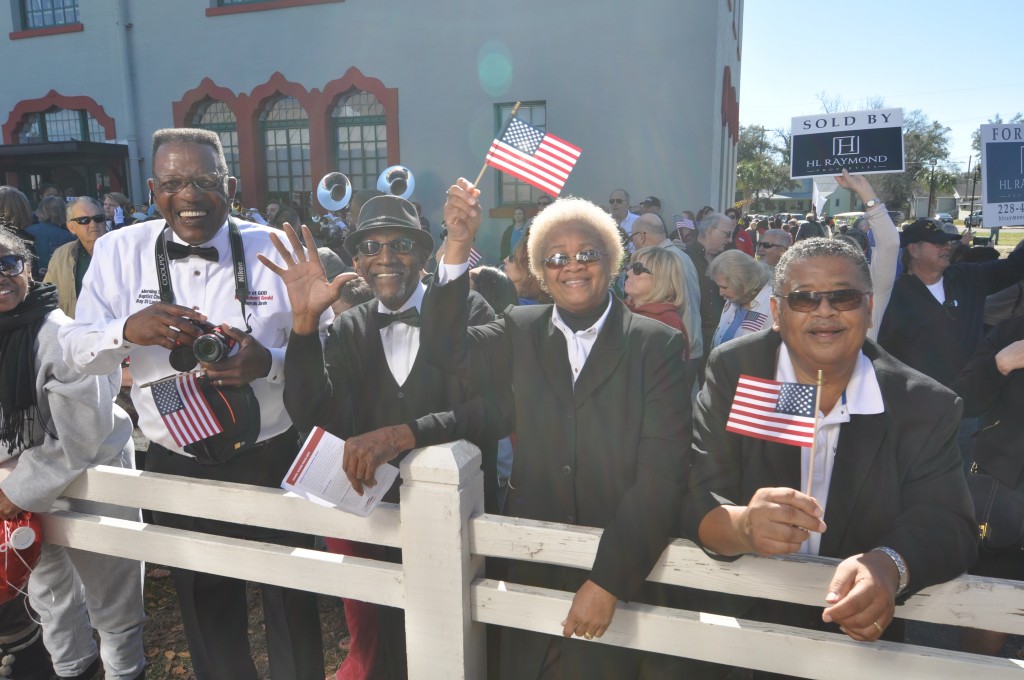
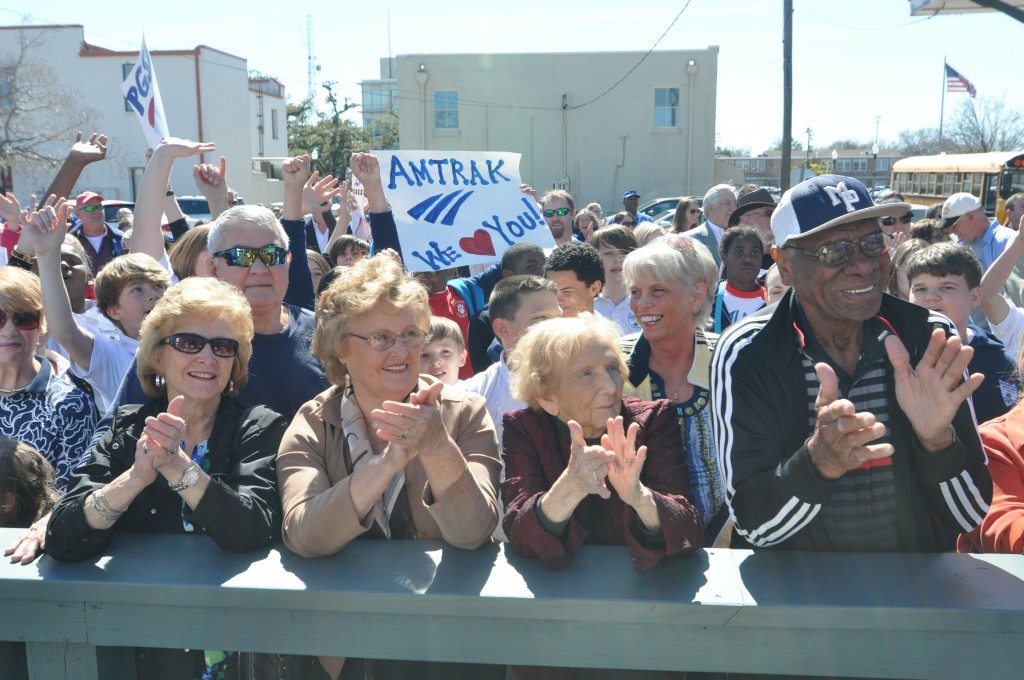
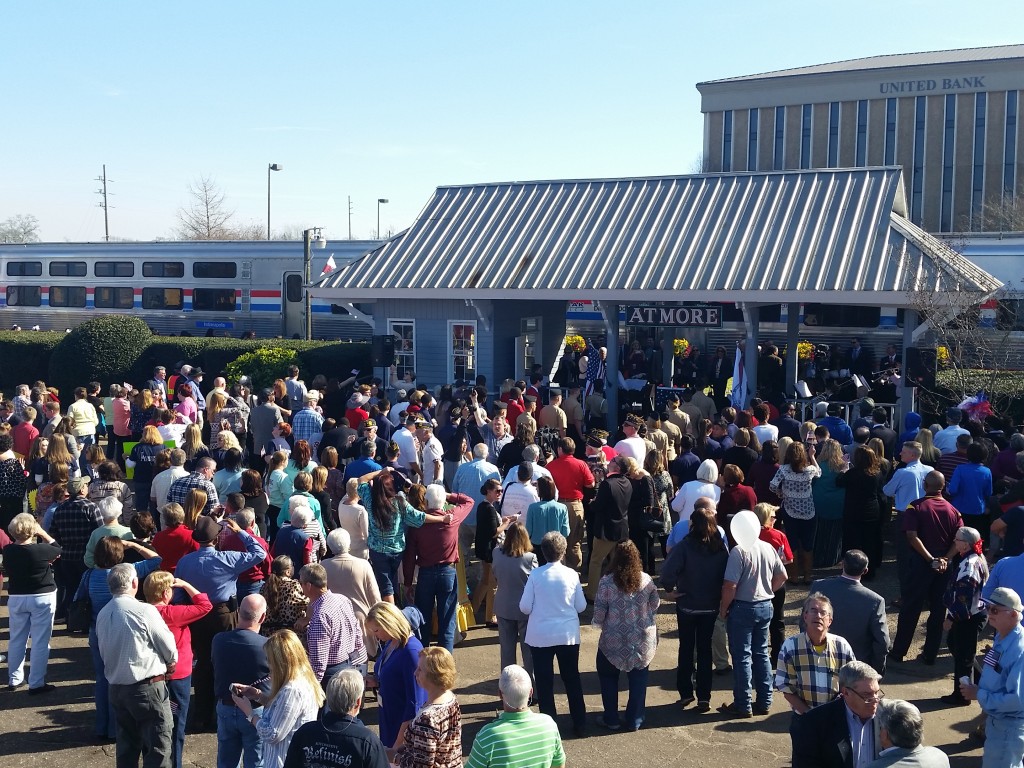
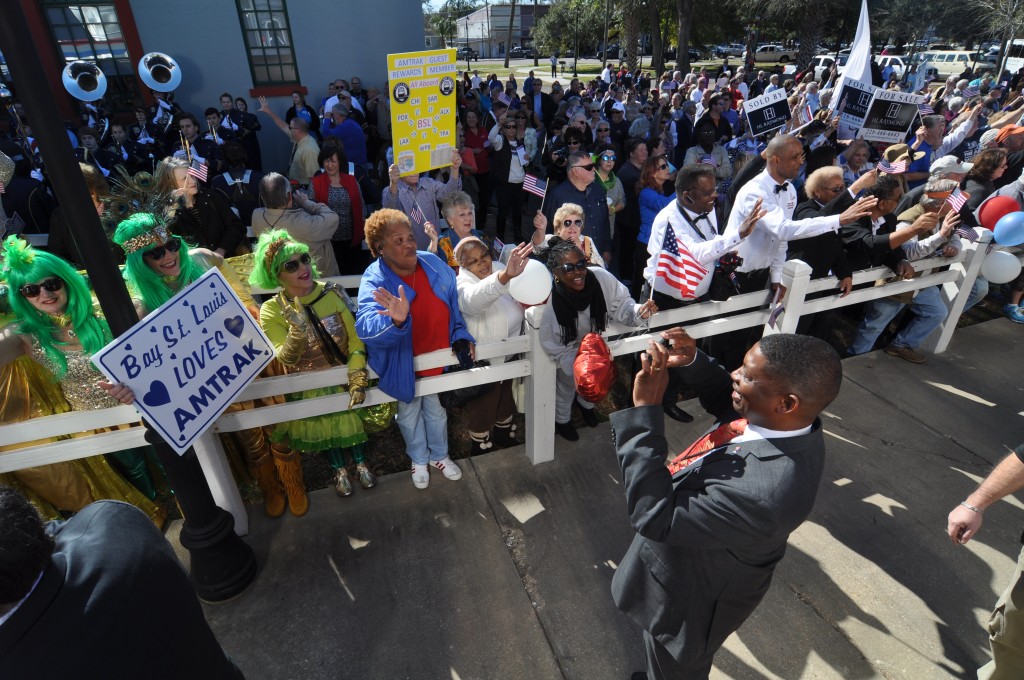
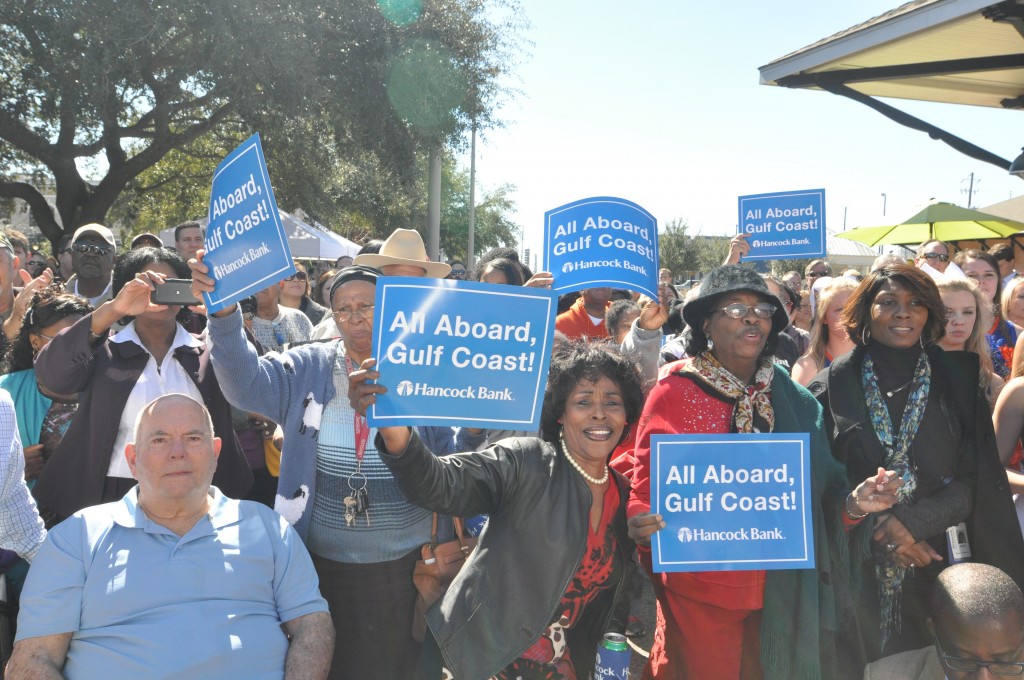
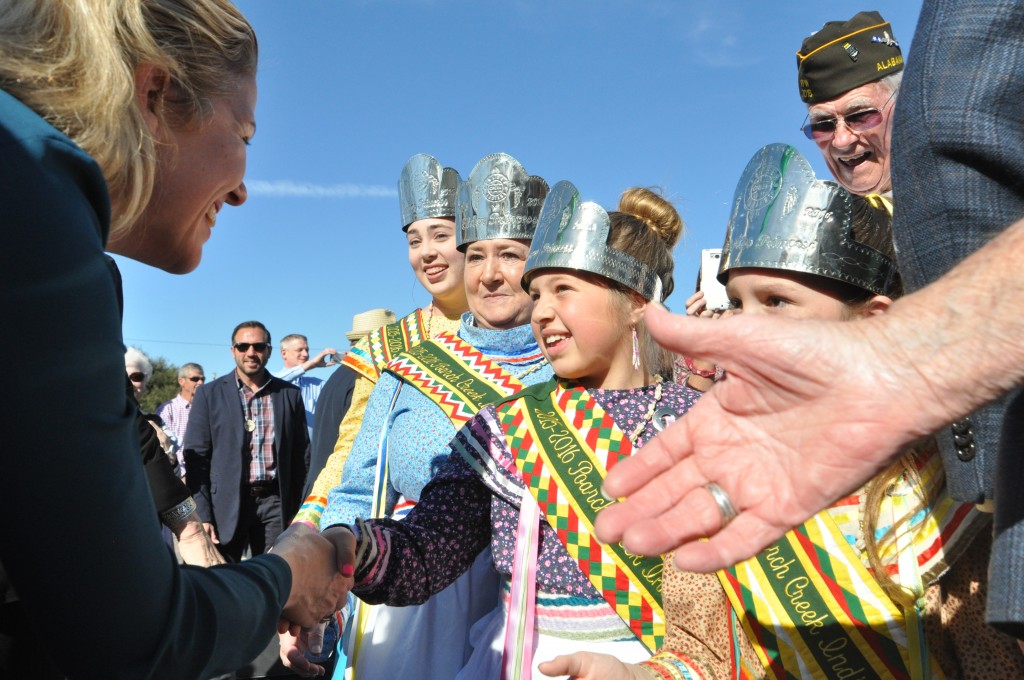
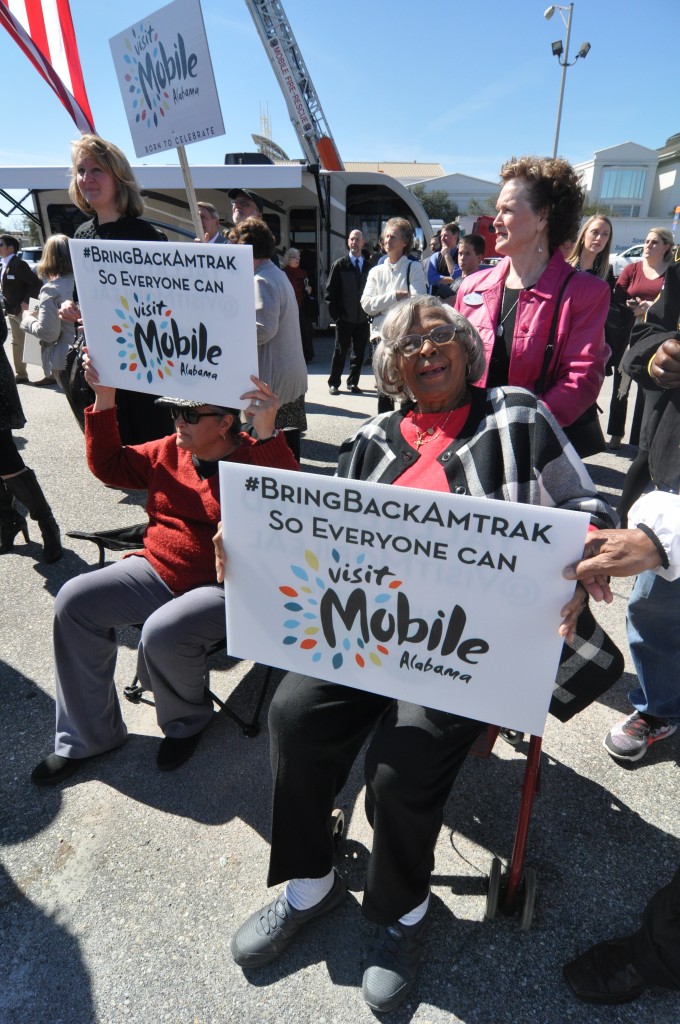While the local residents who turned out along the Gulf Coast last week to support the return of passenger rail through their communities are perhaps most hopeful for a new way to get where they want to go, their leaders are focused intently on the significant economic development potential for their cities, region and states that will come from the new connection.
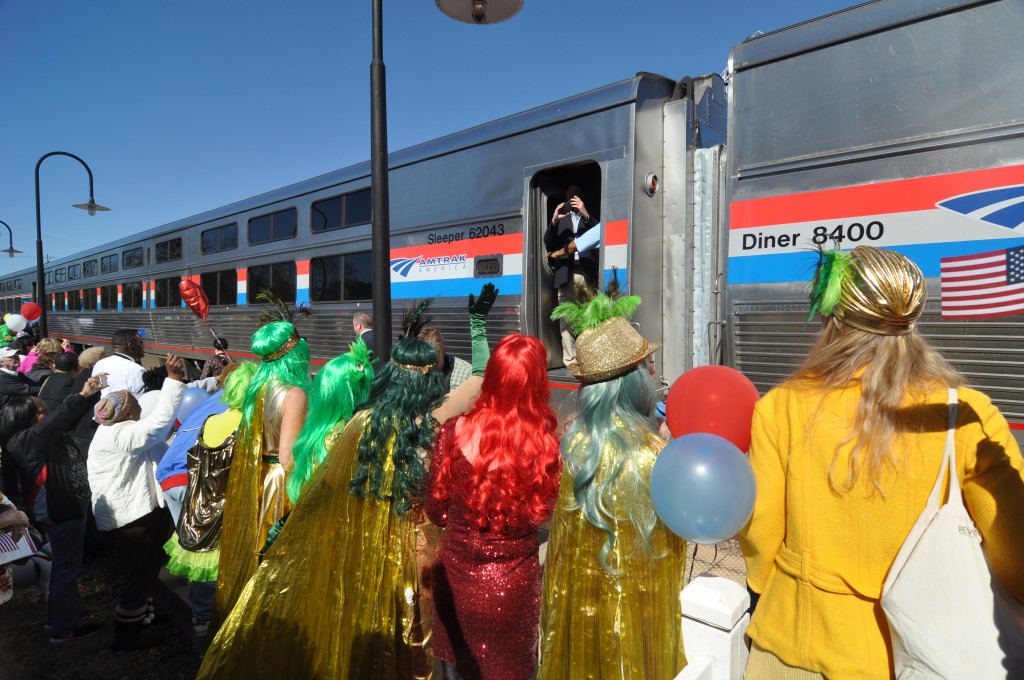

The Gulf Coast inspection train, run by Amtrak in partnership with the Southern Rail Commission (SRC), toured a potential route and examined the CSX tracks on February 18-19. It’s the product of years of work by local residents and elected leaders at almost all levels to restore the passenger rail service wiped out by Katrina over ten years ago. Read our first post for the backstory and our second post on the people we saw along the way. Note: Transportation for America serves in an official capacity as policy advisors for SRC. -Ed.
This prospective Gulf Coast passenger rail line would add a brand new connection, which can provide more bang for the buck than the diminishing returns of making improvements to existing connections. The interstate highway system is a powerful example of this. There were amazing economic impacts when new interstates were built between cities that weren’t well connected, allowing goods and people to flow back and forth like they never could before. But 50 years later, when projects are undertaken to add a lane or two to those existing highways, the cost could be greater than the original project in today’s dollars, but the actual fiscal impacts are far less than that of the original connection.
Adding new passenger rail service would create a brand new efficient connection between these Gulf Coast cities. And no matter their party or political philosophy, every single one of the local leaders that we spoke to along the coast was focused on the economic potential of passenger rail for their communities.
Greater New Orleans, Inc. is focused on helping the entire region stay competitive and focuses significant energy on recruiting new businesses to the region. GNOI’s Lacy Strohschein told us that for New Orleans, which has emerged as a tech hub, to compete against peer cities like Austin and Seattle, “You have to be selling them something.” Quality of life is a huge piece of what they’re selling in New Orleans, but what else does that talent want?
“They want access, they want to be in connected, walkable urban downtowns. Many come from places where they’re used to jumping on the train,” she said as we traveled just east of New Orleans on the train Thursday morning. “We have the most beautiful beaches within five hours of New Orleans, but if they don’t want to drive, there’s no easy way to get there. There’s a bottom line return, and [passenger rail service] is a critical piece to the puzzle for the quality of life that we’re offering.”
Gulfport is the second biggest city in the state of Mississippi. It was hit hard by Hurricane Katrina, though the city has bounced back in the intervening decade.
“I believe [passenger rail] is one more link in the chain that helps us recover,” said Gulfport Mayor Billy Hewes while chatting in the one-of-a-kind Ocean View dome car between Bay St. Louis and Gulfport.

Gulfport Mayor Billy Hewes chatting on the ride into Gulfport on February 18, 2016. Photo courtesy of Charles Gomez / Amtrak
Half a billion dollars come into Gulfport’s state port each year and drawing tourists to the beaches of Gulfport is a critical part of their local economy, according to Mayor Hewes. “We’re doing quite well now, but this is adding another piece of that puzzle that we’re offering,” he said.
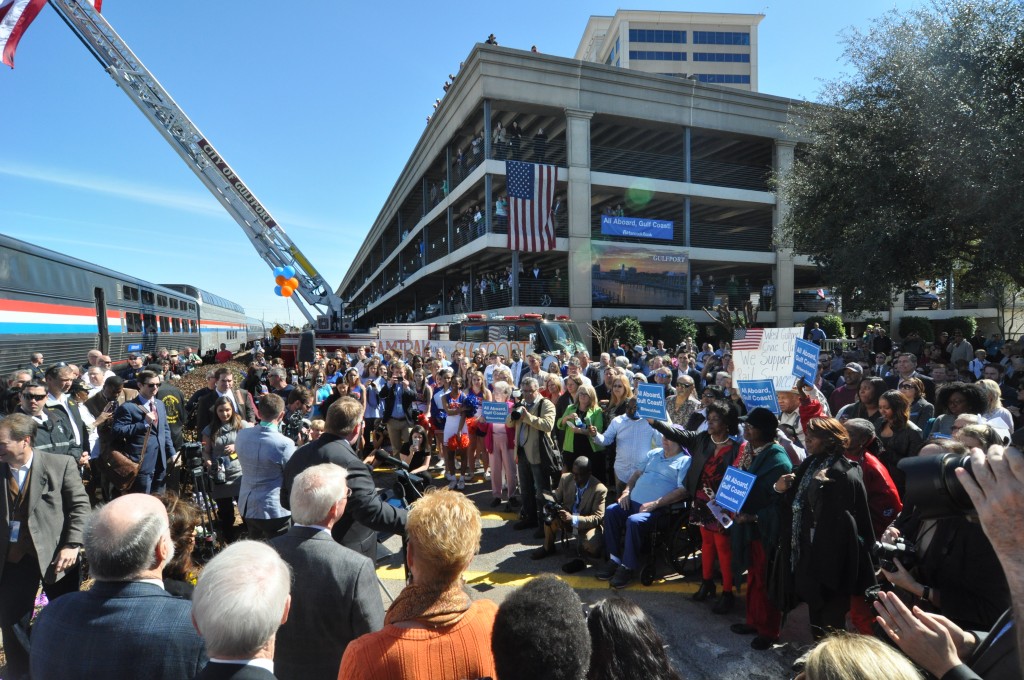
When the train pulled into Gulfport, where a thousand or more people were packed in between the old depot and a downtown parking garage, Mayor Hewes was beaming as he took to the podium.
“Your enthusiasm today is sending a message to Washington and our friends with Amtrak, how much we would like to have [rail service] back,” Hewes spoke into the microphone. “How much this is a real piece — not the final piece, but another piece of the puzzle — for what we’re offering, for the amenities that we have that make us so rich with so much opportunity here in Gulfport and across the entire Gulf Coast.”
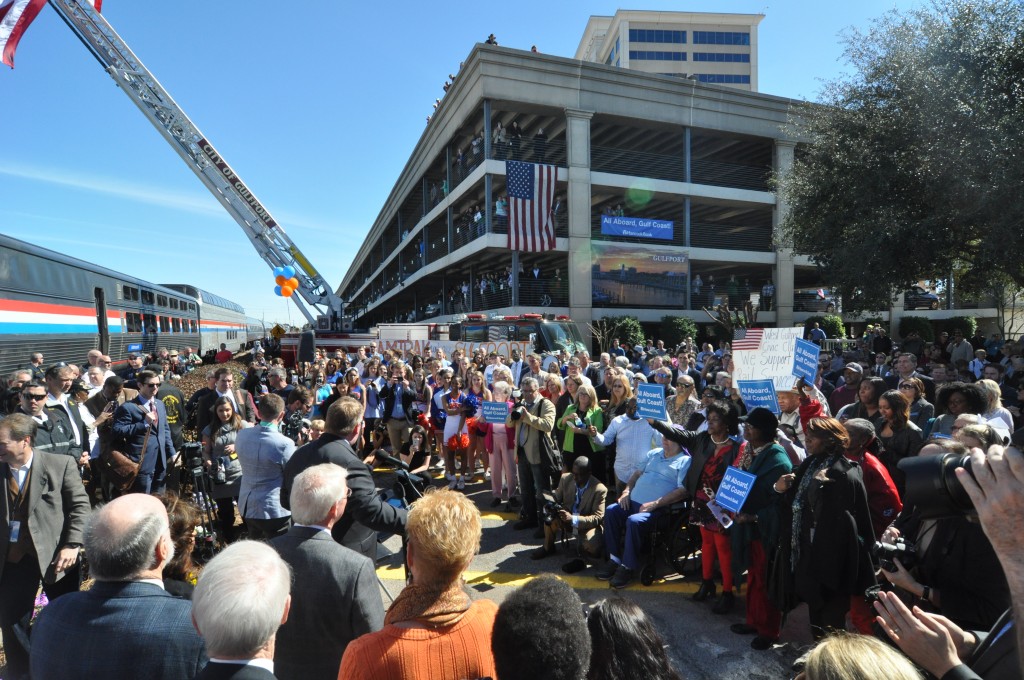

Hundreds of Gulfport residents packed the space next to the depot for the second whistle stop of the Gulf Coast Inspection Train. Photo by Steve Davis / T4America
One of the biggest champions of this project has been Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant, who took several hours out of his busy day to board the train in Bay St. Louis with his wife for all of the Mississippi stops. It’s hard to overstate the impact of his leadership on this issue, as a conservative Republican governor from a deep South state. Gov. Bryant clearly understands the economic potential.
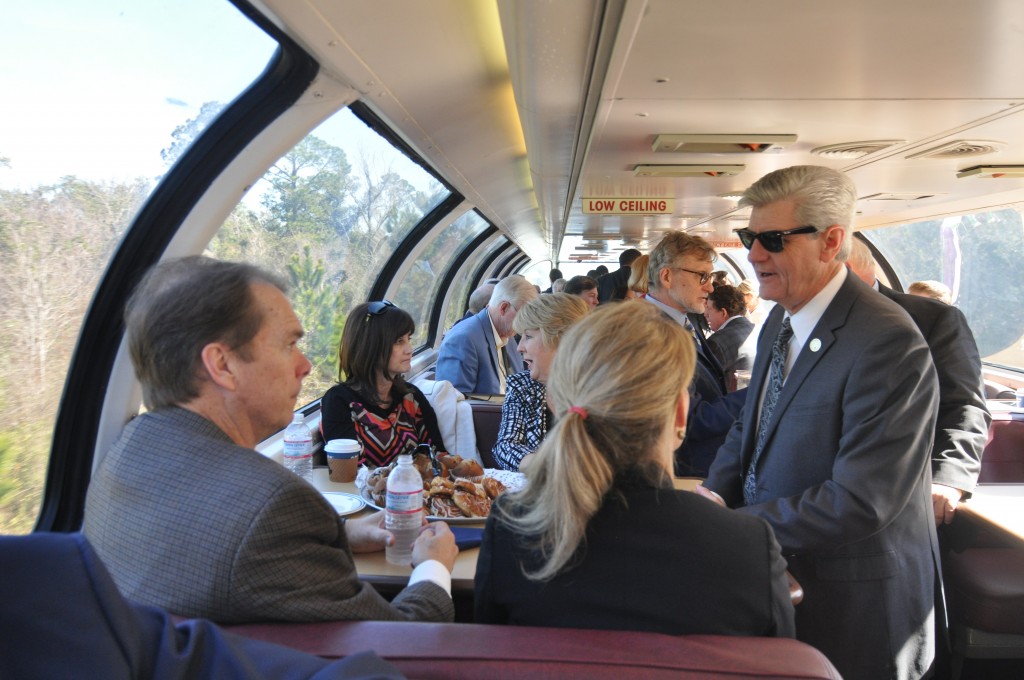

Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant (right) talks to Gulfport Mayor Billy Hewes (left) and Federal Railroad Administrator Sara Feinberg (right of Hewes) on the Gulf Coast Inspection Train on February 18, 2016. Photo by Steve Davis / T4America
“I brought convention after convention here [to the Gulf Coast]. Each time…they say to me, ‘We had no idea how beautiful this Gulf Coast was,'” Governor Bryant told the enormous crowd in Gulfport, hammering home the potential of making it easier for visitors to reach the Mississippi coast.
“Now, we’re going to get them here. We’re going to get them on board and we’re going to get them on this train. And this is going to be where they talk to all of their friends, all across the nation, and say, ‘If you want to see the beauty of God’s great creation, come to the Mississippi Gulf Coast,” he said.
“We just need more people to come and see this beautiful city; come see this beautiful Gulf Coast,” Gov. Bryant bellowed one stop further down the tracks in Biloxi. These people need “to come and stay a week or a month or two — and bring their money with ’em!” Gov. Bryant exclaimed, to an explosion of applause from the residents of Biloxi.
Mobile, Alabama is a huge center of commerce and industry for the state of Alabama and the entire Gulf Coast region. The city has the first Airbus factory on U.S. soil, an active shipbuilding industry, a busy port, interstate access and five railroads, according to Mobile District 1 City Councilmember and Council Vice President Fred Richardson.
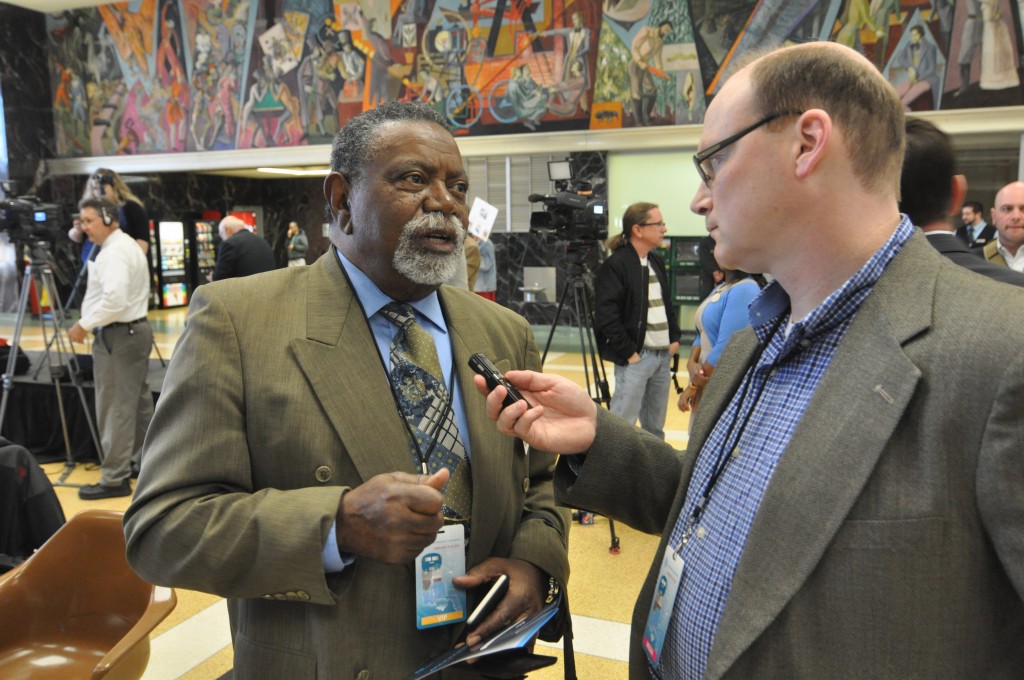

Mobile City Councilmember Fred Richardson talking to a member of the media in New Orleans just before the departure of the Gulf Coast Inspection Train. Photo by Steve Davis / T4America
“We all realize the value of passenger rail,” Councilemember Richardson said, offering a specific example.
“We have the busy Carnival cruise ships in the port…but is there another way to get all these tourists to and into our city? We’ve got air, we’ve got water, but we don’t have rail. So we’re trying to send a message today; a message that old people, young people, black and white people in Mobile — they want Amtrak and passenger rail. It’s galvanized people in our region and they want the train to roll. We’re missing this part of the puzzle that can help us bring another one million tourists into our city.”

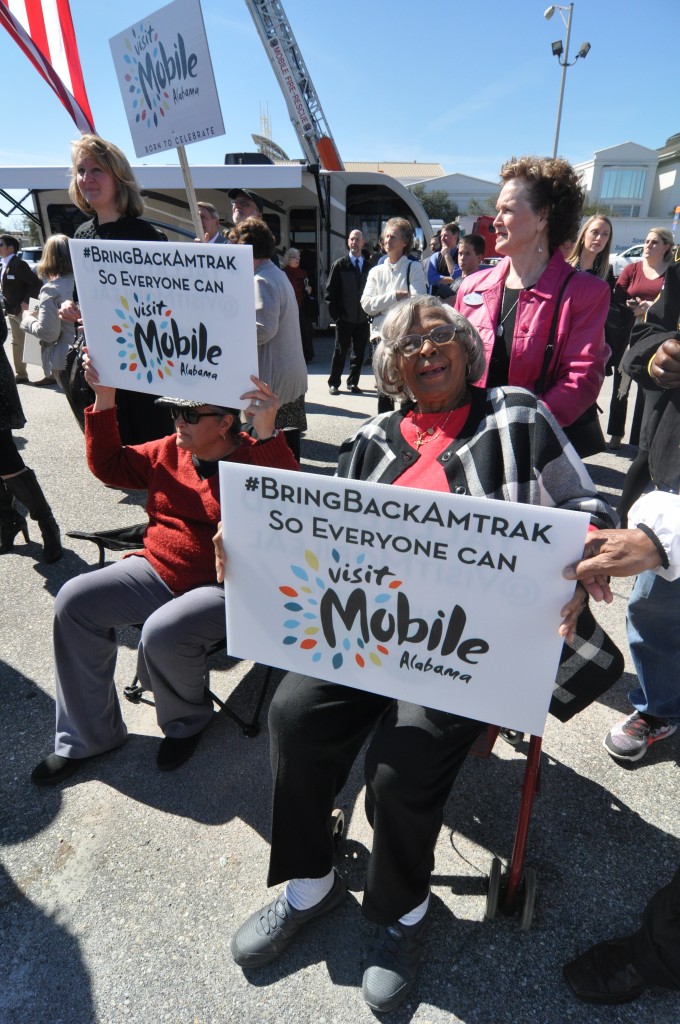
Mobile, Alabama. Photos by Steve Davis / T4America
Senator Roger Wicker (R-MS), who is responsible for the creation of the new Gulf Coast rail study group through his work to include it in the FAST Act, is working to ensure that new passenger rail service on the coast will also be a good deal.
“We’ve got the top brass, we’ve got the local leaders, and we’re gonna make this work for Mississippi and the taxpayers,” The Senator said in Gulfport.
#YallAboard
Update: Find links to all of our posts and photos from the trip as well as a short video we produced on the trip here in this short recap post.
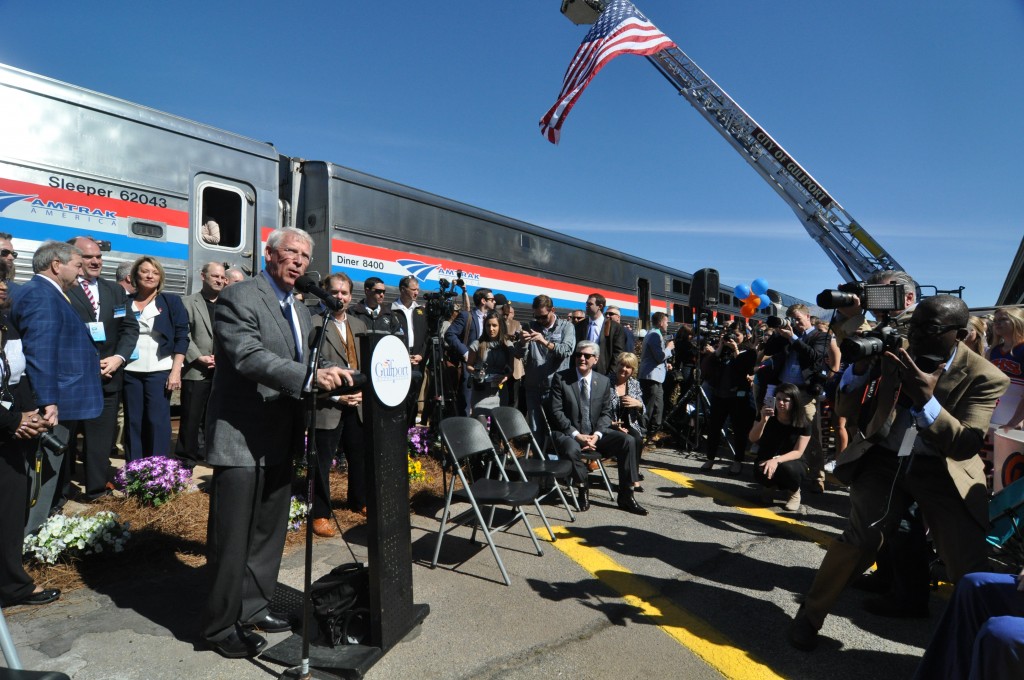

Senator Roger Wicker (R-MS) addresses the enormous crowd in Gulfport on the second stop of the Gulf Coast Inspection Train. Photo by Steve Davis / T4America