About those 66,000+ deficient bridges: What did last summer’s transportation law change?
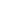
With the second collapse of an Interstate bridge in six years, Americans might expect Congress to leap into action to ensure adequate funding for bridge rehab and replacement. But as we have reminded numerous reporters since an I-5 bridge dropped into Washington’s Skagit River, federal lawmakers took a gamble and eliminated the nation’s dedicated bridge fund last summer.

I-5 photo by the Washington DOT on Flickr.
The bridge fund came into being in 1991, and especially in the first decade afterward, the country made enormous progress repairing deficient bridges. But that progress had slowed to a trickle when Congress took up the transportation funding bill, MAP-21, last summer.
With the I-35W collapse fresh in our minds and progress on repairing deficient bridges slowing, many assumed Congress would think about ways to make bridge repair more of a priority.
Not quite.
Instead, they took a gamble, eliminating the dedicated repair fund so that states could “set their own priorities,” as long as they promised to set targets for the repair of bridges on the National Highway System. That sounds great in principle, until you remember that competition for funds is growing rapidly, with no corresponding drop in the political pressure to build pet projects.
Though they won’t say it out loud, many DOT chiefs like a dedicated maintenance fund because it allows them to say “no” to projects they can’t afford, while helping to ensure existing facilities stay safe and functional. The changes in MAP-21 also don’t give similar attention to bridges not on the National Highway System – 90 percent of all bridges in need of repair – more on this below.
T4America has been a strong advocate of measuring performance against clear targets and goals. But for something as critical as bridge maintenance, there needed to be a well-considered transition period to understand how the new performance management system works, and establish clear targets and guaranteed enforcement mechanisms.
Instead, Congress scrapped the existing bridge repair program and directed USDOT to work with states to cooperate on setting measurable targets for things like bridge condition — but without significant penalties for failure. And considering that MAP-21 is only a two-year bill, states won’t be reporting on these measures until after this bill has already expired.
The second big change made last summer will force state and local communities into painful choices about priorities.
Before MAP-21, all 600,000+ highway bridges were eligible to receive funding for repair under that dedicated bridge repair program.
From the biggest interstate bridge down to that crucial bridge that connects your town across the river to another nearby town, all 66,500-plus deficient bridges could get the dollars dedicated for bridge repair.
Under MAP-21, Congress decided to focus the former bridge repair dollars almost exclusively on a narrow set of roadways known as the National Highway System (NHS). Think of the NHS as the interstates, state highways and most major four-lane and larger highways. The bridges on these roads are our most heavily traveled, no doubt, but they represent only about 10 percent of all structurally deficient bridges.
The other 90 percent will now have to compete with all of the other transportation needs in your community for the flexible funding that can be used on almost anything. And all of those needs will compete for less funding too, reduced from about 60 percent of all funding to 40 percent.
Bridge repair is added into the mix of choices along with regional transit investments, safe streets for all users, congestion relief, other transportation options, and other road repair — leaving communities with tough choices to make.

—-
All this comes as our transportation network begins to show its age. At an average age of 43 years, the typical bridge is nearing the end of its 50-year design life, and many thousands are far older than that. Structurally deficient bridges are more than 20 years older on average.
The federal government should be all about making sure that bridges are being systematically upgraded, repaired or replaced. And in the wake of a calamity like the closure of a key commercial corridor, we Americans ought to be all about letting Congress know we’re willing to pay for a safe and secure transportation network, and making lawmakers pay at the ballot box if they won’t deliver it.


















Pingback: Why are 1 in 9 Bridges in New York, New Jersey, Connecticut Structurally Deficient? | Mobilizing the Region