Welcome to 2014! With a large number of state legislatures convening as the new year gets underway, it’s worth a look back at an important trend from 2013: States stepping forward to raise additional money for transportation. With federal funding remaining flat in 2012′s transportation bill (MAP-21) and after years of deferred action during the long recession, a large number of states, metro areas and local communities moved to supplement federal dollars with new revenues of their own.
In April, we reported that 19 states were looking at ways to increase their own funding for transportation. Some needed the funds just to make ends meet after years of flat or declining state revenues, while others also were looking for funds to match those available from MAP-21 new and updated loan and grant programs (like TIFIA or TIGER).
Here’s how they fared:
Key Successes
We covered Maryland’s ambitious plan on this blog, as well as Massachusetts.
Both of those states’ plans indexed the state gas tax to keep pace with inflation — something the federal gas tax, unchanged since 1993 — does not do. In Maryland, the state also added a sales tax on gasoline, while in Massachusetts, the package included an increase in cigarette taxes and certain business taxes. The good news was that in making the changes, both states recognized the importance of all modes of transportation and the revenues will fund important transit and road projects around the states.
In Virginia, Governor McDonnell began the debate with a proposal to abolish the per-gallon gasoline tax entirely and replace it with sales and wholesale taxes on fuel. That brought together legislators from both parties, who developed an innovative package of revenue increases to put transportation funding on a long-term, stable footing.
New legislation raised vehicle fees, along with local taxes in two of the states’ most heavily populated areas, Northern Virginia (near Washington, DC) and Hampton Roads (near Norfolk/Virginia Beach on the coast). Recognizing that businesses, residents, and visitors to Virginia depend on many types of transportation to move around the state, the new law directs funding to all modes of surface transportation, including transit, passenger rail, roads, and bridges. The package is projected to have more than $9.5 billion in economic impact in the state. As the Gov. McDonnell said in signing the bill: “This legislation will ensure that Virginia’s economy can grow in the years ahead, and that businesses will have the infrastructure they need to create the good-paying jobs Virginians deserve.”
Most recently, legislators in Pennsylvania reached agreement on a package of tax and fee changes that will raise $2.3 billion annually for the state’s transportation infrastructure – $1.65 billion for roads and bridges and $475 million for transit. The debate went down to the wire with agreement finally reached in a special legislative session just before Thanksgiving, allowing the governor to sign the bill on a cold day in late November.
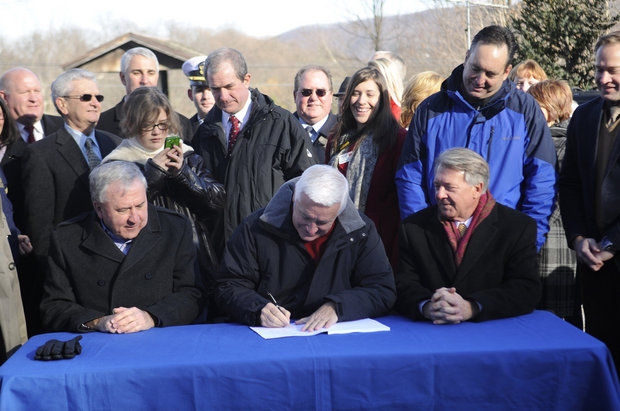

AP photo by Nabil Mark – Gov. Tom Corbett, center, signs into law a bill that will provide $2.3 billion a year for improvements to Pennsylvania’s highways, bridges and mass-transit systems.
The PA legislation eliminates the retail tax on gasoline and a state cap on gas tax paid at the wholesale level and raises various vehicles and driver fees over the next five years. The new funding will help to advance projects like the rehabilitation of the structurally deficient Liberty Bridge in Pittsburgh and of outdated equipment used by SEPTA.
Not all states that raised money recognized the value of investing across the board in all types of transportation to keep their economies moving. Ohio, Wyoming, and Vermont enacted tax increases intended for highway projects only. In Wisconsin, new bonding authority was enacted, with bond funds directed almost entirely to highways.
One positive outcome in Wisconsin: While the governor had proposed kicking transit out of the state transportation fund (similar to what the House of Representatives proposed in 2012), the legislature rejected that proposal and instead transferred general fund money into the fund (much as the federal government has done for its highway trust fund) to keep funding public transportation.
Try again next year!
Some states explicitly punted the issue to next year by creating commissions to report back to the legislature on transportation revenue options.
In Indiana, where a bill had been moving forward to allow the central Indiana region (which includes Indianapolis) to raise their own regional taxes to pay for transit, legislators instead commissioned a study on how to fund transit in the region. In November, the transit study commission voted in favor of allowing counties in the Indianapolis region to impose an income tax or business tax increase, if approved by a voter referendum, to fund regional transit. Reports like these help reinforce the notion — which we agree with — that regions should always have the ability, especially with the blessing of voters, to raise their own revenues to invest in regional transportation needs. We will definitely be keeping Indiana on our “watch list” for 2014.

Another state to watch in 2014 is Washington, where legislators negotiated on transportation funding through mid-December before calling it quits for the year. They promise to resume when the next legislative session begins in January. The current discussion is about increasing the state gas tax, with legislators debating items such as stormwater treatment, how to use the sales taxes collected from transportation projects, and funding for public transportation.
The need is urgent in Washington. Without any increase in state revenue, for example, the bus systems in the Seattle region are facing severe cuts in service that employers and employees depend on, along with fare increases.
A state we also hope will try again is Missouri, where a plan to raise $7.9 billion over 10 years through a penny sales tax passed both the Missouri House and Senate, but was then filibustered at the 11th hour when the Senate took up the package for a final vote. The fact that it was a sales tax was notable because in Missouri, as in many other states, while gas taxes are limited to only funding highway projects, a sales tax can be used for any mode of transportation, giving the state much more flexibility to invest.
Looking back
This movement we saw in 2013 is just the beginning. More and more states are increasingly looking for ways to bring more of their own dollars to the table, as well as making plans to invest in a range of transportation options. For a complete list see our state funding tracker.
The folks on the ground in these towns, cities, and metro areas know how important transportation is to their economic success. And keeping those local economies humming is key to our national economic prosperity.
Other states – and the federal government – need to take a page from their playbook and find a way to invest more money in transportation – it’s vital for our economy. One good place to start the discussion would be with our proposal to raise more revenue for transportation for the price of a weekly coffee and doughnut per commuter.

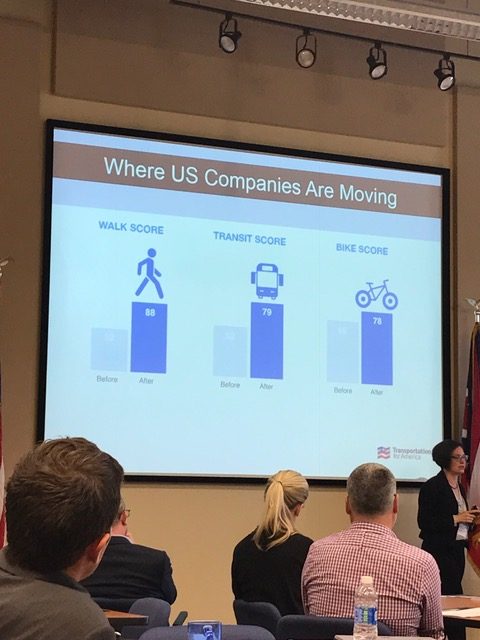 This Ohio-only edition in our series of leadership academies is focused on training and equipping civic leaders from multiple Ohio cities to spearhead a fresh approach to transportation that will foster sustainable economic growth and boost the economy in metro areas and the state. In a state where many cities struggle with either slow or negative population growth, the last generation’s economic development strategies are no longer delivering results. Smart investments in transit, main streets, and walkable communities are part of a new recipe for future success. The academy, co-hosted with the Greater Ohio Policy Center, includes teams from the Akron, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Delaware, and Toledo regions.
This Ohio-only edition in our series of leadership academies is focused on training and equipping civic leaders from multiple Ohio cities to spearhead a fresh approach to transportation that will foster sustainable economic growth and boost the economy in metro areas and the state. In a state where many cities struggle with either slow or negative population growth, the last generation’s economic development strategies are no longer delivering results. Smart investments in transit, main streets, and walkable communities are part of a new recipe for future success. The academy, co-hosted with the Greater Ohio Policy Center, includes teams from the Akron, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Delaware, and Toledo regions.













