Successfully halting construction on the Park East Freeway in Milwaukee in 1977 was a major early win for advocates. But removing highways is more complicated. Milwaukee confronted that problem in the late 1990s and early 2000s when they attempted to remove the portion that had been built—a story which can serve as a model for other highway removal efforts.

Freeways built over communities
In 1966, officials in southeast Wisconsin had penned the quickly growing area’s first comprehensive regional transportation plan, which called for 16 freeway routes in the seven-county region. Many of those (pictured below) would cut through the city itself, destroying thousands of homes and businesses. The plan was created to rearrange Milwaukee’s transportation system around the growing suburban sprawl of the 1940s and 1950s, with a priority on creating ways for suburban residents to quickly drive into and through the city. The needs of city residents in the neighborhoods those people would pass through were never the prime consideration, if their needs were considered at all.
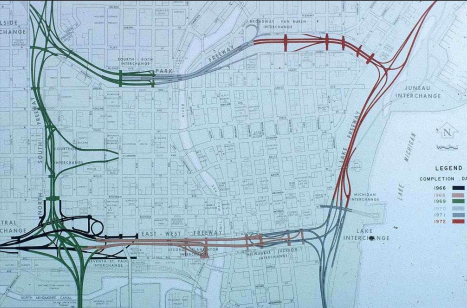
Some Milwaukeeans quickly grew concerned and frustrated over the destruction of thousands of homes, businesses, and parks as the first sections of the region’s freeways were built. One of the most destructive new freeway projects was the Park East Freeway. Black communities, most notably the thriving community of Bronzeville, faced the brunt of the damage and many were largely leveled to pave way for freeway construction. The Park East Freeway destroyed nearly all of what was a thriving community in Bronzeville, which once surrounded Walnut Street west of the Milwaukee River. Other freeways repeated this process across the city.
The staunch opposition of Black Milwaukeeans was ignored by the city and the Southeast Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SWRPC), which jointly completed the first section of the Park East Freeway in 1969 — the east/west segment marked in green and gray on the graphic above. As with many other cities, the tide in the fight against freeway construction would turn only when interstates were proposed to be built in whiter, more privileged neighborhoods.
Residents fight to halt construction
In the early 1970s, residents in nearby, primarily white neighborhoods like Sherman Park and Bay View in north Milwaukee organized citizens’ associations to formally resist construction of the Park East Freeway through their communities. These newly formed groups, which had significant resources at their disposal, turned to the legal system to fight the freeways.
Their legal challenges were enabled by a new law that radically changed the highway construction process. Congress had just passed the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 (NEPA), which required all construction projects utilizing federal funding to conduct environmental impact studies that measured projects’ impacts on the environment, which included tangible impacts to people in the community. Armed with new NEPA regulations, those wealthy Milwaukee residents were able to not only halt the construction of the Park East Freeway, but successfully got the SWRPC to institute a ten-year moratorium on all new freeway construction in the region.
This seemed like a major win, but the fight was far from over. Much of the Park East Freeway and other freeways had already been built, crisscrossing the Milwaukee region with damaging road infrastructure that disconnected scores of communities.
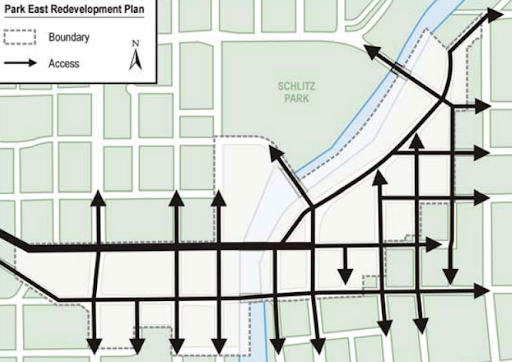
By the time the courts and the SWRPC had halted construction on the Park East, city, regional, and state agencies had already displaced thousands of residents, torn down thousands of homes, and laid miles of asphalt. What was left of the Park East Freeway—a spur of a half-completed highway (pictured below)—remained a gaping hole in the middle of several neighborhoods in north Milwaukee, dividing the people that lived there from neighbors, jobs, and essential services. Repairing these holes would prove to be a greater challenge than halting construction had been.
Removing the Park East Freeway

The one-mile spur of the Park East Freeway from I-43 to North Milwaukee Street destroyed or disconnected 17,300 homes and as many as 1,000 businesses. Only a few decades later, the underutilized and expensive freeway would become a clear candidate for removal.
For decades, the area around the Park East Freeway languished in underdevelopment, devoid of essential services or transportation facilities designed to serve the needs of people living in the area. Developers refused to build anything but surface parking on land adjacent to the freeway, not because parking was in high demand but because other uses were a tough sell right next to the highway. But in 1991, one developer finally took a chance on the area. Mandel Group built a remarkably successful development of luxury apartments and condominiums, selling homes for as much as $500,000.
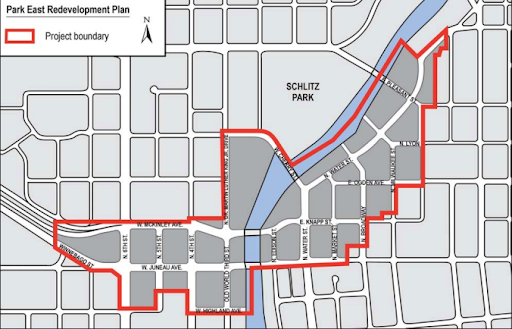
The success of this newly created real estate company—and the buzz of nearby redevelopment activity that followed—caught the attention of Milwaukee’s new mayor, John Norquist. He had been elected to the Wisconsin State Assembly on an anti-freeway platform during the height of Milwaukee’s freeway legal battles of the 1970s, and saw an opportunity to revitalize his home city by removing the old, blighted freeways that divided it. He began drafting a plan to replace the Park East Freeway with McKinley Boulevard, restoring the urban street grid in the area and freeing up 26 acres of land for redevelopment.
Illustrations of the urban street grid overlaid on the former Park East Freeway right-of-way (Source: City of Milwaukee)
Norquist and his allies, however, still needed to convince other regional and state government agencies to approve the removal project and commit funds to it. They opted to make economic development their core message, proving that removing the freeway would draw new investment and economic activity to downtown Milwaukee. In 1998, they drafted a plan for downtown Milwaukee that tied freeway removal to economic development goals. The plan was approved shortly afterward, in 1999. Another 1998 report, this one by the SWRPC, helped to allay fears that removing the Park East Freeway would increase traffic. The Milwaukee Board of Supervisors and City of Milwaukee Common Council were convinced, approving the plan in quick succession in 1999.
Over the years, NEPA has also been utilized in counterintuitive ways to fight proposed highway removals. The well-researched removal plans helped Norquist’s plan survive one of these NEPA-based legal challenges from local businesses concerned about congestion. And in 2002, the city broke ground to remove the one-mile stub of the Park East Freeway and replace it with an urban street grid—dubbed the Park East Corridor—in 2003.
Milwaukee funded the project through a compromise with the State of Wisconsin that redirected $21 million in federal highway dollars originally appropriated to the State of Wisconsin for a bus priority lane on I-94. The state matched this money with $1.2 million of its own, and the city followed suit with $2.5 million to bring the full project funding to $25 million. The SWRPC made this agreement official in its 2001 plan, cementing the joint commitment of all three parties toward removing the Park East Freeway.

As with other similar projects to remove freeways or highways across the country, the hefty congestion predicted by opponents or skeptics never materialized. Traffic just disappeared, as every state DOT’s expensive models consistently fail to accurately predict. The project was a major success, reducing congestion and attracting billions of dollars in new investment to the Park East Corridor. One block of the new corridor, “Block 22”, has attracted over $3 billion in investment. The corridor was slated to host the 2020 Democratic National Convention before the COVID-19 pandemic spoiled the event. The area has attracted several new corporate headquarters, recently including The American Family Insurance Company.
With this proven example in mind, officials in Milwaukee are studying the removal of an outdated portion of State Highway 175 that walls Washington Park off from the Washington Heights neighborhood to the west. As Milwaukee looks to continue healing from its era of roadway-based demolition and division, localities across the country can learn from its successes.
Lessons for budding community connectors
Milwaukee benefitted from a skilled and motivated political leader in John Norquist. Advocates should cultivate political champions of freeway removal of their own, but they also can learn from Norquist’s success in other key ways.
For highways that are still on the books or being advanced toward construction, the NEPA process is as relevant now as it was in the 1970s, still requiring projects of a certain size and scope to engage communities before proceeding. NEPA public engagement processes are a great opportunity for advocacy groups and concerned residents alike to fight for projects that avoid harmful roadway construction.
Mayor John Norquist succeeded with a simple, well–supported argument for removal that focused on a broadly shared value of economic growth. While Norquist and the coalition supported the project for scores of other worthy reasons and benefits, this economic framing was decisive in convincing skeptical public officials in Milwaukee, the greater region, and Wisconsin state government to approve the project. Local policymakers and advocacy groups should document the benefits of their plans, framing them in ways that will resonate with their communities—and with the people they need to convince.
While Milwaukee is a good model, it is not perfect. While the destruction of neighborhoods like Bronzeville can never be undone, officials should seek to replace the freeways that destroyed them with development designed to serve the needs of those affected communities. Other communities have prioritized finding ways to restore some portion of lost wealth and income to those who were affected. Milwaukee has developed the Park East Corridor to include luxury apartments and corporate headquarters, but city officials should also seek out ways to provide affordable housing and invest in Black-owned businesses in the area. Undoing the damage created in the first place has to be part of the equation, as does creating a plan from the ground-up with those left behind or neglected, rather than just delivering a top-down plan to them and asking for their support.
But the bottom line is this: resisting and reversing highway construction is possible. The destruction of American communities is not inevitable, and when it happens it need not be permanent.
Community Connectors: tools for advocates
 You may be fighting against a freeway expansion. You may be trying to advance a Reconnecting Communities project to remove an old highway. You might be just trying to make wide, dangerous arterial roads a little safer for people to cross. This Community Connectors portal explains common terms, decodes the processes, clarifies the important actors, and inspires with helpful real-world stories.
You may be fighting against a freeway expansion. You may be trying to advance a Reconnecting Communities project to remove an old highway. You might be just trying to make wide, dangerous arterial roads a little safer for people to cross. This Community Connectors portal explains common terms, decodes the processes, clarifies the important actors, and inspires with helpful real-world stories.