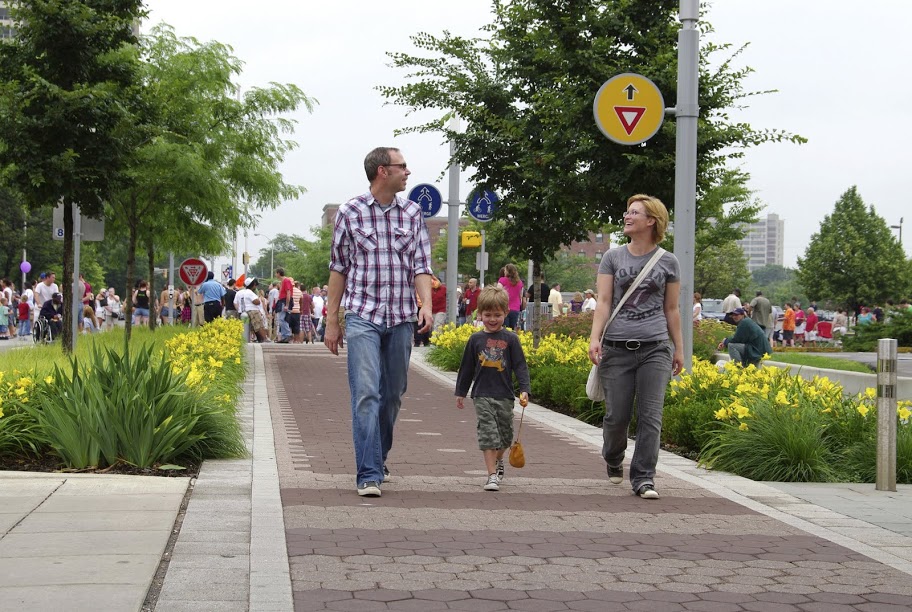
Affirming a trend seen in other cities, Indianapolis’s eight-mile Cultural Trail has been a boon to the neighborhoods adjacent to it — as well as the city as a whole — increasing property values of homes and businesses and giving residents and tourists a convenient, attractive, unbroken path to walk, bike and move around the city.
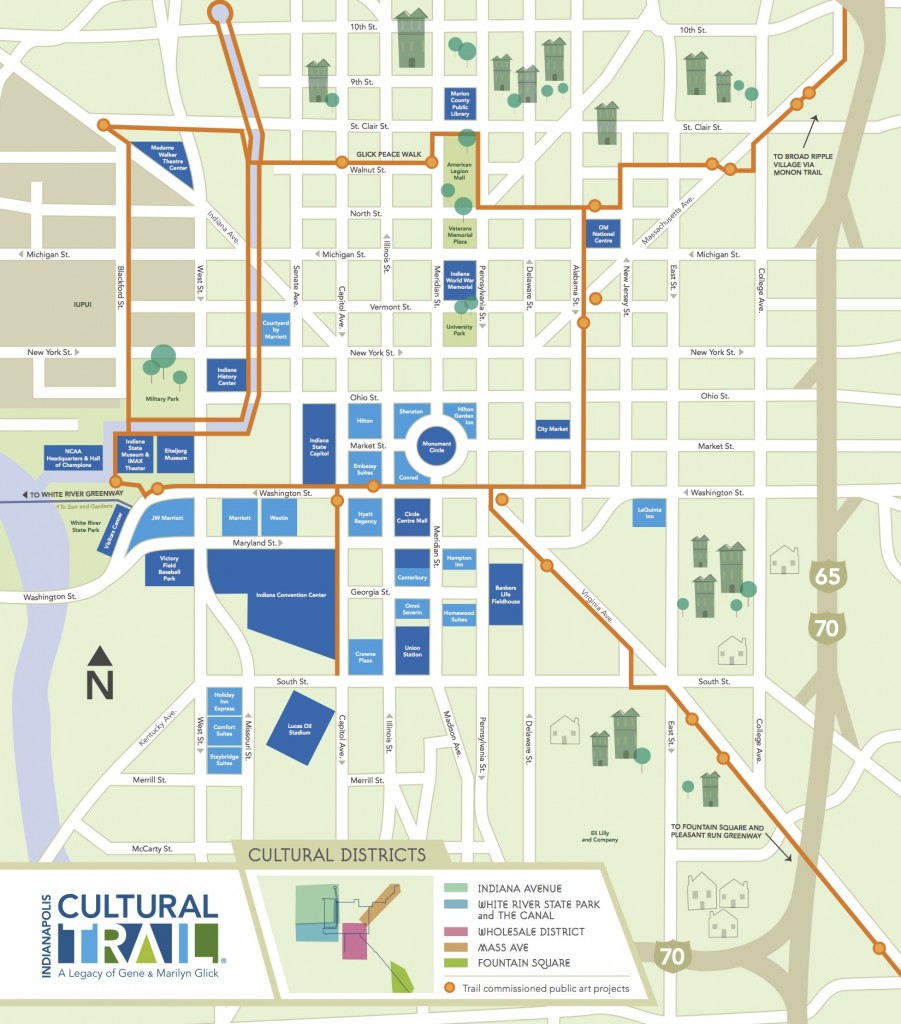 Since opening in 2008, the value of properties within a block of Indy’s high-quality biking and walking trail have increased an astonishing 148 percent, according to this recent report on the impacts of the trail. The value of the nearly 1,800 parcels within 500 feet of the trail increased by more than $1.01 billion from 2008 to 2014.
Since opening in 2008, the value of properties within a block of Indy’s high-quality biking and walking trail have increased an astonishing 148 percent, according to this recent report on the impacts of the trail. The value of the nearly 1,800 parcels within 500 feet of the trail increased by more than $1.01 billion from 2008 to 2014.
The $62.5 million investment, funded mostly by private or philanthropic donations that leveraged a federal TIGER grant, is an eight-mile landscaped bike and pedestrian pathway through the heart of the city that is, in the words of the New York Times in 2014, an “accessible urban connective tissue — an amoeba of paths shot through with lush greenery and commissioned works of public art.”
Residents and tourists alike have been drawn to the trail, and it’s proven to be not just a quality-of-life asset but an economic one as well, with business and property owners witnessing firsthand the benefits of being close to high-quality infrastructure that makes it safe for almost anyone of any age to safely walk or bike through the heart of the city.
The Cultural Trail is an important cog in the city’s transportation network, which the city hopes to dramatically expand through increased public transportation service in and around the city. It provides an unbroken loop around Indy’s downtown that allows cyclists and walkers of almost any age or ability to safely traverse the city. The trail stitches together neighborhoods and connects to various theatres, hotels, sports venues and shopping areas, among other popular destinations. Spurs reach out into neighborhoods and connect to other city trails, making bike commutes to downtown easier.
The numbers in this report are eye-opening, but Indy isn’t the only place where investment in ambitious projects to make cities more livable and functional for people have netted sizable economic rewards over the last few years. Dallas and Atlanta have both invested in their own similar in-town, separated, high-quality multipurpose paths to great economic rewards, just to name two.
Some bars and restaurants in Dallas claimed a threefold jump in business since the first day the new Katy Trail opened, centered in Dallas’s Uptown district. In a story last summer, The New York Times described how the Uptown neighborhood changed after the opening of the Katy Trail:
Since 2006, property value in Uptown has climbed nearly 80 percent to $3.4 billion, based on the improvement district’s assessment income. In the early 1990s, it wallowed around $500 million, said Joseph F. Pitchford, senior vice president for development at Crescent Real Estate Equities, based in Dallas. Crescent will begin building a $225 million, 20-story tower this summer that the law firm Gardere Wynne Sewell will anchor.
Dallas added 95,900 jobs in 2013 and is looking to attract young, talented professionals. While the Katy Trail helps, they still have work to do to change their reputation: Dallas was identified as one of the least walkable cities in America by Smart Growth America and George Washington University in their Foot Traffic Ahead report.
In Atlanta, when fully completed, the Beltline will be a 26-mile loop of walking and biking trails (along with transit eventually) in a loop around the city following mostly old railroad right-of-way. The few finished segments are already making a notable difference in property values of homes and businesses that surround it.
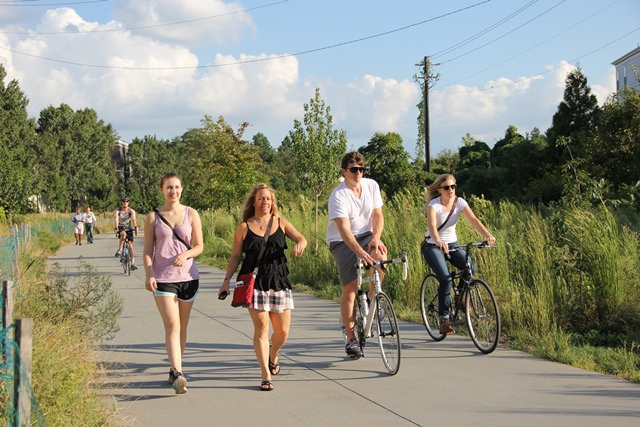

Pedestrians and cyclists enjoy the Atlanta BeltLine’s Eastside Trail. http://beltline.org/explore/photos/?setId=72157651531843045
In a 2013 Curbed article, the REMAX realty firm claimed homes near the BeltLine and other city cycling infrastructure that used to stay on the market for 60 to 90 days were now selling within 24 hours. Maura Neill, a realtor who has specialized in the Atlanta market for over 12 years told Curbed, “The new bike lanes are absolutely an attractive selling point, putting Atlanta in the limelight as a progressive city.”
“When people realize the savings of not relying solely on a car, they’re much more inclined to pay a little more now in exchange for saving a lot later,” said Rebecca Serna, executive director of the Atlanta Bicycle Coalition, pointing to some buyers’ willingness to pay upwards of $5,000 extra for a home if it means less traffic and less time spent commuting.
“The old ‘drive to qualify’ [for a mortgage] paradigm is shifting as people forego the family car. Factors like time and money saved are much more valuable than the number of square feet.”
Other cities have also seen a boost in housing prices thanks to nearby bike trails, including Vancouver, which saw 65 percent of realtors featuring new bike paths as a selling point; Pittsburgh, which “ignited commercial and business activity”; and in North Carolina, where property prices increased by $5,000 or more alongside the small Shepherd’s Vineyard greenway in the town of Apex, outside Raleigh, just to name a few of the many recent examples.
The uptick in property values and economic development are often attributed to the preferences of millennials, whom are shown (in our recent survey and others) to have a clear preference for places that provide a range of mobility and transit options, including biking and walking.
With transportation dollars more limited than ever, it’s clear that even relatively small investments in projects like Indy’s Cultural Trail or the Beltline or Katy Trail in Atlanta and Dallas are smart bets to bring significant economic benefits, and also help attract the younger, talented workforce so envied by many top employers.