Despite a binding requirement to release an updated version more than a month ago, the Federal Highway Administration missed the deadline to release a new edition of a federal handbook with national influence on street design. There were many positive changes proposed for this edition, but unless this delay comes because further improvements are underway, this new edition might ultimately be another green light for increasing traffic fatalities.
Edit 6/30: Language in an earlier version of this post overstated the power of the MUTCD in shaping street design. While this manual is influential, other important resources inform street design, including the Green Book. This language has been changed.

As Smart Growth America wrote in their 2022 report Dangerous by Design, the number of people struck and killed while walking reached yet another new high in 2020. More than 6,500 people were struck and killed while walking in 2020, an average of nearly 18 per day, and a 4.5 percent increase over 2019. This epidemic continues growing worse because our nation’s streets are designed primarily to move cars quickly at the expense of keeping everyone safe, but change can be made on every level to reorient toward protecting the most vulnerable rather than prioritizing the speed of a few.
There’s one Dangerous by Design recommendation that the federal government can take action on right away: an update to the little-known but highly influential Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD), defines standards for traffic control devices, which includes pedestrian crossings and lane markings like green bike lanes and red bus-only lanes. Though the current MUTCD prioritizes vehicle speed over pedestrian safety, the 11th edition MUTCD is an opportunity for the FHWA to make changes that benefit all road users—if they incorporate advocate feedback. Some proposed changes with potential include an update to the notorious 85th percentile speed standard, a decision on colorful crosswalks, and improvements for pedestrian crossing times. However, although these proposed changes might look good on paper, the revised MUTCD will likely leave most existing road networks as dangerous as ever.
85th percentile standard
While there’s no shortage of examples of the MUTCD placing the high-speed movement of cars at the top of the transportation hierarchy, there’s perhaps no greater example than that of the 85th-percentile speed standard. This standard sets what the National Transportation Safety Board calls a dangerous precedent for determining speeds: out of 100 drivers, the 15th fastest driver sets the speed limit.
The intent behind this is to lower the difference in speed between the fastest drivers and the slowest, with the idea being that the cause of crashes is the difference in speed, not speed itself. But this flawed logic ignores that as speed increases, the probability of fatalities for vulnerable road users increases exponentially. Blanket application of the 85th-percentile speed to arterials across the country has helped create the current crisis of pedestrian injuries and deaths—the majority of which now occur on state DOT-owned roads.
In the proposed edits for the new MUTCD, the 85th-percentile standard would be redesignated to a “guidance.” While that sounds better, this does not address the fact that unsafe roads in compliance with the new guidance would still be dangerous by design. Without providing engineers with safe design standards (like standards for road diets, raised crosswalks, chicanes, and narrower lanes), it would be impossible for this minor change to undo the speed status quo. The existence of the 85th-percentile rule is proof we know people will drive as fast as they feel comfortable. By softening the standard to a guidance, the MUTCD still fails to address design. State DOTs would still be responsible for choosing where to implement the rule on their roads, and without a change in standard practice or culture, it’s unclear what effect this change could actually have.
Pedestrian crossings
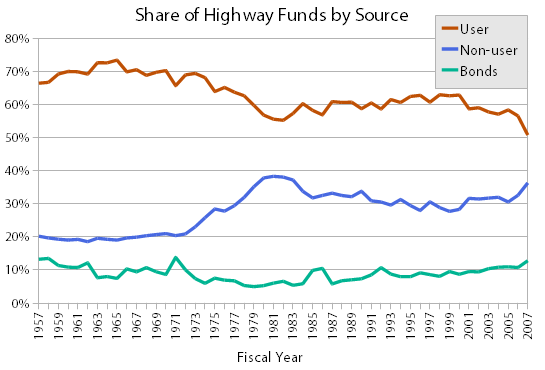
There are plenty of other standards in the MUTCD that foster dangerous design. Pedestrian volume per hour during “peak hours” is a main determining metric of what warrants a pedestrian signal at an intersection or midblock crossing. But peak hours focus on peak times for vehicular traffic, and what might be peak hours for a driver can be the worst, most uncomfortable time for a person to attempt to cross a busy roadway. Worse still, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration’s FARS data has consistently shown that the deadliest hours for pedestrians are often well outside of what’s considered “peak.”
This leads to a deadly feedback loop that works against the most vulnerable—if the road feels unsafe or inconvenient to cross, no one will attempt to use it except for those with the fewest options. Hostile design makes it nearly impossible to safely walk the span of a roadway to reach services when you have to contend with multiple lanes of high-speed traffic.
Just as people are more likely to drive on a wide, comfortable roadway, they’re more likely to walk on a sidewalk that feels safe. However, some MUTCD-compliant designs are so dangerous that cities feel the need to give their pedestrians bright red flags just for them to cross the road—an ineffective solution to a design problem.
Like with the 85th percentile standard, the 11th edition shifts pedestrian volume per hour warrants from a standard to a guidance, and tinkers with other technicalities. Some changes are good, and could even result in longer, safer crossing times or more flashing pedestrian crossing beacons. But even if the proposed changes are adopted, they lack teeth. DOTs would be left to their own devices to enact the changes, and they could still point to the guidance as reason to not install a crossing.

Colored crosswalks
Research has shown that bright, colorful crosswalks and intersections make streets safer by drawing drivers’ eyes to the pedestrian crossing with the added benefit of creating more vibrant streets. However, since 2001, the FHWA has officially discouraged communities from using art at crosswalks and has consistently sent letters to cities ordering them to remove their art, or lose federal funding. FHWA justified their requests by claiming colorful crosswalks do not enhance safety, despite the fact that the agency has yet to conclude research on the topic. There is no apparent plan for public access to the research underlying the next edition’s ruling.
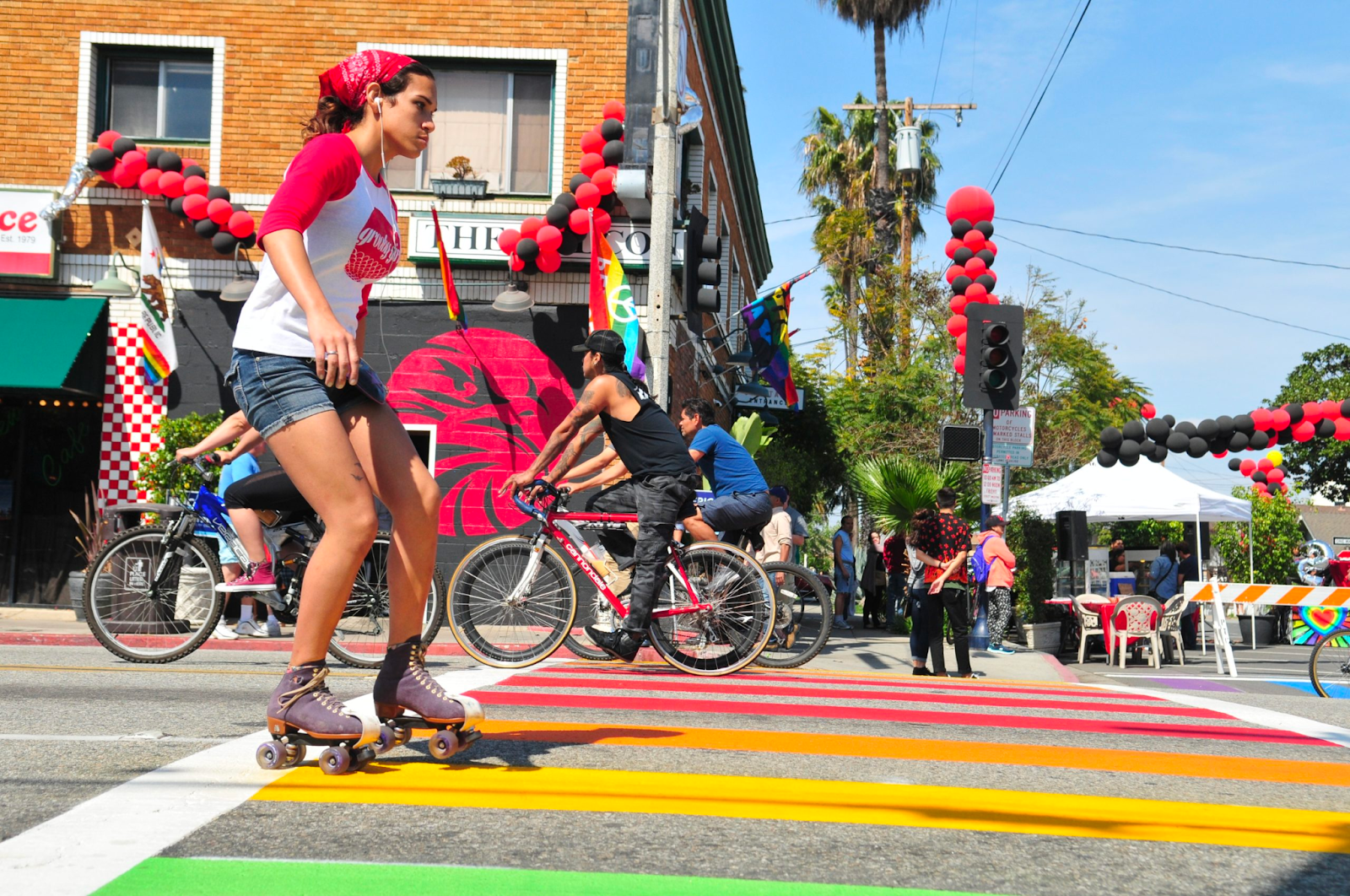

If text in other sections of the proposed changes is any indication, the FHWA has an interest in maintaining total uniformity in crosswalks for the benefit of automated vehicles. Automated vehicles (AVs) see the world through artificial intelligence-based machine vision and have difficulty adapting to the dynamic scenarios common to urban environments, even if these are the same scenarios that are more likely to draw the attention of human drivers.
AVs benefit from road environments with minimal variety and maximum contrast, and the 11th edition will likely propose prescriptive changes that would require road markings to be wider, brighter, and more frequent, explicitly for AVs. It is unclear why the FHWA seems willing to offer new concessions for vehicles that have so far failed to provide a proven safety benefit, but remain unwilling to allow changes that are proving to make vulnerable road users safer.
The bottom line
With speed and throughput of cars as the leading success metric, the so-called best practices outlined in previous editions of the MUTCD have increased the viability of cars at the expense of all other road users, including public transit, pedestrians, and cyclists. We are glad to see changes that allow for safer street design, but in the face of rising pedestrian fatalities, the 11th edition of the MUTCD doesn’t go far enough.
FHWA has made some progress on prioritizing safety over speed in other recent guidance. However, when it comes to the definitive guide to traffic control, making minor revisions in the midst of a crisis of fatalities that seem to increase year after year is a failure to meet the moment. We hope the extra time spent on the new edition has gone toward creating a safer MUTCD.



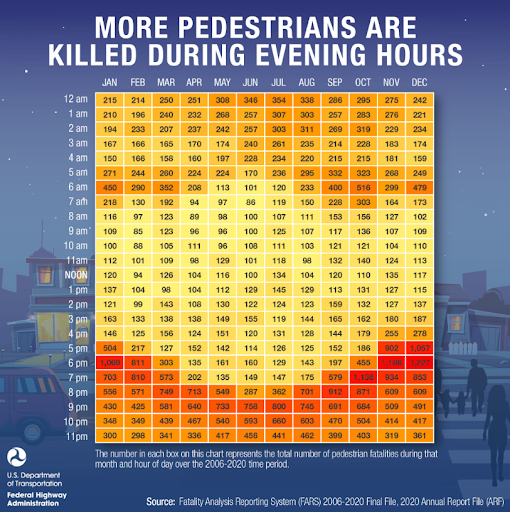




 Critics of public transportation often cling to the canard that government should not subsidize a transportation option that cannot pay for itself. These naysayers reference “self-sustaining” roads and highways, which receive funding from user-fees – in this case, the federal gas tax.
Critics of public transportation often cling to the canard that government should not subsidize a transportation option that cannot pay for itself. These naysayers reference “self-sustaining” roads and highways, which receive funding from user-fees – in this case, the federal gas tax.