States across the country are facing huge deficits in their own transportation budgets — a problem compounded by the uncertainty over the support they’ve always received from the federal transportation fund, which is now just months away from insolvency. However, over the last month or so, at least nine governors have highlighted plans to raise new state transportation revenues in their State of the State addresses, marking the issue as a top priority.
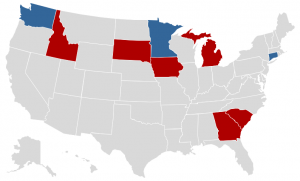 While their speeches are notable for their willingness to take a stand on the issue, these governors (and many state legislators) are stepping out on the issue because states face growing needs and static or falling revenues from state as well as federal sources.
While their speeches are notable for their willingness to take a stand on the issue, these governors (and many state legislators) are stepping out on the issue because states face growing needs and static or falling revenues from state as well as federal sources.
As of press time, six Republicans and three Democrats spanning from Washington to Connecticut have come out in support of raising transportation funding at the state level by various mechanisms in the hopes of providing stable and reliable revenue for years to come. And they’re counting on Congress to do their part and come through with reliable federal funding as well.
After looking over the transcripts of all nine speeches, two major themes stood out: the importance to a state’s economic growth and development of a well-run, well-funded transportation system, and the financial and public safety cost of poorly maintained infrastructure.
After campaigning on the issue, returning Connecticut Governor Dannel Malloy (D) introduced his plan for a 30-year overhaul of the state’s entire transportation system, including the creation of a “transportation lockbox” to ensure transportation revenues are spent on transportation projects. He has promised to propose specific revenue mechanisms in his February 18th budget address.
“We know that transportation and economic growth are bound together,” Governor Dayton said on January 7th. “States that make long term investments in their infrastructure can have vibrant economies for generations. States that don’t, will struggle. It’s that simple.
Transportation connects us – literally – community to community, state to state, nation to nation. It connects us economic opportunity, and it connects us to another.”
Idaho Governor Butch Otter (R) proposed raising transportation fees to help address the state’s ever increasing number of deficient bridges and poorly maintained highways, suggesting that spending some now will save more in the future. While calling for greater investments for transportation and infrastructure in his speech, he did not address any specific plans to do so, only saying to his fellow legislative colleagues, “I am not going to stand here and tell you how to swallow this elephant.”
“I fully understand the misgivings of some about higher transportation costs. But there is something to be said for the old adage about being ‘penny wise and pound foolish.’ In fact, every dollar we invest now in our roads and bridges will save motorists and taxpayers $6 to $14 later.”
In Iowa, with 35 percent of their annual transportation budget coming from the 19 cents per gallon gas tax, Republican Governor Terry Branstad is concerned about the state’s ability to adequately build and maintain the state’s infrastructure and transportation system with that source. The governor did say before his State of the State address that part of the solution could be allowing local governments to add their own gas tax for local projects and transportation needs. He expressed hope that lawmakers and stakeholders could come to a consensus on a specific solution.
“Over the past few years, rhetoric has trumped results when it comes to action on infrastructure funding for Iowa. A recently completed Battelle study demonstrates the need for us to take a hard look at adequate road funding. The study shows that without action funding available for road and bridge maintenance will fall short of what is needed to remain competitive and most importantly, safe.
Without action, Iowa’s roads and bridges face an uncertain future. Our farmers will find it more difficult to deliver their commodities to market. Business and industry will look elsewhere when considering where to invest and grow. As the study found, sound infrastructure remains a prerequisite for economic development. “
While Democratic Minnesota Mayor Mark Dayton has yet to give his State of the State address, his administration did release the details of his $11 billion transportation funding plan this week. It implements a 6.5 percent gross receipts tax on gasoline, raises the current 1.25 percent base on vehicle registration fees to 1.5 percent, and increases the sales tax by a half cent in the Twin Cities Metro area, specifically for improved transit, bicycle, and pedestrian infrastructure.
“Inadequate transportation clogs our lives with worse traffic congestion, longer commutes, more dangerous travel conditions. Those deficiencies restrict our future economic growth and detract from our quality of life,” said Governor Dayton. “If we continue to avoid these problems, they will only get worse. It’s time to begin to solve them.”
South Carolina Governor Nikki Haley (R) called for a 10-cent gas tax increase, as long as the legislation included cutting the state’s income tax by 30 percent and restructuring the state’s Department of Transportation.
“Deficient roads and highways are an economic issue. That’s why we supported $1 billion in new road funds last year, which was the biggest infrastructure investment in a generation. It’s why we proposed in our Executive Budget dedicating an additional $61 million in auto sales tax funds entirely to roads. But we know that’s not enough. We still have very substantial revenue needs that need to be addressed.”
Republican South Dakota Governor Dennis Daugaard outlined his transportation plan that would raise the vehicle excise tax from three to four percent, and increase the motor fuel tax by two cents this year and an additional two cents every year going forward. His plan would also implement a 10 percent increase in vehicle registration fees for local entities. The plan would allow the state to invest $50.5 million more for roads and bridges, with $39.8 million for the state highway fund, and an additional $10.7 million for local towns and cities.
“Our entire economy – our very wellbeing – depends on road infrastructure,” Governor Daugaard said during his State of the State Address. “And right now, our roads are underfunded.”
Addresses from the governors in Georgia, Michigan, and Washington focused on the need to raise revenue because current conditions represent public safety issues — or could soon without adequate investment.
The Republican governor from Georgia, Nathan Deal, has suggested that his state needs an estimated $1 billion to $1.5 billion more to maintain the state’s roads, highways, and bridges — and even millions more to expand. He offered the legislature three options to raise the funding needed to maintain the state’s infrastructure: a regional one percent sales tax designated for infrastructure projects; a plan that will reprioritize funding and focus on the most essential projects; or a “transportation plan that would address the ongoing needs of maintenance and repair, as well as freight corridor and other transportation improvements.”
“We are currently operating at a rate that requires 50 years to resurface every state road in Georgia. If your road is paved when you graduate high school, by the time it is paved again you will be eligible for Social Security.
If we continue to do nothing, we would continue to have to depend on the federal government, whose transportation funds are also dwindling. If we should choose not to maintain and improve our infrastructure, economic development would stall, companies would be unable to conduct their business efficiently, commuters would waste more time and gas sitting in traffic, and no one would be satisfied.”
Michigan Governor Rick Snyder (R) signed a plan to raise $1.3 billion more a year to mend deteriorating roads and other transportation infrastructure, contingent on Michigan voters increasing the state sales tax to seven percent via a May ballot measure. This bipartisan package of 11 laws would restructure and ultimately raise static per-gallon fuel taxes while exempting fuel from the state’s 6 percent sales tax.
“The key issue is public safety. If you look at it and you look at our bridges, one out of nine is structurally deficient. So, when you drive Michigan and you see plywood underneath the bridge, why is it there? It’s keeping crumbling concrete from falling on your vehicle, that’s unacceptable.
When you talk about our roads and you see those potholes, just think about the issues and concerns you’ve had this personally. When you swerve to miss a pothole, you are a distracted driver. You are putting yourself at risk and other drivers and other people. If you hit that pothole and you blow a tire you’re at risk of a major accident. That is unacceptable.”
Democratic Washington Governor Jay Inslee introduced a cap-and-trade program that would require the largest industrial polluters to pay for every ton of carbon they release, and then direct at least a portion of those funds into transportation. It could raise nearly $1 billion in its first year to pay for transportation projects. California is the only other state to attempt such a funding mechanism.
“Without action, there will be 52 percent cut in the maintenance budget, and 71 bridges will become structurally deficient or functionally obsolete. Without action, commute times will continue to rise, robbing us of time with our families. Without action, our ability to move goods efficiently will be diminished.
[This plan] keeps us safe by fixing our bridges, patching our roads, and cleaning out air and water. It also embraces efficiency, saves time and money, and drives results that the public can trust through real reform. Finally, it’s a plan that delivers a transportation system that truly works as a system. A system that transcends our old divides and rivalries. No more east versus west, urban versus rural or roads versus transit.”
Though some plans are certainly better than others, these nine governors are demonstrating true leadership by bucking the conventional wisdom and supporting new revenue to invest in transportation and infrastructure. More could follow in the weeks ahead as a few more State of the State addresses happen and legislative sessions get underway. Transportation for America is pleased to see these leaders take a stand on raising stable transportation funding, and we hope that Congress follows suit to support their efforts by rescuing the nation’s transportation fund from insolvency this spring.





 While their speeches are notable for their willingness to take a stand on the issue, these governors (and many state legislators) are stepping out on the issue because states face growing needs and static or falling revenues from state as well as federal sources.
While their speeches are notable for their willingness to take a stand on the issue, these governors (and many state legislators) are stepping out on the issue because states face growing needs and static or falling revenues from state as well as federal sources.



