After putting out the call far and wide for pictures of streets designed for speeding traffic at the expense of safe travel by people on foot or bike, we’ve been getting some great — and by great, we mean frightening and terrible — photos of inconvenient, poorly-planned, dangerous and downright hostile conditions for pedestrians.
Here is a sampling of some of what we’ve received so far.
 |
| Bladensburg-22 Originally uploaded by wtrecat to Flickr. |
| MD 450 just west of junction with MD 202. Very busy road with no pedestrian crossing at this spot across from El Primo international market, 5403 Annapolis Rd. |
Note that this photo from Maryland just outside D.C. is taken at a Metro bus stop. And there appears to be no safe crossing immediately nearby.
 |
| Incomplete Street Originally uploaded by Boenau to Flickr. |
| No sidewalks? No problem! |
There’s no sidewalk at all along this road. And the overgrowth forces anyone trying to walk out into the roadway. If there is a crosswalk at the light up ahead, pedestrians have to cross at least 8 lanes of traffic and a median to make it across.
 |
| Incomplete Street Originally uploaded by Boenau to Flickr. |
| As if walking on the goat path isn’t bad enough, rainfall drains and collects on the grass, forcing pedestrians into the street. |
Just because there aren’t any sidewalks doesn’t mean that people won’t or aren’t walking. It has to be terrifying to walk on this narrow strip of grass next to 3 straight lanes of high speed traffic. And once again, if there is a crosswalk 200-400 yards down behind this pedestrian, people on foot will have to cross at least 6 lanes of traffic and a median in one light cycle.
 |
| elkton_rd3 Originally uploaded by Transportation for America to Flickr. |
| Submitted photo by Frank Warnock of Bike Delaware. www.bikede.org/ (Please credit photographer, not T4 America.) |
Smooth, graduated turning radii like this are especially dangerous to pedestrians. Turns are engineered like this so traffic can make a right turn while only having to barely slow their speed, making it extremely hazardous for people on foot to cross from the island back to the side of the road.
 |
| IMG_6603 Originally uploaded by Transportation for America to Flickr. |
| Bee Caves Rd/RM 2244 west of Walsh Tarlton Lane in Austin, Texas. Roadway under TxDOT jurisdiction. Submitted photo by Joan Hudson, P.E., of the Texas Transportation Institute. (Please credit photographer, not T4 America.) |
The photos we got from this supporter in Texas were all taken on roads managed by the Texas DOT. Pedestrians here have to walk in a ditch with nowhere to escape to if a car veers slightly out of the lane.
Photos like these could be taken in almost any place in the country. These conditions are far too common and much too accepted by the people who plan and design our streets and roads. Two-thirds of all pedestrian fatalities in the last 10 years occurred on roads much like these — high-speed arterials designed first and foremost for moving speeding traffic as fast as possible with little consideration for the needs or safety of people on foot or bike. Federal dollars and design guidelines have helped create these dangerous situations across the country, and the federal government shouldn’t be able to walk away and pin the problem on the states.
Simple policy changes and priorities for spending at the federal level can help save lives immediately.
We’re not finished collecting these photos — we want to see yours! When you send them in (click here for instructions), feel free to include location information as well and we’ll plot and share the location. And bonus points for photos that show people in them.
Thank you so much to the dozens of people who sent us photos or submitted them to our Flickr group. Keep it up!











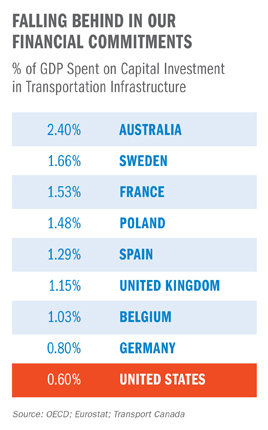
 By 2015, more than
By 2015, more than 
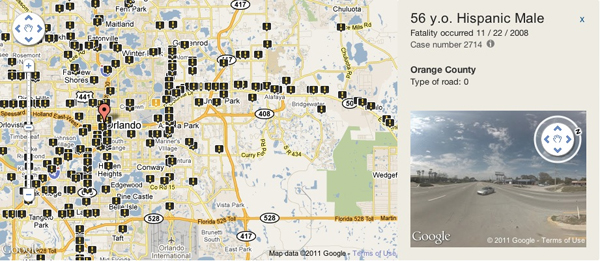

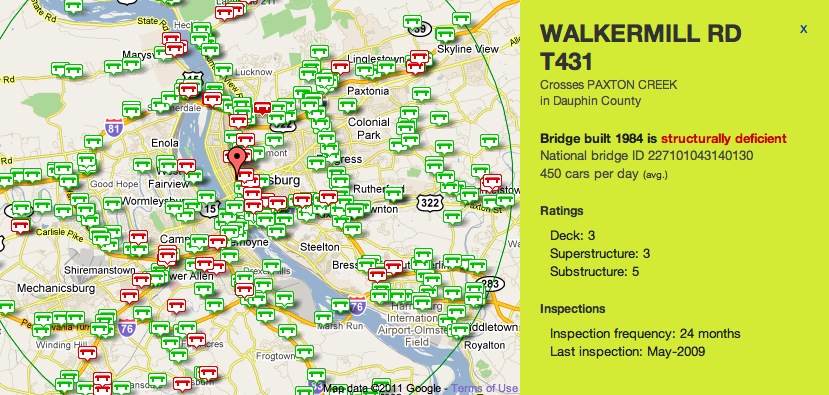

 A report being released Wednesday by T4 America chronicles the state of our nation’s bridges, with accompanying data and reports for all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Our country is facing a backlog of deficient bridges that need repairs and maintenance to stay open and safe, with needs far greater than what we’re currently spending.
A report being released Wednesday by T4 America chronicles the state of our nation’s bridges, with accompanying data and reports for all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Our country is facing a backlog of deficient bridges that need repairs and maintenance to stay open and safe, with needs far greater than what we’re currently spending.

 Earlier this week the House adopted rules for this new session of Congress. It’s a bit of inside baseball that can be hard to decipher, but these rules determine how bills are considered by lawmakers and what bills can and cannot do.
Earlier this week the House adopted rules for this new session of Congress. It’s a bit of inside baseball that can be hard to decipher, but these rules determine how bills are considered by lawmakers and what bills can and cannot do. 

 When a resource is scarce, the first step is always to make sure that you’re using that resource to its fullest. A quick glance at a congested road, a street with no parking or a jam-packed rush hour train might tell you that there’s no excess capacity going unused, but is that really true? While we continue to push for a greater investment in transportation overall to expand options for all Americans, are there ways to better use the resources that we’ve already got?
When a resource is scarce, the first step is always to make sure that you’re using that resource to its fullest. A quick glance at a congested road, a street with no parking or a jam-packed rush hour train might tell you that there’s no excess capacity going unused, but is that really true? While we continue to push for a greater investment in transportation overall to expand options for all Americans, are there ways to better use the resources that we’ve already got?

