Housing and transportation squeeze hitting rural America, new reports concludes
When the Center for Neighborhood Technology released its revised Housing and Transportation Index last week, much of the focus naturally tilts toward cities due to the measurement of metropolitan areas. But CNT’s rural companion report on transportation costs in less-populated areas deserves ample attention as well.
The transportation challenges for rural America have more to do with factors like access and opportunity than congestion and traffic. With volatile energy prices and longer distances between employment, groceries and health services, transportation choices are essential. More than 1.6 million rural households do not have access to a car, making routine trips a strain on a family’s time and budget. For those who do drive, high gas prices take a big chunk out of monthly incomes. Rural residents with cars drive about 17 percent more miles each year than their urban counterparts.
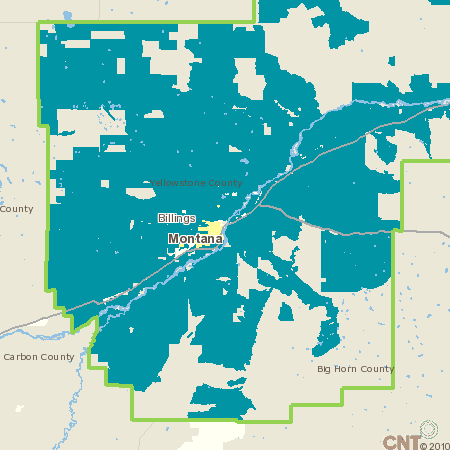
CNT’s analysis finds rural residents feeling squeezed in every corner of America, from Alaska to Alabama. In the areas near Billings, Montana, average annual household gas expenses have reached $5,300 per year, up from just $2000 per year just a decade ago. Costs shot up $3,200 between 2000 and 2008 in Hattiesburg, Mississippi. In the rural pockets surrounding Las Cruces, New Mexico, costs were up $3,100. In the image below, turquoise indicates Billings-area communities where yearly housing and transportation costs exceed the 45 percent threshold.
The CNT formula defines true affordability as less than 45 percent of household income going toward housing and transportation costs combined.
The website features profiles of communities in both rural and metro areas alike.
CNT’s three recommendations for inclusion in a new transportation bill are: 1) making transportation costs as transparent as possible; 2) using a similar yardstick as the true affordability in future policies and funding priorities for transportation; and 3) increasing incentives for projects that increase transit options and proximity to employment and housing. Support for passenger rail and intercity buses — both heavily-relied upon in sparser parts of the country —can and should fit under these policy umbrellas.
But rural livability is much more than just a discussion topic in Washington D.C. Stephen Lee Davis of Smart Growth America (and a Transportation for America colleague,) recently wrote about his experience living in Bentonville, Arkansas, a medium-sized town known best as the world headquarters for Wal-Mart Stores. In a two-part series on the Smart Growth America blog, Steve questioned the political figures who see livability as disconnected from America’s rural areas and small towns:
…for me and my wife and many others living in the older part of the city [street grid] in those weeks [in 2005] with astronomical gas prices, a pretty normal life was still possible, even while trying to cut back driving significantly to save money. Several weekends in a row, we parked our cars entirely, and managed to do our grocery shopping, go to church, visit friends, or listen to bluegrass in the square on a Friday night without having to get in either of our two cars. We walked 5 minutes to the grocery store. We biked to Walmart a handful of times — receiving many strange looks in the process. We went to eat at a new restaurant on the square. We went hiking on a short trail in the woods right on the edge of downtown. We went to the library.
Sounds pretty “livable,” right?
…and explained how current transportation policy has failed the residents of towns like Bentonville.
People who live in classic American small towns like Bentonville know a thing or two about livability. There’s nothing “livable” about being stuck in your subdivision that got built too far from town, work or school when gas prices get too high. Nor is it “livable” to have the federal government incentivizing (through money to the State DOT) the widening of highways into the county to encourage more sprawl outside of town even as the city is clamoring for more investment inside of it.
Like their urban counterparts, many residents in rural areas and small towns hope to preserve what they love about their way of life while making it easier to get by — and get around. CNT’s work helps to bring those challenges to light and move policy in a direction that produces results.