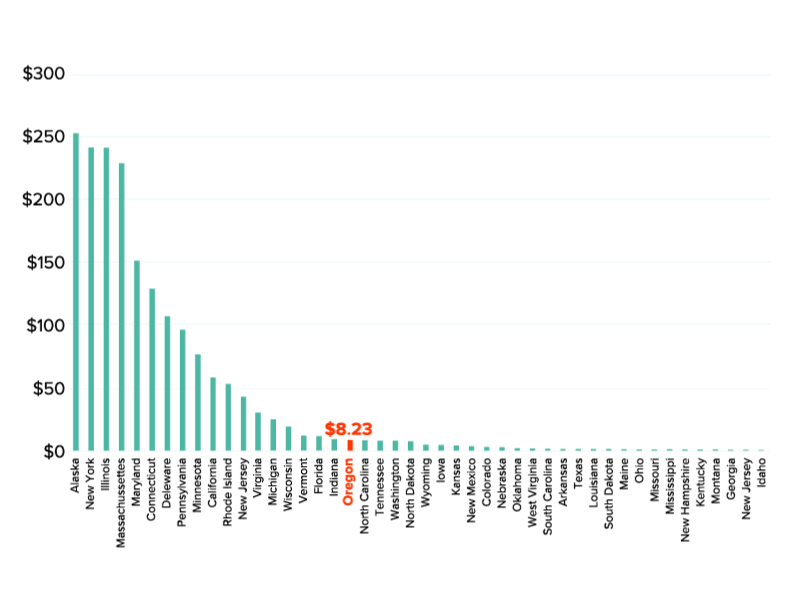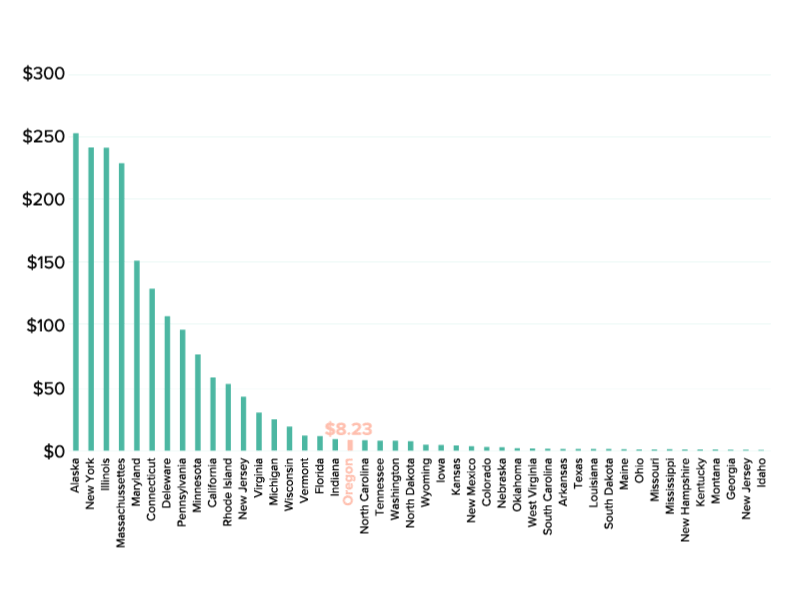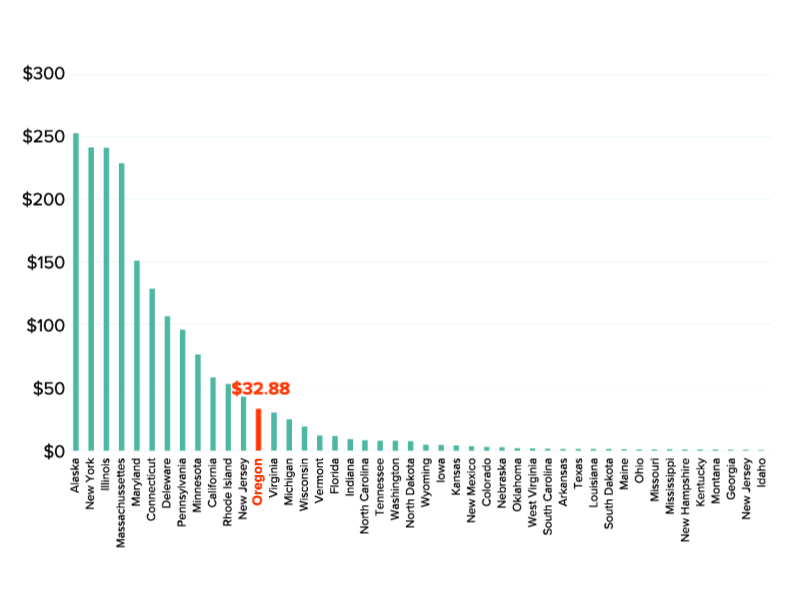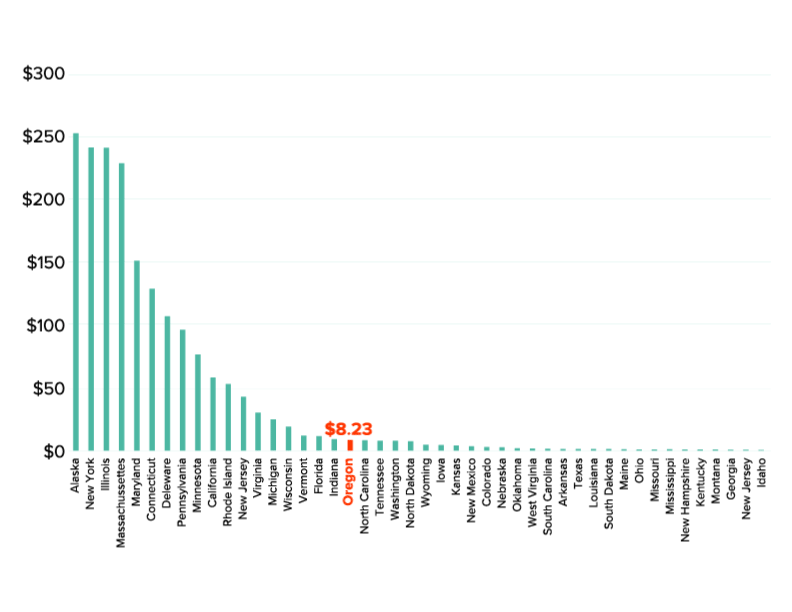
We’re fresh back from Capital Ideas 2018 in Atlanta, and as in years past, this year’s conference was an incredible alchemy of passion, knowledge, inspiration, and amazing people from around the country. For those of you who weren’t able to make it to Atlanta, here are seven things that we learned.

Left photo: Mayor Sly James of Kansas City, MO, right, one of Capital Ideas’ keynote speakers, talks to Toks Omishakin of the Tennessee DOT, and T4America chair John Robert Smith. Right: During a keynote on day two, Rusty Roberts, VP for Government Affairs at Brightline, shared his company’s ambitious plans for private passenger rail currently unfolding in Florida.
1) States that innovate, try new things, and take chances, get rewarded
There’s a common thought when it comes to new mobility or improving transit that it’s really only about cities. While we certainly think cities have a major role to play (see our Smart Cities Collaborative!), the role of the state is still vital.
The City of Gainesville, FL is on the cusp of launching a new automated vehicle shuttle pilot project to connect the University of Florida with downtown Gainesville via an automated driverless shuttle. Dan Hoffman, Gainesville’s city manager, shared their progress to date but made one thing clear: They would never be able to make this happen without the state of Florida’s involvement…and money, with the state contributing over $1 million. But it’s also worth noting that the state isn’t trying to run the pilot project—they’re collaborating to help a city run their own pilot. And the lessons that Dan and his city learn will be shared with the state as they collaborate with other cities. That’s a great recipe for success.

Sometimes states try new things and lose before they taste the eventual reward. But the smart ones learn from the experience. In Georgia, Atlanta bounced back from a painful failure to raise new revenue for transportation at the ballot box in 2012. They dusted themselves off, figured out why they failed, rebuilt trust in the transit agency, and then built vital new relationships with the state (and especially with legislators) that paved the way for a successful ballot measure effort in 2016 that raised money for billions in new transit projects in metro Atlanta.
Suburban Gwinnett County has rejected ballot measures to join the MARTA regional transit system multiple times over the last few decades. However, this March they will vote on a measure to finally join the MARTA system and dramatically expand transit service in a rapidly changing county where 25 percent of the population was born outside of the United States.
While others may have written off their state legislatures, the Metro Atlanta Chamber and the rest of their coalition did the hard work required between 2012 and 2016 to turn skeptical state legislators into outspoken champions for transit. Michael Sullivan from the American Council of Engineering Companies in Georgia so aptly summarized at the end of this panel discussion: never assume that your opponent today has to be your opponent in the future.
As Commissioner Charlotte Nash from Gwinnett County noted on the panel, their work paid off: action by that same legislature is enabling her county to go to the ballot this March to raise new funds for transit. Never write off your opponent or a skeptic.
States that refuse to take chances might avoid some failure, but they are also likely to avoid great success.

Our sincere thanks to Dave Williams from the Metro Atlanta Chamber for his commitment to transportation in the region and to taking selfies whenever he moderates a panel for T4America. From left, Dave Williams, Michael Sullivan, Georgia State Rep. Kevin Tanner, and Gwinnett County Commissioner Charlotte Nash.
2) “Transit access is the #1 factor in upward economic mobility”
Our opening keynote speaker on the first day summed things up when it comes to the “why” for improving access to transit:
As a different speaker would explain later, exactly how we measure access matters a great deal, but is there anything more that needs to be said? If we want to lift up those on the lower socio-economic rungs of our communities, then improving transit service and expanding access to it should always be a primary goal.
3) We are swimming in data, but very little of it has anything to do with the people who use the system.
A few audible cheers went up in the room when Stephanie Pollack, the Secretary of MassDOT, made that statement during an incredible panel moderated by T4America director Beth Osborne about the role of the state in new mobility services. She was joined by Commissioner Polly Trottenberg of the NYC DOT and Lilly Shoup, the Senior Director of Transportation Policy for Lyft. (More on that in a moment.)
On the second day, we took a deep dive into measuring accessibility and how so many of our metrics and data poorly assess what really matters. Nick Donohue, assistant secretary of the Virginia DOT, shared a story about the oft-cited Travel Time Index that measures congestion, and how it’s so far removed from the experience of real people and what really matters to them.
Congestion measures treat every road the same and have an implicit bias: always moving as fast as possible is the preferred goal. But streets are all about creating a place and a framework to create and capture value—not just a place for vehicles to move fast. This difference is often best illustrated with an image:
4) We don’t always agree with one another, but we have to keep working together
The panel discussion on new mobility definitely got “spirited!” Sec. Pollack is a provocative quote machine, but we also had a representative from Lyft sitting a few feet away from the person charged with keeping America’s biggest city moving. And as Commissioner Polly Trottenberg noted, congestion and VMT are both up in NYC while transit ridership is down since TNCs like Uber and Lyft arrived on the scene.
Though there were some (entertaining!) disagreements on this panel, the most important lesson we learned was that at the end of the day, many of these companies do want to try and accomplish the same things that the cities do, and we have to find a way to work together. As an example, Lyft’s long-term goals are to have fleets of vehicles in cities that are shared, electric, and automated, which certainly dovetail with the goals of a city like New York, as described by Commissioner Polly Trottenberg.
Ultimately it’s more productive for state or local officials to find ways to work together with private industry rather than against one another. And as Sec. Pollack noted, we have a lot of work to do to make more of these trips shared, and we won’t be able to make that happen without the private providers at the table.

5) You have to be ready and willing to listen
If you show up to a meeting about a transportation project or issue, you’ll have to talk about more than just the item at had: everything that came before you will be on the table. For example, in the public sector, you might have to address and resolve your agency’s past sins in a community first, even if the project proposed is an attempt to try and rectify the damage. As Sec. Pollack said, state DOTs might have to do something radical: listen to the people that they serve.

Our first panel on the second day was focused on making development around transit more equitable. Carol Wolfe from the City of Tacoma—which is in the midst of a rail extension through their city—noted that all too often planners and officials forget that there’s already a “place” that needs to be kept at the center of the process.
And it’s a little thing, but when an agency or planning firm makes renderings of future development, do they incorporate existing places and people? Does the community see themselves in the picture, or do the renderings include the same generic details as every other rendering?
6) People are hungry to exchange information and learn from one another
As we did in 2014 and 2016, we spent the first afternoon in roundtable discussions. Participants got to choose two of 12 topics, sit down with an expert, and then have a completely open-ended discussion with them and a dozen others interested in the same thing. These roundtables are one of the best features of Capital Ideas, and many of them are just a starting point for a longer exchange of information that will continue for weeks or months to come.
This year, our roundtables covered the Smart Scale project funding process in Virginia, the mileage-based user fee pilot in Washington State, the deployment of automated vehicles, strategies to compete for competitive federal transportation grant funds, the Metropolitan Planning Council’s Transit Means Business Report, and the Partnership for Southern Equity’s “Opportunity Deferred” report, among many others.

7) Atlanta is a wonderful city with lots of momentum (including on the soccer front!)
It may have partially been due to the fact that Atlanta United, the city’s Major League Soccer team, was preparing to host MLS Cup last weekend and beat the Portland Timbers in front of 73,000 screaming crazy fans for the city’s first championship since the Braves in 1995, but the energy in the city was palpable.
The capital of the New South has made tremendous progress. It’s a terrific city loaded with momentum and possibility, within a region that is making huge strides to invest in transportation and capitalize on their numerous walkable downtowns. All of this is occurring inside a state that has done a complete about-face on the importance of transit for their economic future.

We wrapped up the conference with two concurrent tours, one of a selection of TOD sites in the city with representatives from MARTA, and the second of the ongoing BeltLine project of trails and transit around the city with representatives from Atlanta BeltLine and the Rails-To-Trails Conservancy. To close things out, here’s a short thread from the BeltLine tour collected in a Twitter moment:
Participants: Have a story to share? Learn something new? Reach out to us at info@t4america.org. All photos by Stephen Lee Davis, T4America director of communications.
Our sincere thanks to our sponsors and host committee for making Capital Ideas possible. And to our many participants from around the country who came to Atlanta and hopefully took some helpful information—and inspiration—back home with them.
SPONSORS


Promotional Partner