Transit still more popular with millennials, despite their upbringing

One of the deepest studies of attitudes about public transportation, published yesterday, finds that core fundamentals like speed, reliability and cost are far more important to millennials than wi-fi or smartphone apps. They’re open to riding it even more, but like everyone else, find that there just aren’t enough neighborhoods being built that have great transit options.

Flickr Creative Commons photo by wowwzers.
Our own recent poll explored the attitudes of millennials in relation to cities and their general positive attitudes about public transportation, but this terrific survey from TransitCenter goes even deeper with questions to people of all ages from all over the country on what they think of transit and where they live as a whole.
What type of neighborhood are they currently living in? What type of neighborhood would they like to live in? What is the ideal type of neighborhood to live and raise a family in? How does one make a decision to change how he or she gets around?
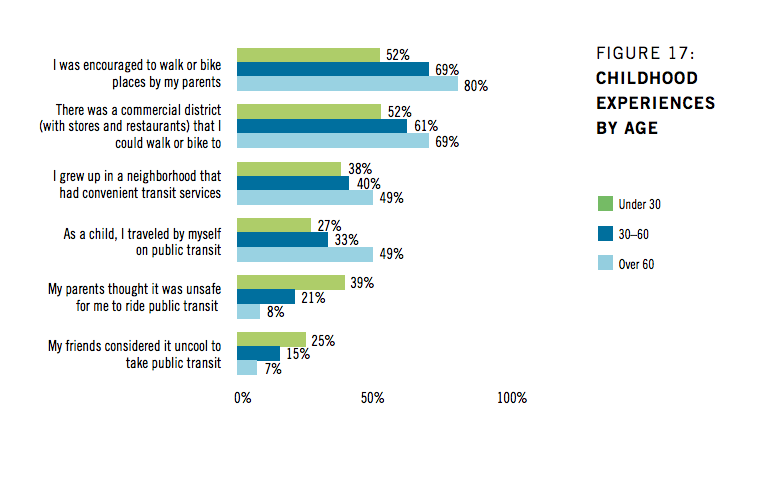
According to this 12,000-person survey by TransitCenter, a civic philanthropy, unsurprisingly, people under age 30 use public transportation the most, across the 46 metros surveyed. They looked at a variety of places that broke into two distinct categories; metros considered “transit progressive” akin to San Francisco or Washington, D.C., or “transit deficient,” like Little Rock, Arkansas and El Paso, Texas. Age was the greatest factor overall, non-dependent on region, education level, or income.
One of the more interesting findings in the report was that “there is no unique ‘cultural bias’ against transit in [the South, Midwest], and that if you build a quality transit system (and the land use is supportive), people will ride it no matter where they are from.”
While it’s been proven that younger generations are most likely to use public transportation, it’s largely happening in contrast to their upbringing. The report shows that millennials were less likely to: have been encouraged to walk or bike by their parents, to have grown up within walking or biking distance of a commercial district, and less likely to have traveled by themselves on public transit as children. In fact, 39 percent of them said their parents thought it was unsafe for them to ride transit.
This shows a huge generational shift (though maybe just an insight to human nature) from their Baby Boomer parents who grew up in denser urban neighborhoods and might have used transit as children. The over-60 group is now the least likely group to want to live in urban areas and rides public transit the least. As the report states, “Put simply, Baby Boomers don’t live in – and largely don’t want to live in – places well-served by transit.”
Some surprising findings upended the conventional wisdom that’s been reported about millennials. Better smartphone apps or wi-fi on their buses or trains are near the top of the list of things that would induce them to ride more often, right? Nope. Across every single age group, the fundamentals were the most important consideration of all: quicker trips (speed), more stations near them, cheaper, and more reliable than other options.
The findings on housing confirmed much of what’s been reported by Smart Growth America, the National Association of Realtors, and a handful of other recent polls: the market is not building enough of the kind of neighborhood that is in the highest demand these days.
TransitCenter found that 58 percent of all respondents wanted to live in neighborhoods that consisted of a mixed use between housing, retail, offices, and restaurants that provided a variety of options to get around including public transportation and safe walkable streets. However, only 39 percent currently live in such a neighborhood, creating a huge demand for this ‘ideal’ neighborhood.
Meeting the demand for that type of neighborhood — especially in places connected to today’s or tomorrow’s transit lines — will create a positive feedback loop of boosting ridership. Supply more neighborhoods connected to transit, and you’ll create more riders out of the people who say they’d ride it if they could, but don’t live somewhere it’s available.
While a majority of Americans may not necessarily want to live downtown in a big city, they do want their neighborhoods to transform into better towns or suburbs centered around a mix of uses with more options for getting around.
The findings in this smart survey should inform the elected officials, commissioners, and policy advocates planning for the needs of our growing and diversifying population in towns and cities of all sizes.