
California officially dumped the outdated “level of service” metric — your state should too

California made a small but crucial change to how they measure the performance of their streets in 2013, shifting away from a narrow focus on moving as many cars as fast as possible and taking a more holistic view and measuring a street’s performance against a broader list of other important goals. So what is this outdated “level of service” measure and how can other states follow California’s lead?
Wanting to rejuvenate their local economy, a community cooks up plans to redesign the local street running through downtown that was perhaps even short-sightedly widened or converted to one way travel in the 1960’s or 70’s. But as the street is also a state highway, they soon hear from the state department of transportation (DOT) that their proposed changes will slow down traffic and fail to meet “level of service” requirements and won’t make the cut of the state’s short list of projects. Worse yet, the community is told that in order to make a street safer, they actually need to widen it and smooth out any curves, making it a virtual speedway, undercutting their plans to build a place with more enjoyable places to walk and visit — a framework for creating economic prosperity. Heard this story before?
What is level of service, and how do DOTs come to this conclusion?
Though there are no formal or federal requirements to do so, most DOTs, metropolitan planning organizations and traffic engineers rely on a metric known as level of service (LOS). According to Jason Henderson, professor of geography at San Francisco State University, “Every city I’ve ever come across has some use of [LOS].” Because of the ubiquity of LOS, this largely misunderstood measurement has profound influence on the design of our communities.
Level of service is a system by which road engineers measure how well a road is performing based on the number of cars and the delay that vehicles experience on that roadway. Letters designate each level, from A to F. A, B and C represent free-flowing conditions and F is stop-and-go traffic. The score is assessed based on the highest level of congestion on that roadway, even if it only occurs a few minutes a day. Traditionally, roadway conditions are acceptable if they score a C or higher on non-urban streets and a D or higher on urban streets.
The LOS measurement is calculated by first measuring the amount of traffic during the busiest 15 minutes of an evening rush hour. Next, traffic engineers project the amount of traffic on the road in 20 or 30 years to determine if the road has enough capacity to cover the lifespan of the asset. If a road is projected by traffic engineers to lack capacity 20 years in the future — an incredibly fuzzy practice that’s far more art (or magic?) than math — that road still receives a failing LOS grade today, even if the road is adequately suiting capacity needs.
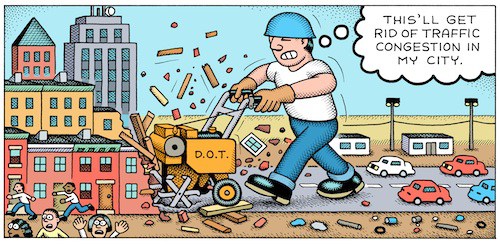
This heavy reliance on LOS has dramatically shaped our cities. As Gary Toth from the Project for Public Spaces brilliantly put it in this piece, transportation professionals, “in search of high LOS rankings, have widened streets, added lanes, removed on-street parking, limited crosswalks, and deployed other inappropriate strategies” all because LOS has been the de facto standard over the last 50 years. This terrific cartoon from Andy Singer that Toth includes shows the rationale in practice:
Where did this measure come from?
The 1965 federal Transportation Research Board Highway Capacity Manual introduced the LOS metric and it quickly became accepted as the standard measure of roadway performance. One reason that states adopted the LOS so quickly was that it suited our country’s transportation goals in the 1960’s of building out a network of interstates and prioritizing automobiles to travel quickly.
Although LOS quickly became the standard, transportation agencies at any level are not explicitly required to use it: there are no planning or project design requirements that mandate the use of either LOS or travel modeling. FHWA recently issued a memo clarifying that level-of-service was never a federal requirement. Read more about that (and some other important changes) in this recent story:
If we are going to change the way our streets and communities are designed, we will need to change the way we measure their performance. And that’s exactly what California has set out to do. In 2013, California legislature passed a law that began the shift, directing the Office of Planning and Research (OPR) to use an alternative of measuring vehicle-miles traveled (VMT).
In 2013, Governor Jerry Brown signed into law SB 743, eliminating the use of LOS for projects within designated transit priority areas (TPAs). As Streetsblog LA reported in 2013, because most urban areas fall within the state-defined parameters of a TPA, this means that LOS is largely eliminated for urban projects. Additionally, SB 743 authorized Governor Brown to develop a new way of measuring traffic impacts of major projects statewide and based the new way on total vehicle miles traveled (VMT) rather than intersection congestion. This will change how development projects are analyzed and scored in traffic impact studies and thus the type of projects that match up with the state’s goals for development.
In short, instead of measuring the success of a project by only the limited measure of whether or not it will make it less convenient to drive, CalTrans will now measure whether or not a project contributes to other state goals, like reducing greenhouse gas emissions, developing affordable multimodal transportation options for residents, preserving open spaces, and promoting diverse land uses and infill development. It is expected that this change will make it easier to build transit projects, as well as bicycle and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure — instead of encouraging more development that works against California’s own environmental and other goals.
How can other states replicate this move?
Great question.
This change in California is just one of the many smart policy changes that we’ll be covering in detail in Sacramento this November at Capital Ideas II, our one-of-a kind conference on state transportation policy. We’ll have experts on hand from California who will be discussing their legislative and policy shift away from level of service. Expect to hear more about that as we finalize the agenda in the coming weeks and share it here with you.
Learn More & Register




