With the Trump administration readying both an annual budget and discussing a possible large infrastructure package, Transportation for America yesterday urged a key Senate subcommittee to protect the investments in programs that promote innovation, encourage collaboration and maximize benefits for local communities.

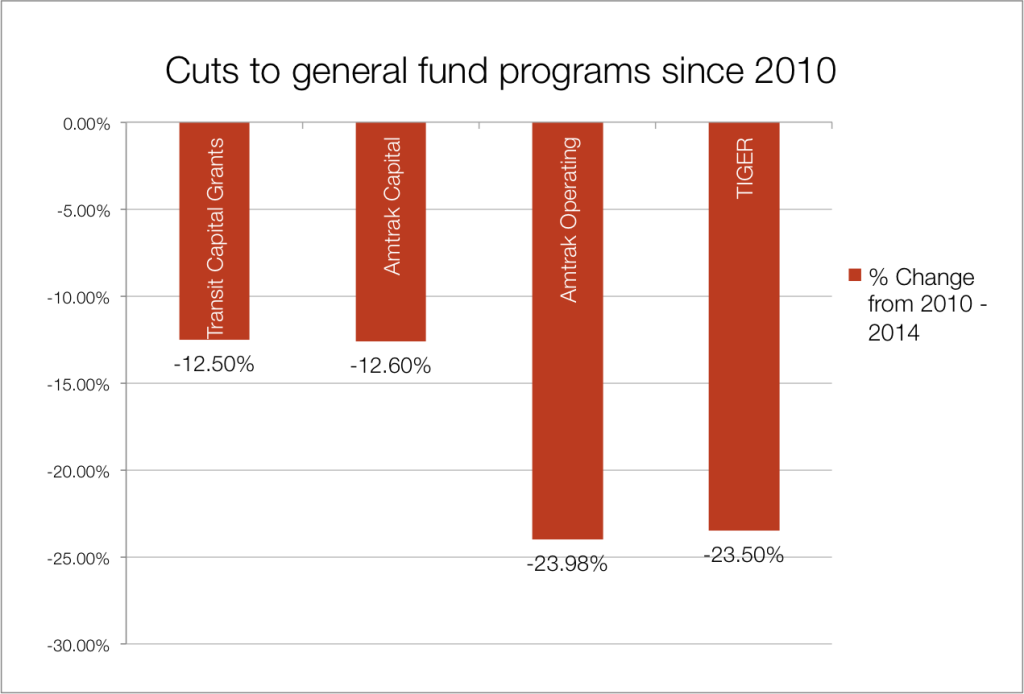
The President’s first budget will almost certainly propose big cuts to discretionary spending programs. While the bulk of annual federal transportation spending is sourced from the highway trust fund and should be more insulated from these cuts, discretionary cuts would fall disproportionately on funding for new transit construction (New and Small Starts) and multimodal and local priority projects (TIGER).
House and Senate appropriators will have two decisions to make: a) whether to appropriate the amounts prescribed by the current long-term transportation law (the FAST Act) for the core programs, which is uncertain as well, and, b) how much to allocate for these other discretionary transportation programs.
As expected, with the heads of a few national trade groups also testifying yesterday alongside T4America before the Senate Appropriations Subcommittee on Transportation, Housing and Urban Development, there was the usual rhetoric about America’s “crumbling” infrastructure amidst calls to invest more money overall in the federal transportation program.
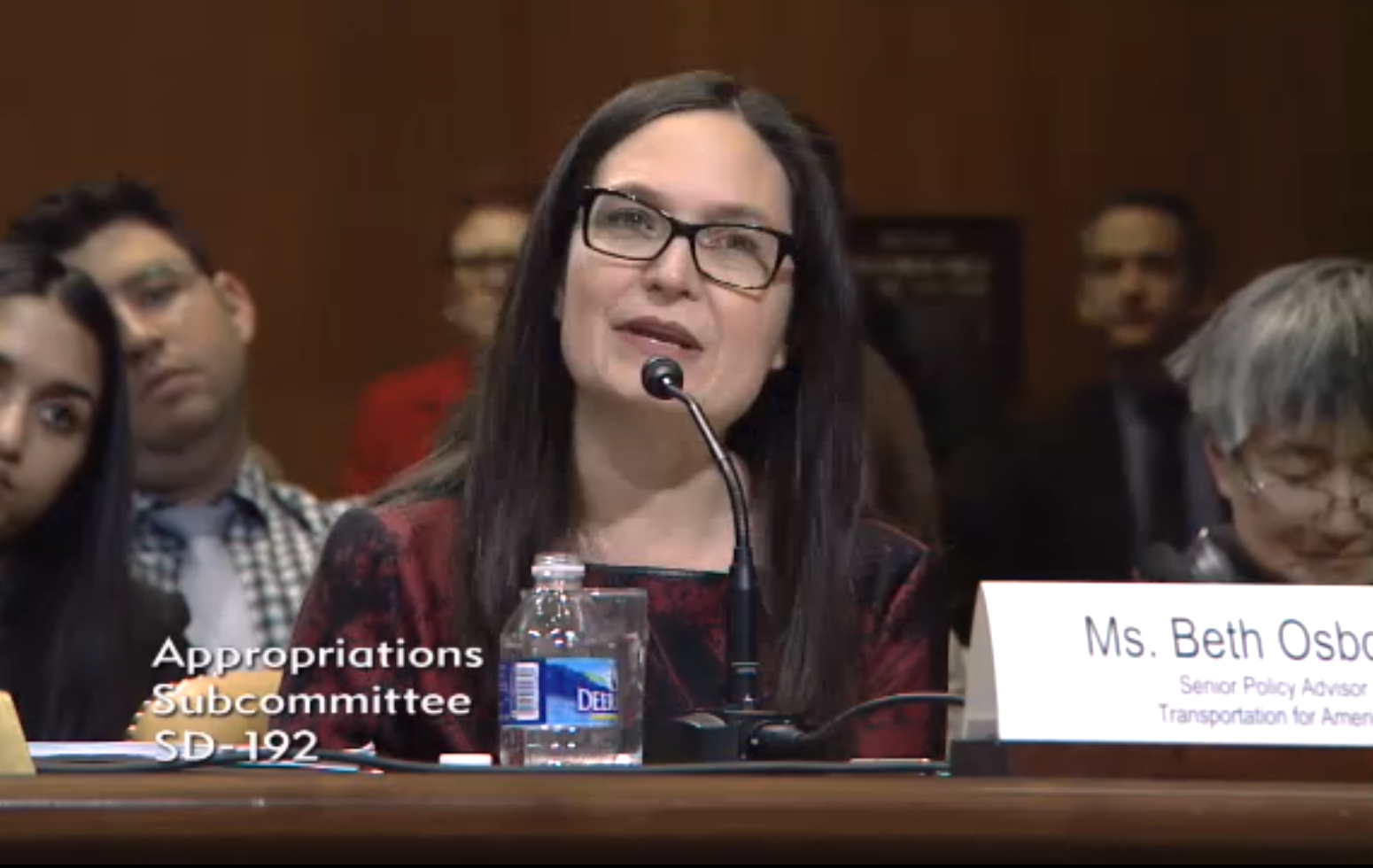

And while T4America agrees on the need for greater levels of overall investment, T4A senior policy advisor Beth Osborne (pictured above) differentiated our overall position.
“As everyone testifying today will say,” she noted in her opening remarks, “we have great need to invest in our transportation system, including our roads, bridges, and transit systems. However, Transportation for America also believes that our problems run far deeper than just an overall lack of funding.”
When we have these discussions about the need to invest in infrastructure — especially in Washington — all sorts of ominous numbers are thrown around. Tens of thousands of deficient bridges. Pavement condition that’s worsening by the day. Backlogs of neglected maintenance and repair.
But where does the money go once we increase transportation spending and dole it all out to the states? Beth Osborne explained:
In fact, while we talk about the need for more funding to address our crumbling infrastructure, that is not necessarily where the funding goes. A 2014 report conducted by Smart Growth America called “Repair Priorities” found that between 2009 and 2011 states collectively spent $20.4 billion annually to build new roadways and add lanes. During that same time, states spent just $16.5 billion annually repairing and preserving the existing system, even while roads across the country were deteriorating. As we talk about large infrastructure packages, it’s only fair to ask that the priorities of our transportation program more closely match the rhetoric we use to justify more spending on it.
Why do we keep spending hefty sums on new roads and new lanes while repair backlogs get ignored? One reason is that transportation and development decisions are rarely well coordinated and we end up trying to address bad land use decisions with more transportation spending, and vice versa.
More from Beth:
I think about the two houses in Florida that are 70 feet apart but require a seven-mile drive to get from one to the other. Such a roadway and land use pattern seems almost designed with the express purpose of generating traffic snarls. But the problem is not categorized as a development or local road connectivity problem. It is put to the state and the federal government as a congestion problem that requires big spending to widen roads. Now no one is calling for the federal government to get involved in local land use decisions. However, there should be a way to reward cities and states consider these and take action improve outcomes and lower costs. Competitive programs can help to do that.
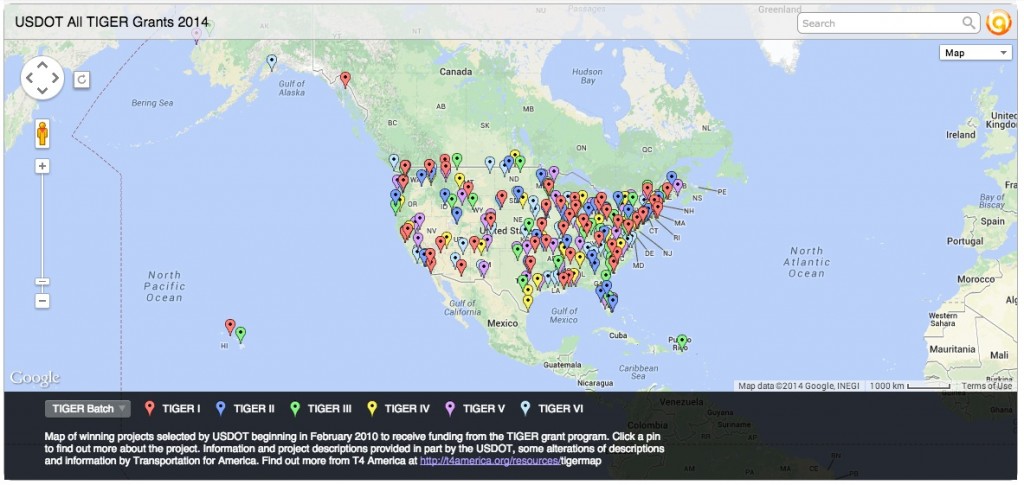
One of those competitive programs is the TIGER grant program, which could be one of the programs targeted for severe cuts — or elimination — in this looming budget proposal from the President.
TIGER has awarded more than $4 billion since 2010 to smart local projects, bringing 3.5 local dollars to the table for every federal dollar through just the first five rounds. Though only 5-6 percent of all applicants have successfully won funding, local leaders still love the programs, and the process encouraged applicants to try new strategies or approaches to be as competitive as possible to win funding — “like design-build project delivery or complete street designs or public-private partnerships,” Beth noted.
Rather than just sidling up to the table for their share of dollars allocated by some federal formula, communities have been trying to produce the best, most competitive applications that will bring the highest returns on both the federal investment and their local commitment.
This is the kind of innovation that Congress should be encouraging, not targeting for cuts.
In the New and Small Starts transit capital programs, there’s over $6 billion already promised to shovel-ready transit projects all across the country that have already raised local or state funding and are just waiting on capital dollars from the federal government to proceed. Projects like Indianapolis’ Red Line bus rapid transit project that has already been promised more than $70 million in federal dollars to pair with nearly $20 million in local funds from an income tax increase that Indianapolis voters approved back in November at the ballot box.
Indianapolis and a multitude of other communities small and large “are stretching themselves to raise their own funds and to innovate, but they cannot bring these important projects to fruition without a strong federal funding partner,” Beth said in closing this morning. “The programs that this committee funds are often the lynchpin for aiding states and localities in meeting these demands.”
We hope that this Senate subcommittee heard the message loud and clear and will stand up for these vital programs as the budget process moves forward. We’ll keep you updated.















.jpg)