Drop in driving growth is likely permanent, FHWA acknowledges, compounding the threat to transportation revenues

The slowing growth in the number of miles we drive each year looks like a permanent trend, according to the Federal Highway Administration, adding still more fuel to the fire in the debate over how to pay for a transportation program with dropping gas-tax revenues.
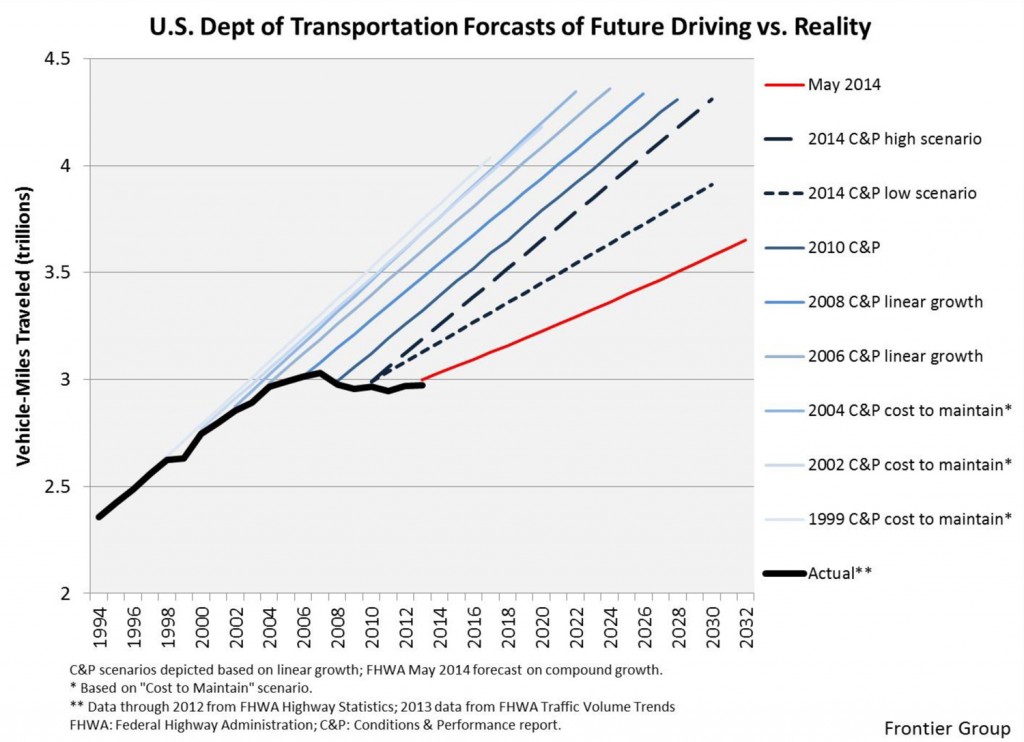
The most recent projections, released quietly last year but highlighted this week by USPIRG, are a significant departure for the federal agency charged with projecting the need for highway capacity and expected gas-tax receipts in the U.S. For the last several years, projections have substantially over-estimated the growth of “vehicle miles traveled”, which actually declined for several years before rebounding to a tepid pace more recently.
In this short document, FHWA projects that the amount of driving done by each American is unlikely to grow in the years to come. According to PIRG’s research, the agency had issued 61 straight forecasts that overestimated the actual increase in driving. FHWA is to be commended for taking a problem, rethinking it, and coming up with a better projection. The action clears up a discrepancy with the potential to hamper planning and decision-making, as we have noted in the past along with number crunchers at the State Smart Transportation Initiative, the Frontier Group and U.S. PIRG.
In this new FHWA projection, though the actual amount of vehicle miles traveled (VMT) is still projected to increase by 0.75 percent annually from 2012 to 2042 (the red line in the chart below), U.S. population is projected to grow by about 0.7 percent each year in that period, which means that driving per person is likely to remain flat. As FHWA’s report notes: “This represents a significant slowdown from the growth in total VMT experienced over the past 30 years, which averaged 2.08% annually.”
It’s worth noting that this change also has huge implications for toll roads. Building a new road, tolling an existing one, selling the rights to toll a road to a private company — those decisions are often being made using these outdated VMT projections.
This adjustment by the feds underscores the trouble ahead for transportation funding, absent congressional action.
The gas tax has already lost a third of its value due to inflation, improvements in fuel efficiency, and the overall reduction in driving over the last decade. All of this means that the gas tax doesn’t bring in as much money as it used to — leading to the perpetual annual shortfall in the Highway Trust Fund that has required numerous bail-outs from the general fund, using increasingly creative accounting gimmicks.
The excessive projections of expected driving have allowed some to point to an expected rebound that would help overcome some of the losses due to increased fuel efficiency. That will be tough to do in the face of the new estimates.
As Congress returns to face a May deadline for figuring out how to continue funding for transportation, members will have to come to terms with the likelihood that the gas tax will continue to lose value. The pensions have all been fully smoothed and the couch cushions have been emptied out. If Congress plans to make up the funding gap, they’ll have to be willing to raise the gas tax or index it to inflation, or increase some other revenue source.
We live in a different time today. We aren’t flush with gas tax revenues. We have a backlog of maintenance that can’t be ignored. The amount of driving Americans are willing to do has come close to reaching a peak. People are looking for different ways to get around each day. More Americans are moving into walkable neighborhoods where their commutes are shorter and options are greater.
We need a system of funding transportation and making investment decisions that recognizes these realities.