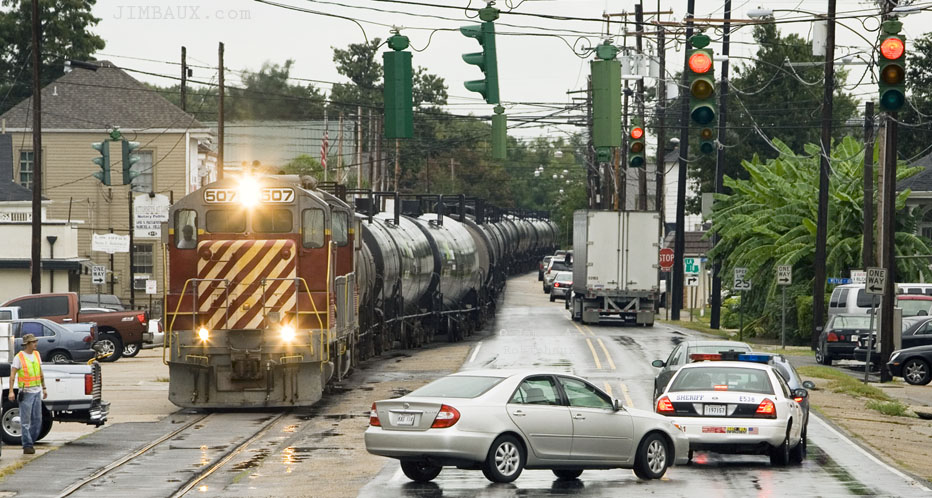
In an astonishing sight in this small southern city across the Mississippi River from New Orleans, daily freight trains run right down the center of their main street. Local elected leaders and the busy nearby port are hoping to relocate this incredibly disruptive freight rail line, but they’ll have to raise local and state money, negotiate with freight companies, and apply for federal support to make it happen.

For the people of Gretna, Louisiana, miles-long freight trains are a part of daily life. But in a far different way than other smaller cities with a few at-grade crossings. Multiple times a day, freight trains cruise down the middle of their main street at 15 miles per hour through 120 unprotected intersections, grinding the city to a halt. Vehicles stop, people can’t cross the street, and the noise swallows nearby conversations. If a parked car is in the way of the train, the train stops, blocking traffic, as the operator tracks down the owner to remove their vehicle.
But the people of Gretna aren’t taking this lying down.
This project is one of 15 that we are supporting through our Community Connectors grant program to help small and mid-sized communities repair the damage of divisive infrastructure. Learn more about that program from our parent organization, Smart Growth America.
Impact on Gretna
Situated just across the Mississippi River from New Orleans, the small city of Gretna is a vibrant, historic, and diverse community that functions as a critical trade hub for the region due to its proximity to the Plaquemines Port Harbor & Terminal District. Gretna, like many communities on the lower Mississippi River, developed around the railroad to house the industrial workforce that the freight rail companies served. One side effect of this complementary growth, however, was that daily freight trains continued to run through Gretna. And we do mean through Gretna.
Today, in one of the most astonishing sights around, freight trains from Union Pacific (UP) and the New Orleans and Gulf Coast (NOGC) railroads run right down the middle of 4th Street and Madison Street in historic Gretna, dividing the city in half and stunting the city’s growth. To appreciate the full impact on the city and the people of Gretna, watch this video:
For 12 minutes, the train blocks all of Madison Street and passes through 120 intersections, blocking emergency vehicles, personal travel, and economic activity. In 2006, a resident’s home burned to the ground as an emergency vehicle was held up for 20 full minutes, separated from the house by a passing train.
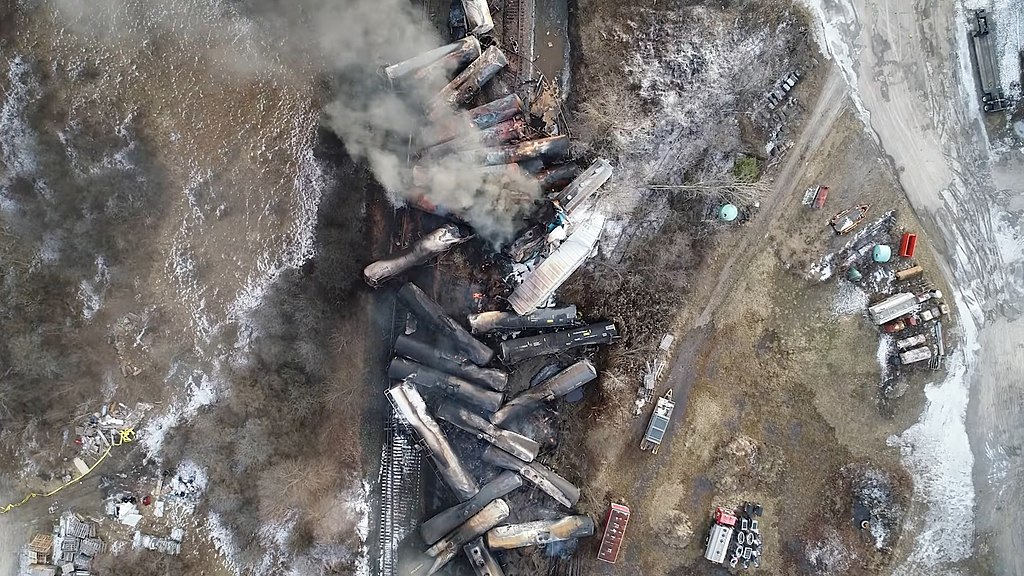
In addition to the dozens of crashes between vehicles and trains in Gretna over the years, trains have also derailed in the city several times. Luckily none of them were carrying hazardous materials, but consider the impact of a massive toxic derailment—like the recent one in East Palestine—right in the middle of a city street surrounded by homes and businesses.The public health and environmental damages would be orders of magnitude worse.
Call to action
In 2014, NOGC announced that it would be increasing freight service through Gretna to serve a new coal export terminal in Plaquemines Parish. This announcement sparked outrage from community members and catalyzed the pursuit of an alternative route as residents and public officials realized they could no longer ignore the problem. They collectively decided: the tracks had to go.
The first step was getting everyone to the table. A coalition that included Gretna’s Mayor Belinda Constant and representatives from Jefferson Parish and the New Orleans Regional Planning Commission quickly hammered out a plan with NOGC and UP to move the tracks several miles to the west, cutting through an industrial zone and away from the residents of Gretna. While this deal was good news, the freight companies were unwilling to chip in a cent to turn the city’s plan into a reality, preferring the local governments pick up the tab (for what would also be a more convenient route for the railroads).
But this agreement with NOGC and UP did allow the coalition to enlist the help of the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) in conducting an Environmental Assessment of the plan, finding that the realignment would eliminate 97 at-grade railway-roadway crossings, relieve congestion downtown, improve emergency access and evacuation routes, and even improve NOGC and UP rail service in the process. And, well, remove giant trains from the middle of a city street. The project was a slam dunk.
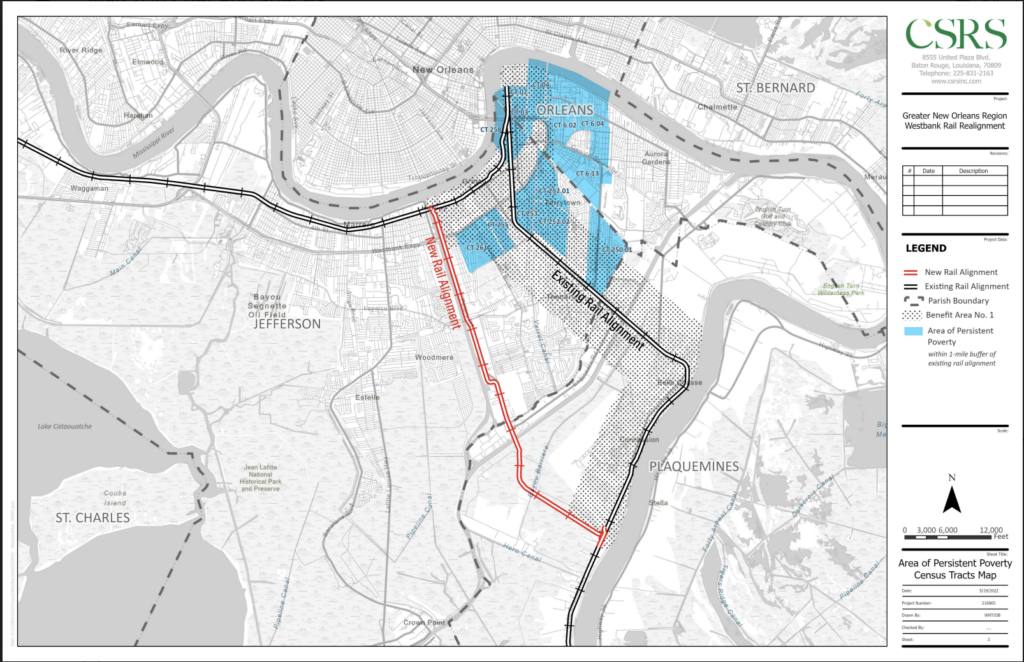
Though the coalition was able to quickly garner support for the project, they’ve struggled to overcome its large price tag, especially with the railroads unwilling to contribute. Jefferson Parish and Gretna are willing to foot part of the bill, but will need federal support to get it over the finish line. They unsuccessfully applied for a Mega Grant from the U.S. Department of Transportation in 2022, and have applied for another one this year, which is currently pending before the FRA. Until they come up with the necessary funds, this badly needed project will not move forward.
In the meantime, Mayor Constant and Jefferson Parish President Cynthia Lee Sheng have focused on stopping the problem from getting worse. When NOGC and Union Pacific wanted to build even more tracks through Gretna, Mayor Constant bought up portions of the land and halted further plans by the railroads to take city lands because the city felt that it had a stronger public purpose. The city was able to establish in court that the people of Gretna had more of a right to use their community’s land than the freight companies did.
Lessons for budding Community Connectors
This is an incredibly complicated and ambitious project, possibly the most among the 15 projects T4America and Smart Growth America are supporting through the Community Connectors grant program.
Gretna and Jefferson Parish, along with new stakeholders like Plaquemines Parish and the Port of Plaquemine, continue to seek funding for the project, regularly engaging the Federal Railroad Administration and their congressional delegation on the matter. Additionally, they continue to work through the finer points of negotiations with the railroads to ensure that there is a win-win project. Of note, the United States Department of Transportation has recently asked them to include improvements to the existing alignment (greenways, transit connections or other interventions) as part of a larger request that would showcase a range of public safety, freight efficiency and community revitalization benefits.
There will surely be dozens of lessons to come in the future, but here are a few things learned so far during this project:
In some instances, there are ways to challenge railroad, state, and federal land rights. This will not be feasible everywhere, but the case in Gretna proves that some courts are sympathetic to the public purpose arguments presented by a city. If you’re an advocate looking to stop a disruptive rail construction project, see if you can engage your local government to strategically acquire land, granting you leverage in court and otherwise.
Build as big of a coalition as possible. The real win in Gretna came from the extensive collaboration between all levels of government, and with the railroads, to move the costly realignment project to the point where it could possibly happen. The combined authority of Mayor Constant, Jefferson Parish, the New Orleans Regional Planning Commission, and the Federal Railroad Administration made the partnership with NOGC and UP possible, especially with the significant price tag attached to the coalition’s proposed solution.
Your most powerful advocates may be your elected officials—get them on board to fight for you. Gretna’s fight has taken more than a decade of persistent effort, but having a unified set of elected leaders to take the message to the railroads and negotiate was key. Advocates fighting similar David and Goliath battles against freight railroads, highways, or any other divisive infrastructure should take inspiration from Gretna and remain persistent. Proactively engage stakeholders to find mutually beneficial solutions. Understand competing perspectives and be willing to work through them. Engage your federal, state, local—and when applicable—railroad partners early and often.
Community Connectors: tools for advocates
 You may be fighting against a freeway expansion. You may be trying to advance a Reconnecting Communities project to remove an old highway. You might be just trying to make wide, dangerous arterial roads a little safer for people to cross. This Community Connectors portal explains common terms, decodes the processes, clarifies the important actors, and inspires with helpful real-world stories.
You may be fighting against a freeway expansion. You may be trying to advance a Reconnecting Communities project to remove an old highway. You might be just trying to make wide, dangerous arterial roads a little safer for people to cross. This Community Connectors portal explains common terms, decodes the processes, clarifies the important actors, and inspires with helpful real-world stories.













