
We can have it all: a federal transportation program that reduces carbon emissions while boosting our economy. The House of Representatives led the way last summer with the INVEST Act, a bill that starts the work of connecting federal funding to the transportation outcomes Americans—including our businesses—need. Here’s how.

Transportation is the largest source of carbon emissions in the United States, and the majority of them come from driving. Infrastructure investments that give people more options than hopping in the car are key to reducing these emissions. And luckily, these investments are great for our businesses, too.
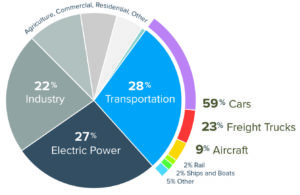
When the House of Representatives passed the INVEST Act last summer—a transportation bill that took huge steps toward aligning funding with the outcomes Americans want (getting to where they need to go)—we took a deep dive on the parts of the bill that do the most to reduce emissions. It’s not just one “climate title”—reducing emissions is in the bill’s DNA.
With the House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee holding a hearing this Wednesday on the “business case for climate solutions,” let’s revisit the climate measures in the INVEST Act to see how they boost our economy.
Investing in public transit = good for business
As our partners Smart Growth America found in their report Core Values, businesses are relocating to transit-accessible downtowns to attract talent, bringing economic development with them. Yet the federal transportation program works against this trend. Public transportation has been underinvested in for decades, with the few federal funds transit receives undermined by overwhelming highway funding that doubles down on sprawl—an environment where transit can’t succeed.
The INVEST Act increases transit funding by 47 percent, while also overhauling policies that have long obstructed transit as a truly viable option in communities, as we wrote last summer. The bill incentivizes transit agencies to increase service frequency, reversing policies that in practice incentivized agencies to do the opposite in order to decrease operating costs to the detriment of transit service.
Members of Chambers for Transit—our coalition of over 35 local chambers of commerce fighting for robust public transit investment—know that increased transit investment improves access to jobs, sparks new development, and creates the kinds of vibrant communities that can attract a talented workforce. (That’s why Chambers for Transit sent a letter to the House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee last week.) It also improves access to the economy for people of color and low-income people, who make up larger shares of transit riders.
Measuring access, not vehicle speed = good for businesses
Businesses want the federal transportation program to invest in projects that improve people’s access to jobs and services—not increase vehicle speeds. That’s why so many of our Chambers for Transit members support using new technologies to prioritize projects that improve people’s access to the things they need. (This is one of our three principles for transportation policy).
For decades, the federal transportation program has done the opposite, measuring the success of its investments by vehicle speed. This doesn’t take into account whether or not people actually arrived at their destination. And it encourages states and planning organizations to build more and wider roads. This pushes homes and businesses farther apart from each other, making it much more difficult to walk, bike, or use transit, while in the long-haul, making congestion worse and increasing vehicle miles traveled and emissions. It also limits access to the economy to people who can afford to and are able to operate a car.
To build the type of communities where you don’t have to drive everywhere, we need to measure success by access: how many destinations you can reach from your home by any mode. The INVEST Act transitions the federal transportation program to just that.
Through a new performance measure, the INVEST Act requires recipients of federal transportation funding to improve people’s access to jobs and services, whether they drive, take transit, walk or bike. This will direct more funds to projects that shorten or eliminate the need for driving trips. The bill also requires states to measure and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from their transportation system. States that reduce emissions can be rewarded with increased flexibility, while states that fail to reduce emissions will face penalties.
Improving safety to make it easier to walk and bike = good for business
Connected, walkable neighborhoods vastly economically outperform neighborhoods where the only way to get around is by driving—especially in terms of real estate. For-sale housing in dense, walkable neighborhoods in the 30 largest metropolitan areas were valued nearly double more than the rest of the for-sale housing market in those regions, as found in Foot Traffic Ahead, a 2019 Smart Growth America report.
It’s not just real estate: businesses thrive on streets safe for biking and walking, as expertly highlighted (with great photos, too) by our friends at Strong Towns. You’re much more likely to cross the street to grab a cup of coffee if it’s safe and easy to do so. And with pedestrian fatalities skyrocketing across the country, there are too many streets where that is impossible.
The INVEST Act takes a comprehensive approach to make walking and biking safer through a combination of increased funding, policy reform, and better provisions to hold states accountable, as we wrote last year. Some of the bill’s safety provisions include:
- Requires states to adopt Complete Street design principles and makes $250 million available for active transportation projects including Complete Streets
- Changes to how speed limits are set to prioritize safety results over a faster auto trip.
- Requires states with the highest levels of pedestrian and bicyclist fatalities to set aside funds to address those needs.
- Prohibits states setting annual targets for roadway fatalities that are negative—in other words, targets that assume the current trend line of increased fatalities is unstoppable, essentially accepting more fatalities every year as an unavoidable cost.
Reducing transportation emissions has a host of other benefits
To reduce transportation emissions, we have to give people more viable transportation options than driving. That means public transportation, biking, walking, and incentivizing community growth where destinations aren’t sprawling.
Not only are these investments good for our businesses, but they improve equity too, by removing the $10,000 barrier to enter the economy—the average annual cost of car ownership. These investments also increase transportation access for people with disabilities or people unable to drive, and they significantly reduce air pollution, too—one of the largest risk factors for bad cases of COVID-19.
If Congress wants to help our businesses embrace the 21st century and fight climate change, it’s time to invest in transportation that works—not new roads to nowhere.












 Yet if the region doesn’t continue making smart transportation investments and developing the kind of policies that have already reduced the share of people commuting alone by car into downtown, that prosperity could be threatened — killing the goose that laid the golden egg.
Yet if the region doesn’t continue making smart transportation investments and developing the kind of policies that have already reduced the share of people commuting alone by car into downtown, that prosperity could be threatened — killing the goose that laid the golden egg.
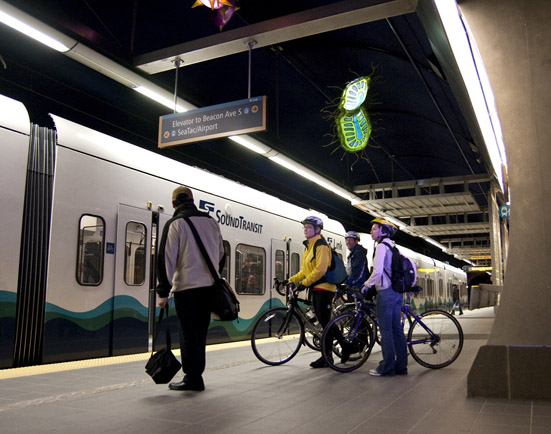 To address this Seattle worked with the business community and Metro to incrementally improve 3rd Avenue and set aside space for use as a transit mall. If you visit 3rd Avenue at 5 p.m., you’ll be struck by the volume of buses and the crowds of passengers boarding them.
To address this Seattle worked with the business community and Metro to incrementally improve 3rd Avenue and set aside space for use as a transit mall. If you visit 3rd Avenue at 5 p.m., you’ll be struck by the volume of buses and the crowds of passengers boarding them.








 A “comprehensive, but bottom-up approach to transportation” may sound like an oxymoron, but to a panel of regional planning experts on the frontlines of reform, it sounds a lot like common sense.
A “comprehensive, but bottom-up approach to transportation” may sound like an oxymoron, but to a panel of regional planning experts on the frontlines of reform, it sounds a lot like common sense.