
A proposed bridge is haunting the Bay Area

The Southern Crossing over the San Francisco Bay, proposed repeatedly over the past 77 years, has been rejected over and over again. Even as Reconnecting Communities funds will help Oakland study repairing the damage resulting from the interstate spur rammed through the heart of Oakland to serve as the eastern approach for this never-built bridge, the Southern Crossing shows how past choices continue to haunt the present—and future.

History of the Southern Crossing
The Southern Crossing is an additional Bay bridge highway crossing that has been proposed over a dozen times since the plan was developed (in 1946) by various departments of California’s state government. The proposed bridge would be the fourth bridge to cross the San Francisco Bay, partner to the built “northern crossing” pictured above in yellow. As shown above, the “southern crossing” would originate from the east side near Bay Farm Island (fed by a new interstate, I-980), cross to the west side, and land on the San Francisco peninsula in the Bayview neighborhood, at Hunters Point. The vision was to provide East Bay motorists on I-580 and Highway 24 with a direct connection to I-280.
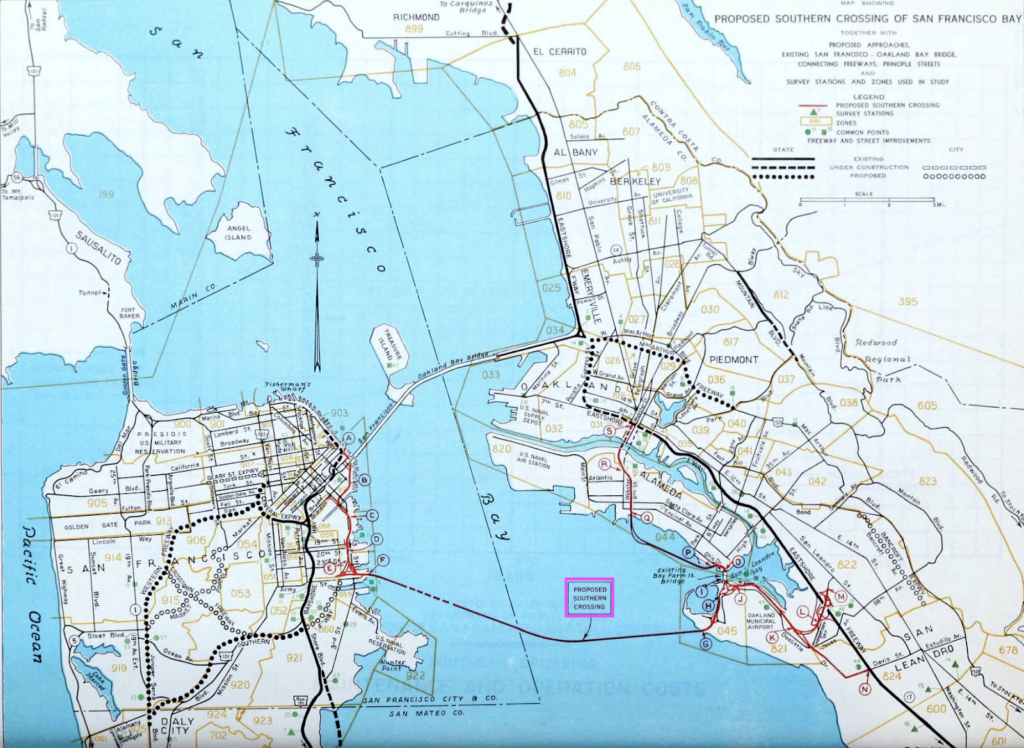
In 1961, the Southern Crossing bridge came close to construction, but white environmental activists concerned about the environmental degradation of the Bay prevented the project from moving forward. Even though the bridge was dead (for now), construction of I-980 moved ahead in the heart of Oakland, starting over two decades of work that would ultimately divide Black residents in West Oakland from downtown and demolish over 500 homes and nearly two dozen businesses and churches.
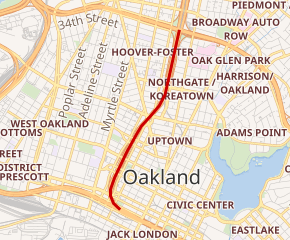
In 1971, a bill for the construction of the Southern Crossing was passed in the California State Assembly by both houses but vetoed by then-Governor Ronald Reagan, who believed that the citizens of the Bay Area should weigh in on the decision to construct such an expensive and controversial infrastructure project. Voters rejected a bond measure in 1972 that would have paid for the construction of the bridge via a toll increase on existing bridge infrastructure by a three-to-one margin. Without the bridge, the finally completed, roughly two-mile stretch of I-980 ended abruptly at 18th Street, and in the decades that followed, the underused strip became little more than a redundant eyesore.
Every iteration of the Southern Crossing proposed across nearly eight decades has failed due to costs, environmental concerns, or interference with air flight operations from the nearby but now-decommissioned Naval Air Stations of Treasure Island and Alameda. But notably, never because of the desires of the low-income, historically Black and brown communities on either side of the Bay, as they have always been excluded from the project’s discussion and decision-making process.
State departments of transportation in the U.S. have a documented history of systematically targeting low-income communities of color, wiping them out with highway infrastructure construction. These development patterns have been repeated since the 1950s under the guise of urban renewal. I-280 and U.S. Route 101 already surround the historically Black neighborhoods of Hunters Point and Bayview on the San Francisco side of the Bay, subjecting them to air pollution and water runoff and cutting them off from the rest of San Francisco.
Hunters Point and Bayview collectively have 110,200 residents within approximately nine square miles—a population density of 12,762 people per square mile. The median home was built in 1966 and is valued at $690K. The construction of the Southern Crossing bridge could destroy hundreds of those homes and local businesses, a disproportionate number of which belong to low-income residents of color.
A path forward

The San Francisco Bay has five highway bridges and an underwater tube carrying BART trains in each direction in separate tunnels. Billions of dollars have been spent to build this infrastructure, along with miles and miles of other interstates, highway connections, and arterial roadways. Even so, a 2017 Metropolitan Transit Commission (MTC) study found that Bay Area traffic congestion has only increased, going up by 80 percent from 2010-2017. Leaders continue to turn to new vehicle lanes to solve the congestion problem. Though the Southern Crossing proposal has never garnered the political support needed to proceed, since its inception in 1946, it’s been raised again and again to “solve” San Francisco’s traffic.
In 2017, Senator Dianne Feinstein (D-CA) revived the Southern Crossing proposal. The resulting 2019 joint study between the MTC and the Association of Bay Area Governments considered seven different scenarios to relieve traffic congestion based on growth projections by 2050. Only three of the options involved new bridges for vehicle travel, while six of the seven options were scenarios that involved transit solutions. The study found that the most cost-effective options were transit-only solutions, recommending these over the Southern Crossing highway bridge.
Still, nearly eight decades later, no full, final decision has been made on the Southern Crossing bridge, which keeps the specter of a massive, destructive project hanging over both the region and specific neighborhoods.
Induced demand is the phenomenon where an increase in supply results in a decline in price and an increase in consumption. To frame this within the context of highway construction, adding more lanes to a roadway creates more space for vehicle travel, attracting more cars, and ultimately exacerbating traffic congestion. Learn more in our report The Congestion Con, and use the SHIFT calculator to find out how much more driving new lanes can produce.
In Oakland, residents like the advocates at ConnectOakland have pushed for years for a project to reconnect low-income communities of color divided by I-980, which was intended primarily as a connection for the Southern Crossing. The Reconnecting Communities Program recently granted the city and Caltrans (California’s department of transportation) $680,000 to study possible projects to tackle the divisive and underused highway, including the possibility of removal, though that’s not necessarily the stated purpose of the project at this point. Clearly, once built, highways are difficult and expensive to remove—even when built to connect to a bridge that has ultimately never been built. But this study, funded by the first-ever federal program of its kind, is an important step towards repairing the damage wrought by I-980 and closing the longstanding divide.
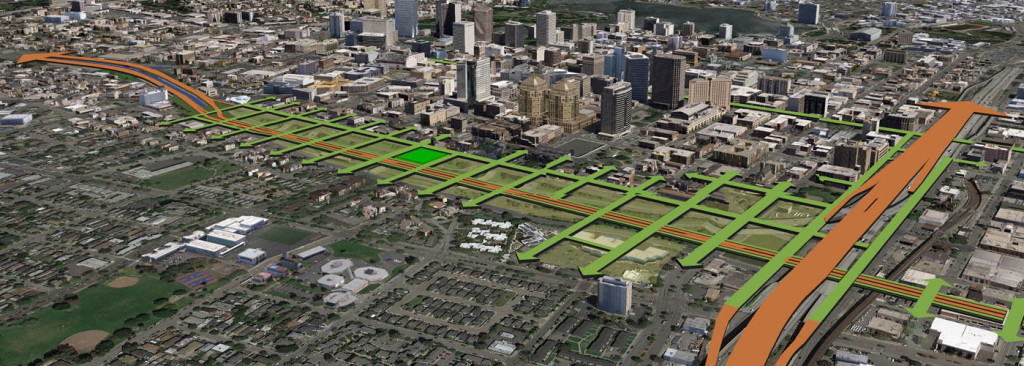
Even as I-980 gets a chance at a new fate, as long as the Southern Crossing bridge refuses to die, it could threaten the best efforts to reconnect Oakland. Even as all facts point to the contrary, some are likely to say that this underutilized highway is still needed to feed an unbuilt bridge. To get the most out of the Reconnecting Communities dollars they’ve received, decision makers will need to stand firm in what has already been proven time and again—it’s time to put the Southern Crossing to bed.
Lessons for Community Connectors
Even when it’s over…it’s not always over. It can feel like a victory when a divisive infrastructure project is halted, but proposed projects like the Southern Crossing won’t always go away after being stopped once. Once these lines get drawn on official maps and planning documents, these projects are never truly dead—they’re just waiting for a different leader (or the availability of new funding, as with the infrastructure law) to bring them back to life. It’s hard to stop a proposed infrastructure project, but it’s even harder to stop one permanently.

The mere suggestion of divisive infrastructure can lead to harm. I-980 would likely have never been built without the proposal for the additional Bay bridge, Southern Crossing. This is one example of how divisive infrastructure can harm a community even before it’s built, or if it’s never built at all (here’s another example from Shreveport). Notably, the Hunters Point and Bayview neighborhoods on the San Francisco side of the Bay have survived decades of Southern Crossing proposals and still managed to attract investment such as the T-Third light rail line and the Indian Basin Waterfront Park, but original residents haven’t been properly protected and many were ultimately displaced by rising property values as demand for the area grew.
Include the voices of the community being impacted. As decision-makers weigh the options to reconnect communities divided by I-980 in Oakland, they should learn from their recent and past mistakes. Whether West Oakland or the Bayview and Hunters Point neighborhoods were destroyed or allowed to flourish, the residents of color that called these communities home were never included in the decision-making process. Any reconnection projects should include the voices and perspectives of Black and brown residents and ensure that these residents are able to benefit from the changes that are made.
Community Connectors: tools for advocates
 You may be fighting against a freeway expansion. You may be trying to advance a Reconnecting Communities project to remove an old highway. You might be just trying to make wide, dangerous arterial roads a little safer for people to cross. This Community Connectors portal explains common terms, decodes the processes, clarifies the important actors, and inspires with helpful real-world stories.
You may be fighting against a freeway expansion. You may be trying to advance a Reconnecting Communities project to remove an old highway. You might be just trying to make wide, dangerous arterial roads a little safer for people to cross. This Community Connectors portal explains common terms, decodes the processes, clarifies the important actors, and inspires with helpful real-world stories.



