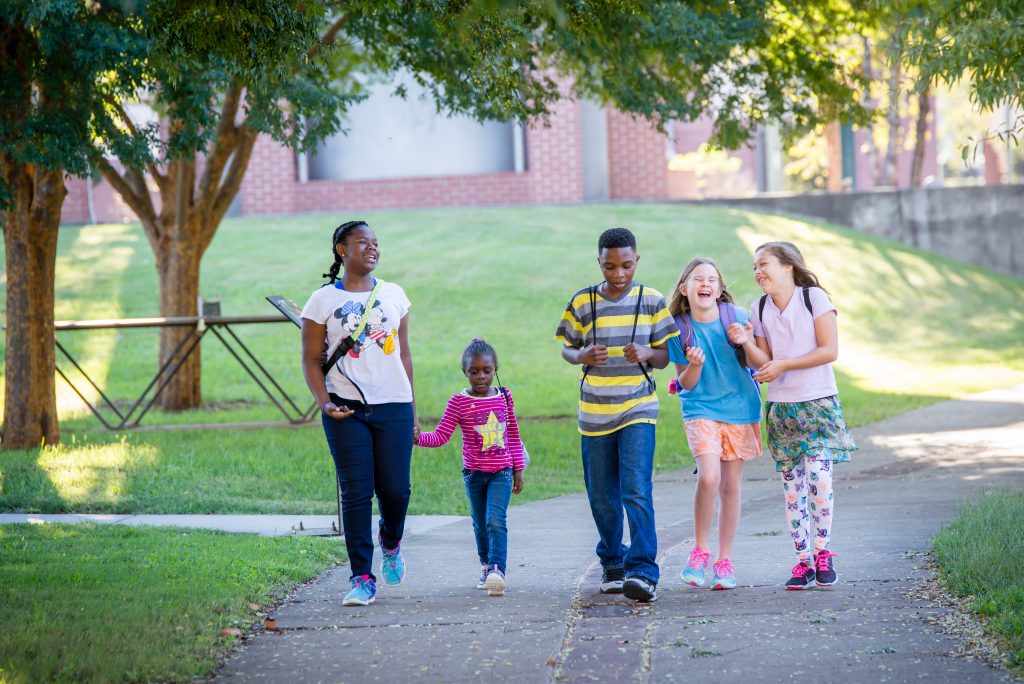What’s the connection between healthy residents and a healthy bottom line? Why should a local business community care about improving the health of the residents that live there? Representatives from five regions gathered last week in Nashville to learn how providing better transportation infrastructure and building more walkable communities can help improve residents’ health — and boost local economic prosperity and competitiveness.
This post was written by Rochelle Carpenter and Stephen Lee Davis with Transportation for America.
The Nashville Area Metropolitan Planning Organization, responsible for planning and allocating federal transportation dollars in the seven-county Nashville region, has become a nationally recognized leader in prioritizing health when selecting transportation projects.
Getting to that point wasn’t easy, but their hard work to make that shift was kick-started by two related developments: the widespread recognition of a looming health crisis in the least active state in the nation, and the realization that there was pent-up demand among Nashville residents for healthier options to get around —whether safer streets with new sidewalks, trails, transit, or bikeshare.
One economic connection is obvious: employers are often the ones paying a large share of healthcare costs for employees. If those employees are living in a place where it’s challenging to get or stay healthy because of factors inherent to the built environment, that’s a cost that those companies have to bear. If those costs become a known challenge within the business community, it presents a major roadblock when recruiting new employers or trying to retain them.
Whether by continuing to make ambitious plans to bring new bus rapid transit to the city, building new projects that make it easier to walk or bike, or through incorporating health considerations into their process for funding transportation projects, Nashville is trying to stay ahead of their growth challenges, remain competitive for new talent and ensure that their residents can be healthy — all helping to boost the bottom line for the region. It’s a region experiencing some of the fastest job growth in the country, but they know they can’t rest on their laurels.
We’ll be publishing an in-depth profile of how Nashville began to integrate health considerations into their planning efforts sometime in the next few weeks. Watch this space, and sign up for our emails to be notified if you haven’t already. –Ed.
To learn from Nashville’s experiences, T4America and the Nashville MPO — through an ongoing grant from the Kresge Foundation — brought civic leaders and agency staff from Seattle, San Diego, Detroit and Portland, OR, to the Music City last week; sharing best practices and hoping to build on what the others have done.

MPO staff and advocates from Nashville, San Diego, Detroit, Portland and Seattle along with Nolensville staff and leadership during last week’s gathering in Nashville.
Meeting in the Bridge Building overlooking downtown Nashville and the Cumberland River, the group of leaders from across the country saw the rapid changes made in the downtown core to improve streetscapes and public spaces to create vibrant, welcoming places for the many families, professionals and visitors.
While Nashville proper is making significant strides, other communities around the MPO’s seven-county region are also eager to expand their options for walking, bicycling and transit.
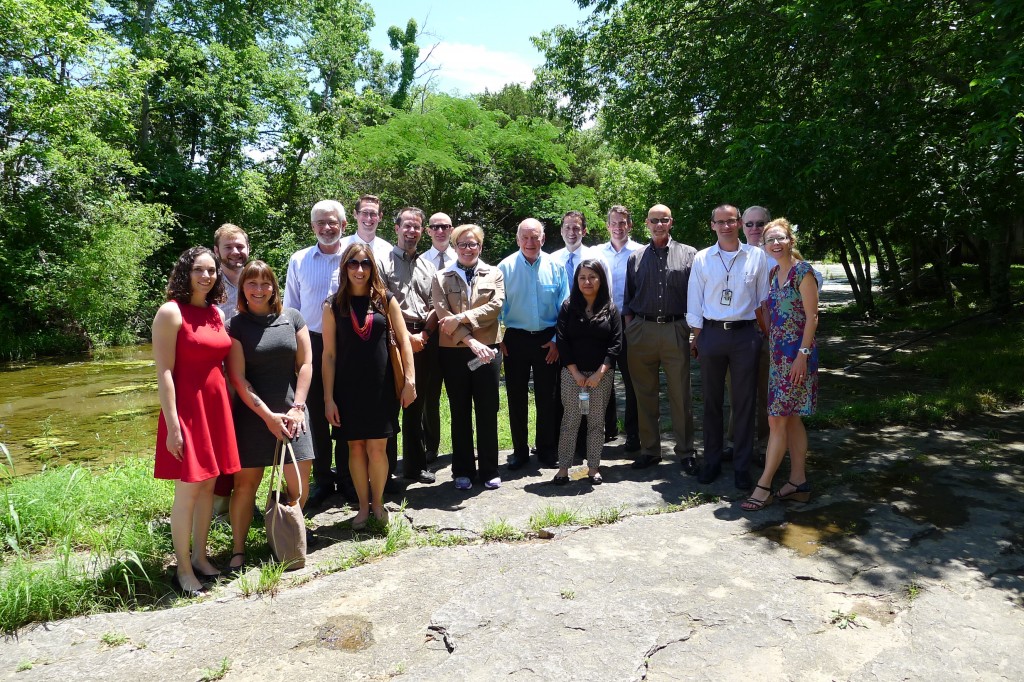
The delegation visited the rapidly growing town of Nolensville (pop. 8,000) on the south side of the region.
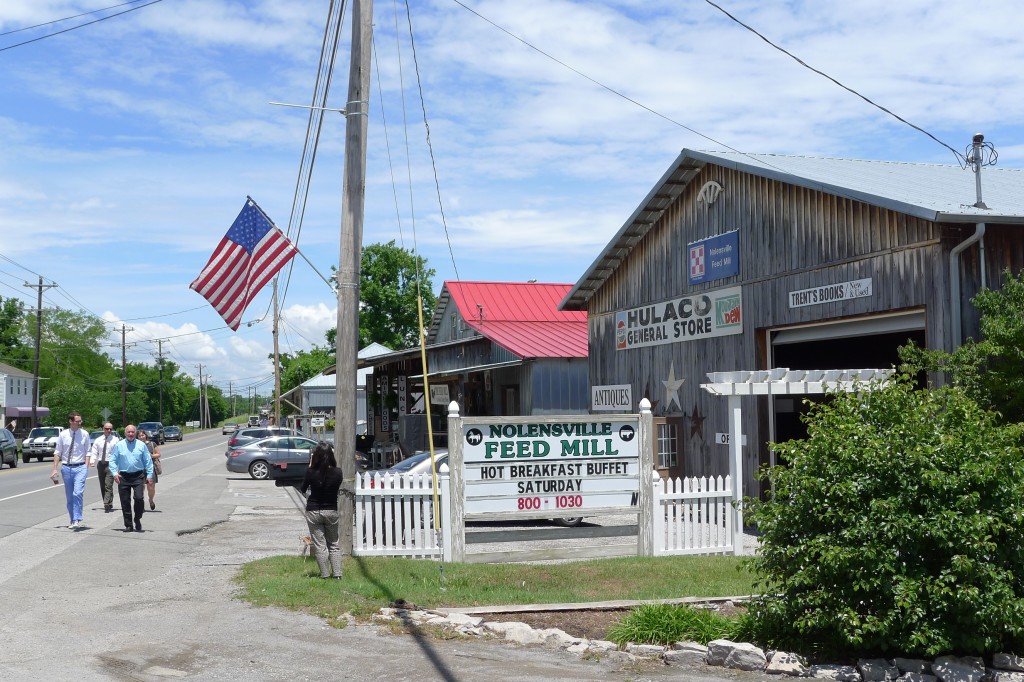

Nolensville Mayor Jimmy Alexander led Transportation Choices Coalition Executive Director Rob Johnson, Upstream Public Health Policy Manager Heidi Guenin and Transportation for America Field Organizer Chris Rall along Nolensville Road. The town was recently awarded half a million dollars to construct a greenway parallel to Nolensville Road, providing a new safe and convenient route between popular destinations.
Nolensville Mayor Jimmy Alexander described the town’s ambitious goal that local leaders see as critical for their local economy and competitive advantage. “We want to make it possible for every student in Nolensville to be able to walk to school,” he told us. The town has passionately sought and secured federal, state and local funding for multi-use paths, sidewalks and greenways that will eventually link the community’s most-visited destinations: residential neighborhoods, the historic district and commercial town center, schools, Nolensville Ball Park and the Williamson County Recreation Center.
Nolensville’s early leadership in clamoring for more of the infrastructure that makes it easier to safely get around on foot or bike — and the Nashville MPO’s response in providing technical assistance, policy and funding — will help them reach their goal in just a few years time.
The tour of new, energetic thinking on transportation and community development in the area would not be complete without a visit to Casa Azafrán, a community center and home to several nonprofits that serve the thousands of recent immigrants and refugees that are settling in Nashville and helping shape its future.
Renata Soto, Executive Director of Conexión Américas, led the delegation on a tour of Casa Azafrán, including a day care center, culinary incubator, health clinic and classrooms. But since moving to their new location on busy Nolensville Pike in south Nashville two years ago, Soto has witnessed first hand the challenges of poor transportation infrastructure. She took it upon herself to get the city to install the city’s first bilingual crosswalk to allow clients and visitors to safely cross busy Nolensville Pike while welcoming non-English speakers.
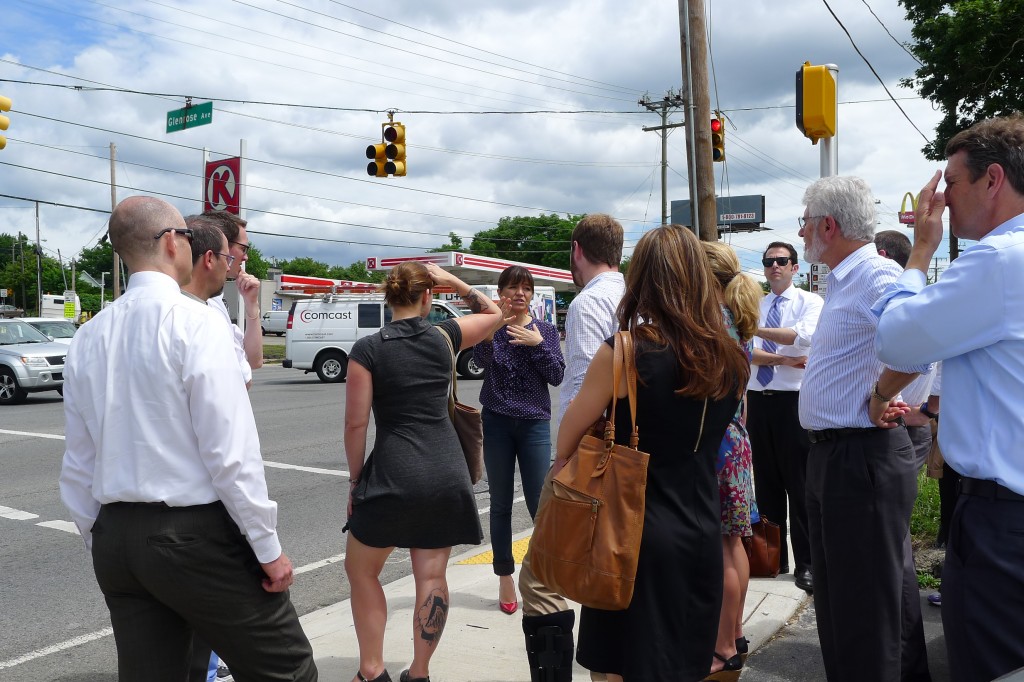

During a visit to Casa Azafrán, a community center and home to nonprofits serving New Americans, Renata Soto explains the new bilingual crosswalk installed to make it safer to get to work, the bus stop and several restaurants on both sides of busy Nolensville Pike.

The signs on the new bilingual crosswalk on busy Nolensville Pike.
The promise of a new rapid bus line coming later in the year will help, but challenges remain. “There are so many high school students who could use our facilities,” Soto explained. “But they can’t get here — they’re so close, but so far away.”
This gathering last week in Middle Tennessee offered inspiration, new information and a meeting of the minds to generate new ideas and discuss how to overcome political and technical challenges in our path. Stay tuned as we report more from each of these regions over the coming months.